Earth S History
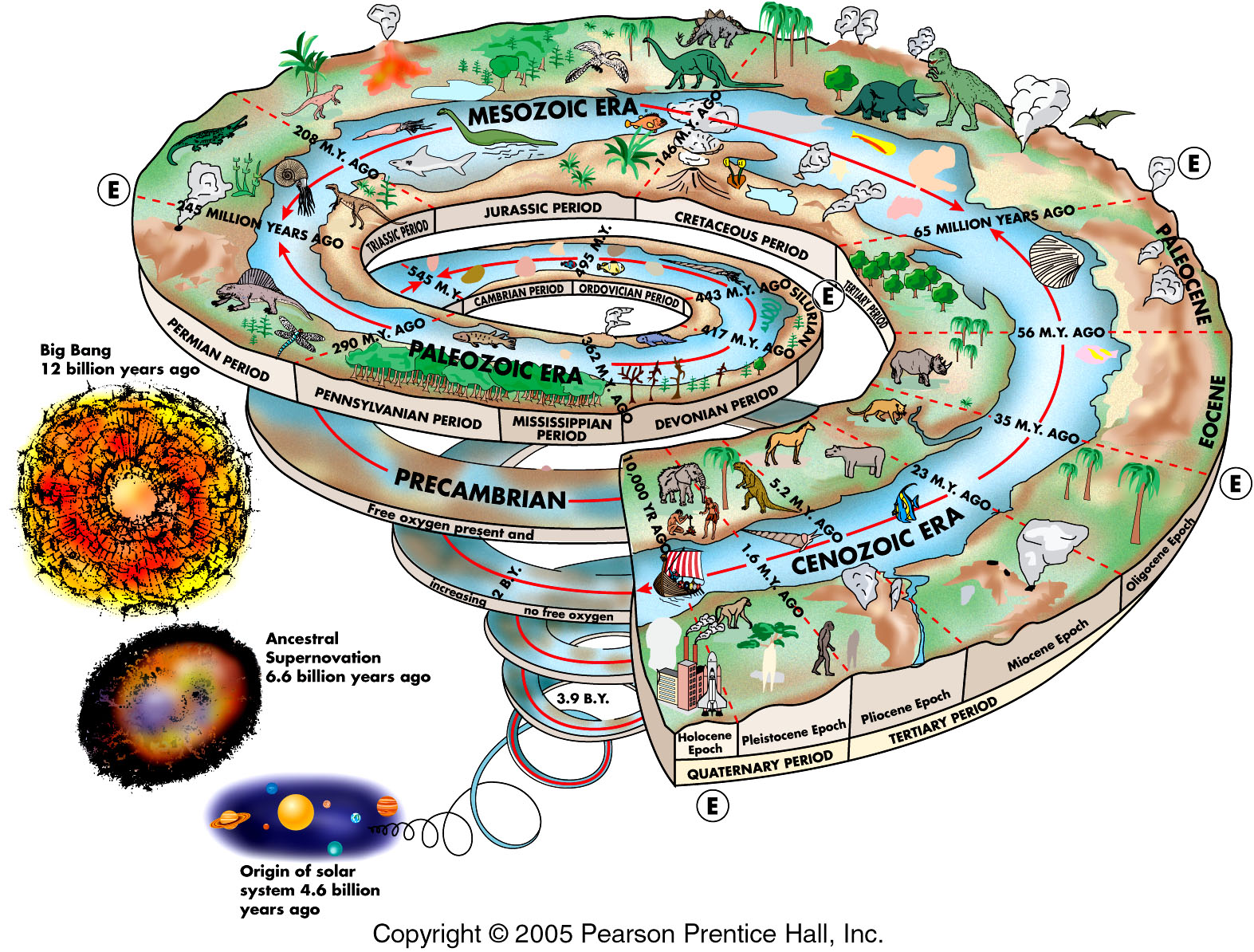
What Is Earth S History Socratic The history of earth is divided into four great eons, starting 4,540 mya with the formation of the planet. each eon saw the most significant changes in earth's composition, climate and life. each eon is subsequently divided into eras, which in turn are divided into periods, which are further divided into epochs. eon. A brief history of earth. the geological clock: a projection of earth’s 4.5 ga history on a clock (“ma” = a million years (megayear) ago; “ga” = a billion years (gigayear) ago). the circle starts at 4.6 billion years ago, then loops around to zero. author: woudloper derivative work: hardwigg; wikimedia commons. learning objectives.

Ppt юааearthтащs Historyюаб Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 5776835 The geological history of the earth follows the major geological events in earth's past based on the geological time scale, a system of chronological measurement based on the study of the planet's rock layers (stratigraphy). earth formed about 4.54 billion years ago by accretion from the solar nebula, a disk shaped mass of dust and gas left. The pregeologic period. from the point at which the planet first began to form, the history of earth spans approximately 4.6 billion years. the oldest known rocks—the faux amphibolites of the nuvvuagittuq greenstone belt in quebec, canada—however, have an isotopic age of 4.28 billion years. there is in effect a stretch of approximately 300. Earth’s timeline and history. 4,567,000,000 years ago, earth was covered in molten lava. earth was completely unrecognizable. in its earliest stage of formation, it was uninhabitable as it clumped from a cloud of dust. about 1,000,000,000 years ago, earth had its first signs of life. single celled organisms consumed the sun’s energy. Noun. an opening in the earth's crust, through which lava, ash, and gases erupt, and also the cone built by eruptions. our planet began as part of a cloud of dust and gas. it has evolved into our home, which has an abundance of rocky landscapes, an atmosphere that supports life, and oceans filled with mysteries.

Geologic Time Periods Time Scale Facts Britannica Earth’s timeline and history. 4,567,000,000 years ago, earth was covered in molten lava. earth was completely unrecognizable. in its earliest stage of formation, it was uninhabitable as it clumped from a cloud of dust. about 1,000,000,000 years ago, earth had its first signs of life. single celled organisms consumed the sun’s energy. Noun. an opening in the earth's crust, through which lava, ash, and gases erupt, and also the cone built by eruptions. our planet began as part of a cloud of dust and gas. it has evolved into our home, which has an abundance of rocky landscapes, an atmosphere that supports life, and oceans filled with mysteries. Geology earth history, stratigraphy, plate tectonics: one of the major objectives of geology is to establish the history of the earth from its inception to the present. the most important evidence from which geologic history can be inferred is provided by the geometric relationships of rocks with respect to each other, particularly layered rocks, or strata, the relative ages of which may be. Earth’s interior is a complex structure of superheated rocks. most geologists recognize three major layers: the dense core, the bulky mantle, and the brittle crust. no one has ever ventured below earth’s crust. earth’s core is mostly made of iron and nickel. it consists of a solid center surrounded by an outer layer of liquid. the core is.

Comments are closed.