Discrete Math Trees What Is A Tree A Tree Is A Connected Graph That
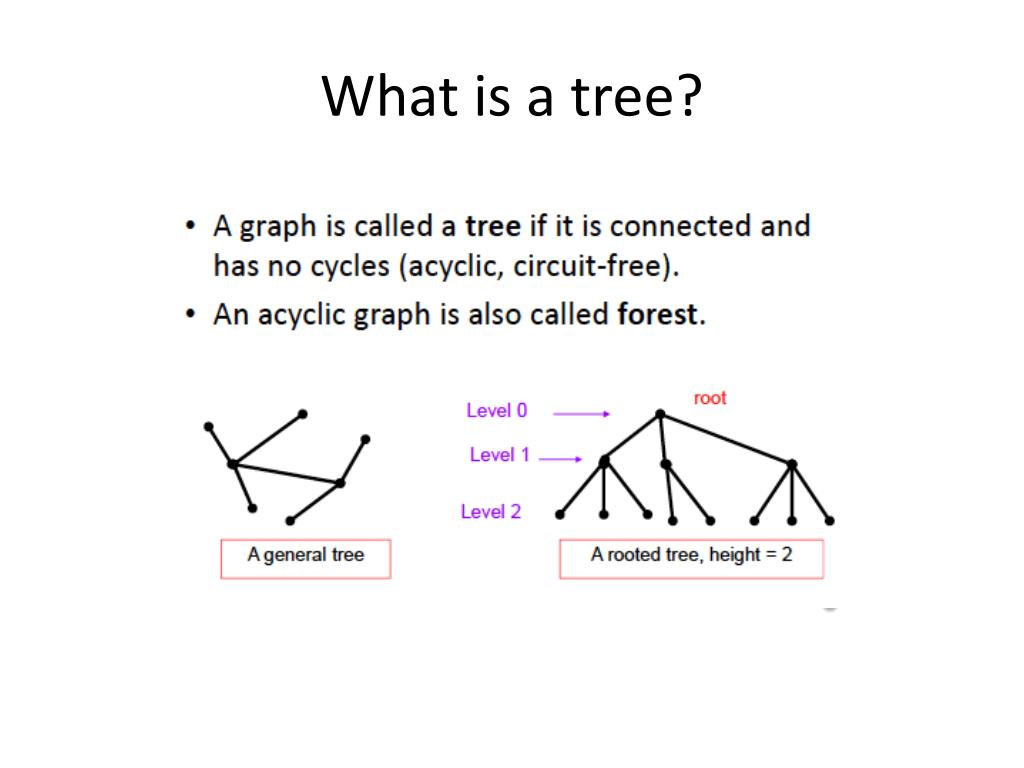
Ppt 22c 19 Discrete Structures Trees Powerpoint Presentation Free For the base case, consider all trees with v = 1 vertices. there is only one such tree: the graph with a single isolated vertex. this graph has e = 0 edges, so we see that e = v − 1 as needed. 🔗. now for the inductive case, fix k ≥ 1 and assume that all trees with v = k vertices have exactly e = k − 1 edges. Tree. definition 1. a tree is a connected undirected graph with no simple circuits. theorem 1. an undirected graph is a tree if and only if there is a unique simple path between any two of its vertices.

Discrete Math Trees What Is A Tree A Tree Is A Connected Graph That Free trees. a free tree is just a connected graph with no cycles. every node is reachable from the others, and there’s only one way to get anywhere. take a look at figure \(\pageindex{1}\) . it looks just like a graph (and it is) but unlike the wwii france graph, it’s more skeletal. V − 1. chromatic number. 2 if v > 1. table of graphs and parameters. in graph theory, a tree is an undirected graph in which any two vertices are connected by exactly one path, or equivalently a connected acyclic undirected graph. [1] a forest is an undirected graph in which any two vertices are connected by at most one path, or equivalently. Discrete mathematics chapter 10 trees §10.3 tree traversal preorder traversal de–nition let t be an ordered rooted tree with root r. if t consists only of r, then r is the preorder traversal of t. otherwise, suppose that t 1,t 2, ,t n are the subtrees at r from left to right in t. the preorder traversal begins by visiting r. it continues by. A cycle in g is a path (v1, v2, , vk) such that k ≥ 4 and v1 = vk. connected graphs. an undirected graph g = (v , e) is connected if, for any two distinct vertices u and v, g has a path from u to v. a property. lemma: a tree with n nodes has n − 1 edges. the proof will be left to you as an exercise.
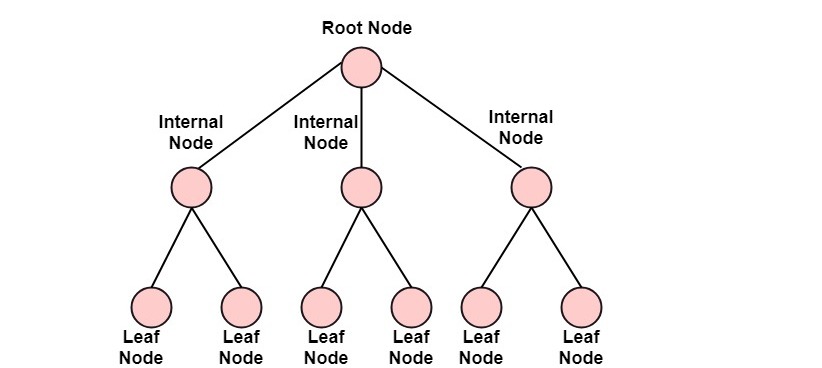
Discrete Mathematics Introduction Of Trees Javatpoint Discrete mathematics chapter 10 trees §10.3 tree traversal preorder traversal de–nition let t be an ordered rooted tree with root r. if t consists only of r, then r is the preorder traversal of t. otherwise, suppose that t 1,t 2, ,t n are the subtrees at r from left to right in t. the preorder traversal begins by visiting r. it continues by. A cycle in g is a path (v1, v2, , vk) such that k ≥ 4 and v1 = vk. connected graphs. an undirected graph g = (v , e) is connected if, for any two distinct vertices u and v, g has a path from u to v. a property. lemma: a tree with n nodes has n − 1 edges. the proof will be left to you as an exercise. Let g be a connected undirected graph. the subgraph t is a spanning tree for g if t is a tree and every node in g is a node in t. de nition if g is a weighted graph, then t is a minimal spanning tree of g if it is a spanning tree and no other spanning tree of g has smaller total weight. mat230 (discrete math) trees fall 2019 6 19. Section 6.2 trees and their representations 1 tree terminology a special type of graph called a tree turns out to be a very useful representation of data. definition: a tree is an acyclic, connected graph with one node designated as the root of the tree. an acyclic, connected graph with no designated root node.
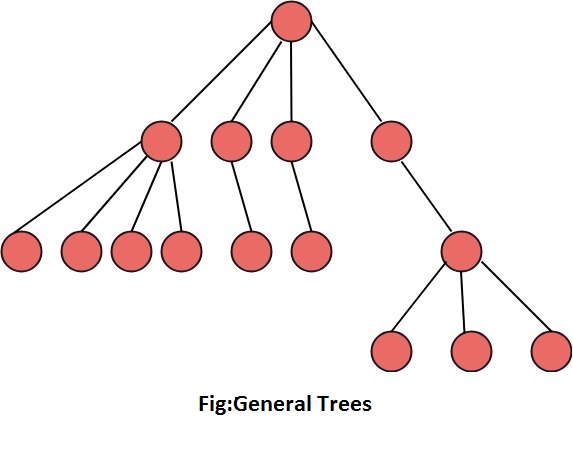
Discrete Mathematics Introduction Of Trees Javatpoint Let g be a connected undirected graph. the subgraph t is a spanning tree for g if t is a tree and every node in g is a node in t. de nition if g is a weighted graph, then t is a minimal spanning tree of g if it is a spanning tree and no other spanning tree of g has smaller total weight. mat230 (discrete math) trees fall 2019 6 19. Section 6.2 trees and their representations 1 tree terminology a special type of graph called a tree turns out to be a very useful representation of data. definition: a tree is an acyclic, connected graph with one node designated as the root of the tree. an acyclic, connected graph with no designated root node.

Discrete Mathematicsq Ppt Download

Comments are closed.