Dilated Cardiomyopathy Causes Symptoms Pathophysiology And Treatment
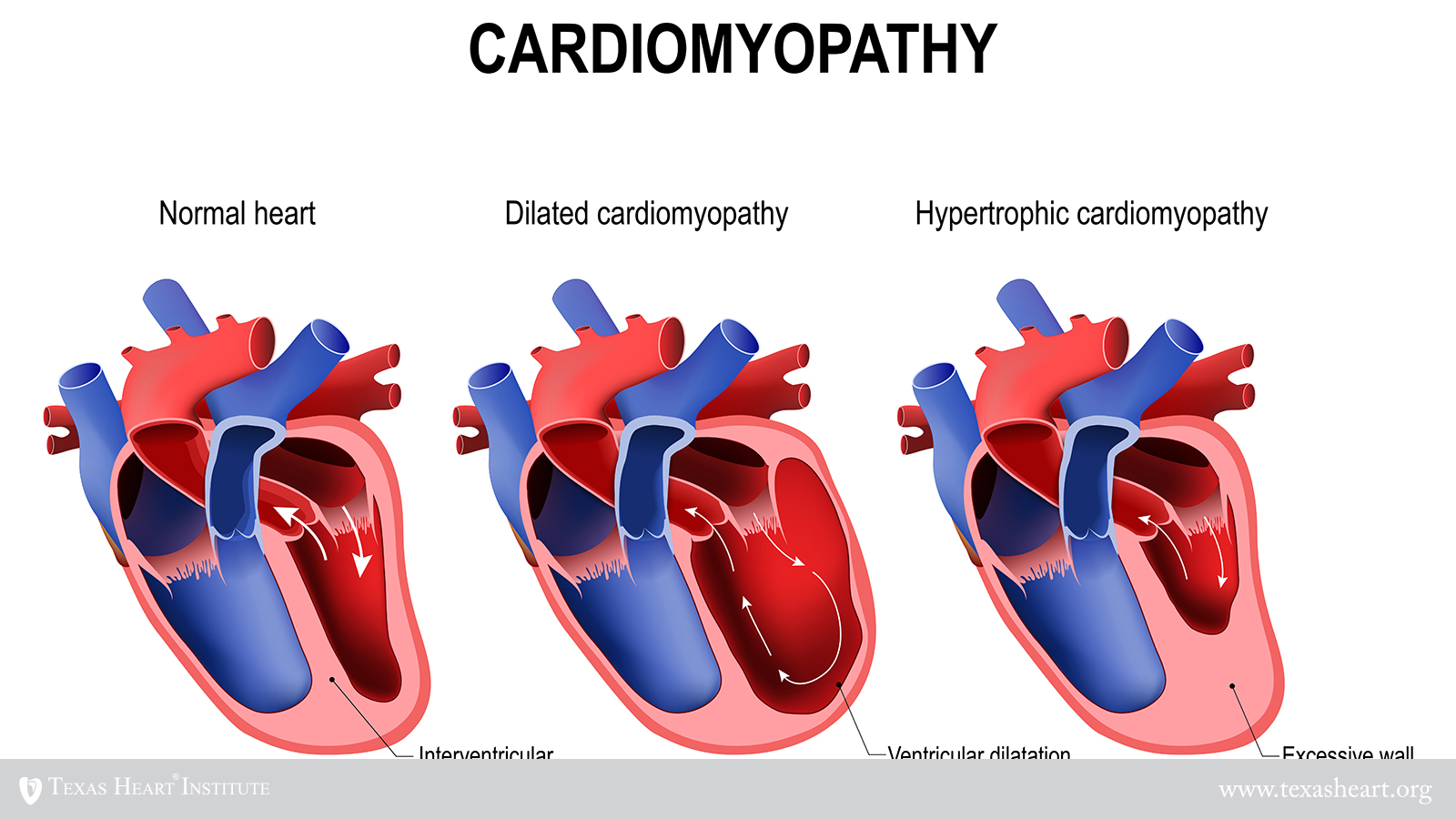
Dilated Cardiomyopathy Texas Heart Institute As heart function worsens, symptoms become more noticeable. the first symptom is often a heart murmur. additional dilated cardiomyopathy symptoms may include: cough and congestion. dizziness or lightheadedness. fainting. fatigue, unusual tiredness. palpitations or fluttering in your chest. shortness of breath (dyspnea). Dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is a disease of the heart muscle characterized by enlargement and dilation of one or both of the ventricles along with impaired contractility defined as left ventricular ejection fraction (lvef) less than 40%. by definition, patients have systolic dysfunction and may or may not have overt symptoms of heart failure. this disease process can be classified as either.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dilated-cardiomyopathy-heart-failure-17461741_Final-bffba3a42f4f462eb0fa767b5fed55da.jpg)
Dilated Cardiomyopathy Symptoms Causes Diagnosis And Treatment Signs and symptoms of dilated cardiomyopathy may include: fatigue. shortness of breath (dyspnea) during activity or while lying down. reduced ability to exercise. swelling (edema) in the legs, ankles, feet or belly (abdomen) chest pain or discomfort. fast, fluttering or pounding heartbeat (palpitations). Dilated cardiomyopathy (dcm) is the most common type, occurring mostly in adults younger than 50. it affects the heart's ventricles and atria, the lower and upper chambers of the heart. dilated cardiomyopathy is more common in black people than in white people. it's also more prevalent in men than in women. frequently, the disease starts in the. Diabetes. infections of the heart, including endocarditis. other causes include: exposure to certain toxins, including lead. exposure to drugs such as cocaine, methamphetamine, and alcohol. Treatment of dilated cardiomyopathy depends on the causes. the goals of treatment are to reduce symptoms, improve blood flow and prevent further heart damage. dilated cardiomyopathy treatment may include medications or surgery to implant a medical device that helps the heart beat or pump blood.

Dilated Cardiomyopathy And Chronic Cardiac Inflammation Pathogenesis Diabetes. infections of the heart, including endocarditis. other causes include: exposure to certain toxins, including lead. exposure to drugs such as cocaine, methamphetamine, and alcohol. Treatment of dilated cardiomyopathy depends on the causes. the goals of treatment are to reduce symptoms, improve blood flow and prevent further heart damage. dilated cardiomyopathy treatment may include medications or surgery to implant a medical device that helps the heart beat or pump blood. Dilated cardiomyopathy, or dcm, is when the heart chambers stretch and become thin. it often starts in the left ventricle. as the disease gets worse, it may spread to the right ventricle and to the atria. as the muscle stretches, it becomes weak and does not contract well. eventually, the heart can't pump as much blood forward as it normally would. this causes fluid to back up in the lungs and. Dilated cardiomyopathy is myocardial dysfunction causing heart failure in which ventricular dilation and systolic dysfunction predominate. symptoms include dyspnea, fatigue, and peripheral edema. diagnosis is clinical and by elevated natriuretic peptides, chest x ray, echocardiography, and mri. treatment is directed at the cause.

Comments are closed.