Differential Scanning Calorimetry Type

Differential Scanning Calorimetry Type Dielectric thermal analysis. differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is measured as a function of temperature. [1] both the sample and reference are maintained at nearly the same temperature throughout the. Differential scanning calorimetry is a specific type of calorimetry including both a sample substance and a reference substance, residing in separate chambers. while the reference chamber contains only a solvent (such as water), the sample chamber contains an equal amount of the same solvent in addition to the substance of interest, of which.
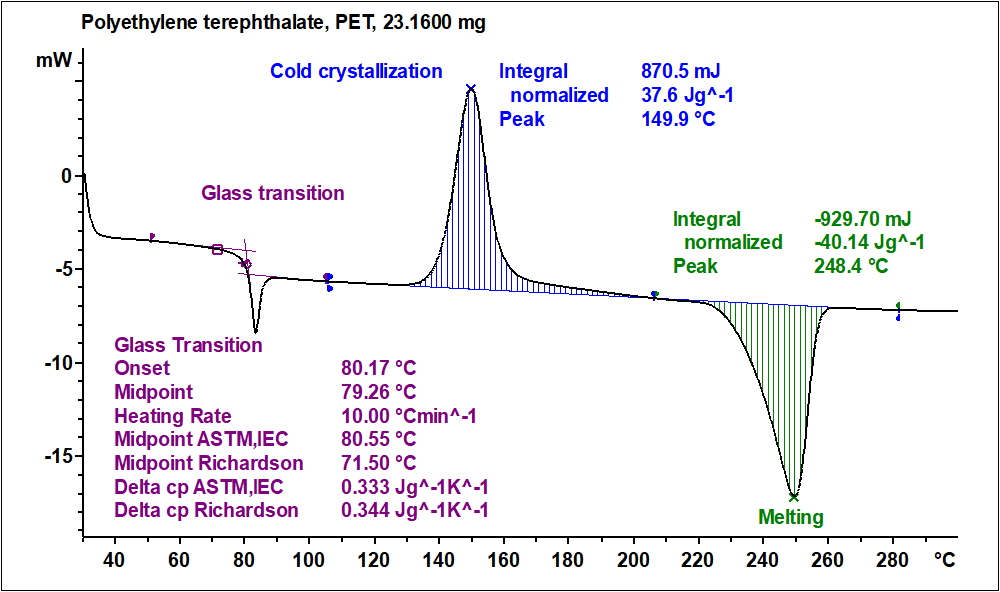
Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc Surface Science Western Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) has become the most widely used thermal analysis technique. in this technique, the sample and the reference materials are subjected to a precisely programmed temperature change. dsc is very similar to dta and gives much the same sort of information but dsc is more often used for quantitative measurement. Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. furthermore, the chemical reaction such as thermal curing, heat history, specific heat capacity, and purity analysis are also measurable. recently, with the development of the highly functional polymeric material, these thermal properties. Figure 31.2.2 31.2. 2: components of instrument for a differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) experiment. the sample and the reference material are (a) placed in small aluminum pans, each with a separate lid, and then (b) the lid and the pan are crimped together. the sample chamber in (c) allows for applying heat to the sample and the reference. Differential scanning calorimetry grew out of differential thermal analysis (dta). dta was developed by great scientists like le chatelier, roberts austen, kurnakov and saladin in the 19th century and at the beginning of the 20th century ( lechatelier, 1887 , lechatelier, 1904 roberts austen, 1899a , roberts austen, 1899b kurnakov, 1904.

Different Types Of Differential Scanning Calorimeters Dsc A Figure 31.2.2 31.2. 2: components of instrument for a differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) experiment. the sample and the reference material are (a) placed in small aluminum pans, each with a separate lid, and then (b) the lid and the pan are crimped together. the sample chamber in (c) allows for applying heat to the sample and the reference. Differential scanning calorimetry grew out of differential thermal analysis (dta). dta was developed by great scientists like le chatelier, roberts austen, kurnakov and saladin in the 19th century and at the beginning of the 20th century ( lechatelier, 1887 , lechatelier, 1904 roberts austen, 1899a , roberts austen, 1899b kurnakov, 1904. 4.22.3.3.1 differential scanning calorimetry. differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a technique that can be used to determine phase transition temperatures (tg, tm) and heat capacities (cp) of the analyzed samples. the samples are loaded into a pan of known dimensions (hermetically sealed in some cases) and heated at a fixed rate (°c min. A practical introduction to differential scanning calorimetry paul gabbott contents 1.1 introduction 2 1.2 principles of dsc and types of measurements made 2 1.2.1 a definition of dsc 2 1.2.2 heat flow measurements 3 1.2.3 specific heat (c p)3 1.2.4 enthalpy 5 1.2.5 derivative curves 5 1.3 practical issues 6 1.3.1 encapsulation 6 1.3.2.
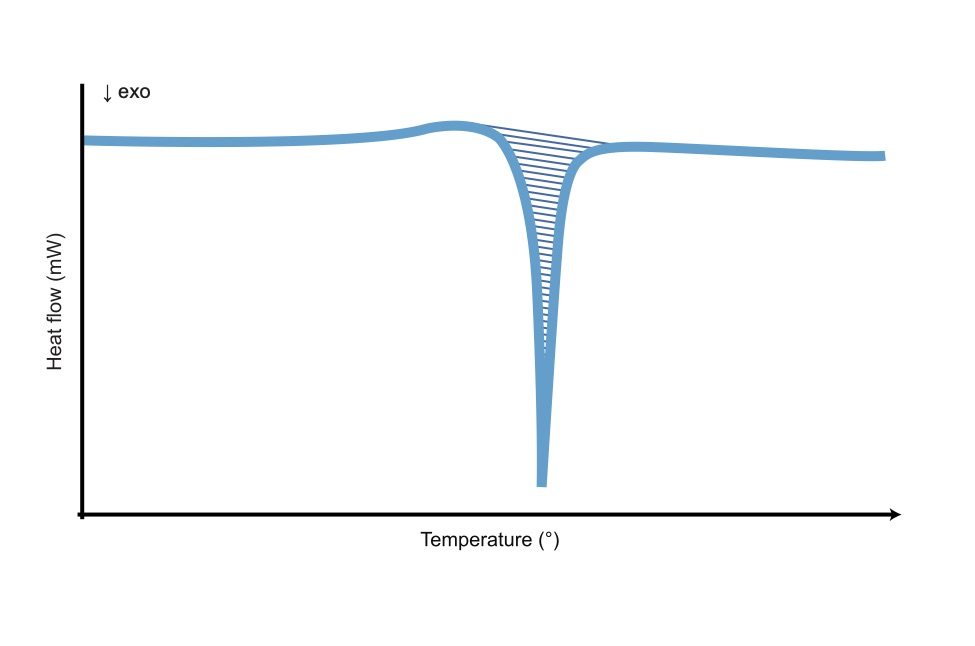
Differential Scanning Calorimetry Type 4.22.3.3.1 differential scanning calorimetry. differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a technique that can be used to determine phase transition temperatures (tg, tm) and heat capacities (cp) of the analyzed samples. the samples are loaded into a pan of known dimensions (hermetically sealed in some cases) and heated at a fixed rate (°c min. A practical introduction to differential scanning calorimetry paul gabbott contents 1.1 introduction 2 1.2 principles of dsc and types of measurements made 2 1.2.1 a definition of dsc 2 1.2.2 heat flow measurements 3 1.2.3 specific heat (c p)3 1.2.4 enthalpy 5 1.2.5 derivative curves 5 1.3 practical issues 6 1.3.1 encapsulation 6 1.3.2.

How To Understand Analyse And Interpret Dsc Differential Scanning

Comments are closed.