Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc Principle Instrumentation
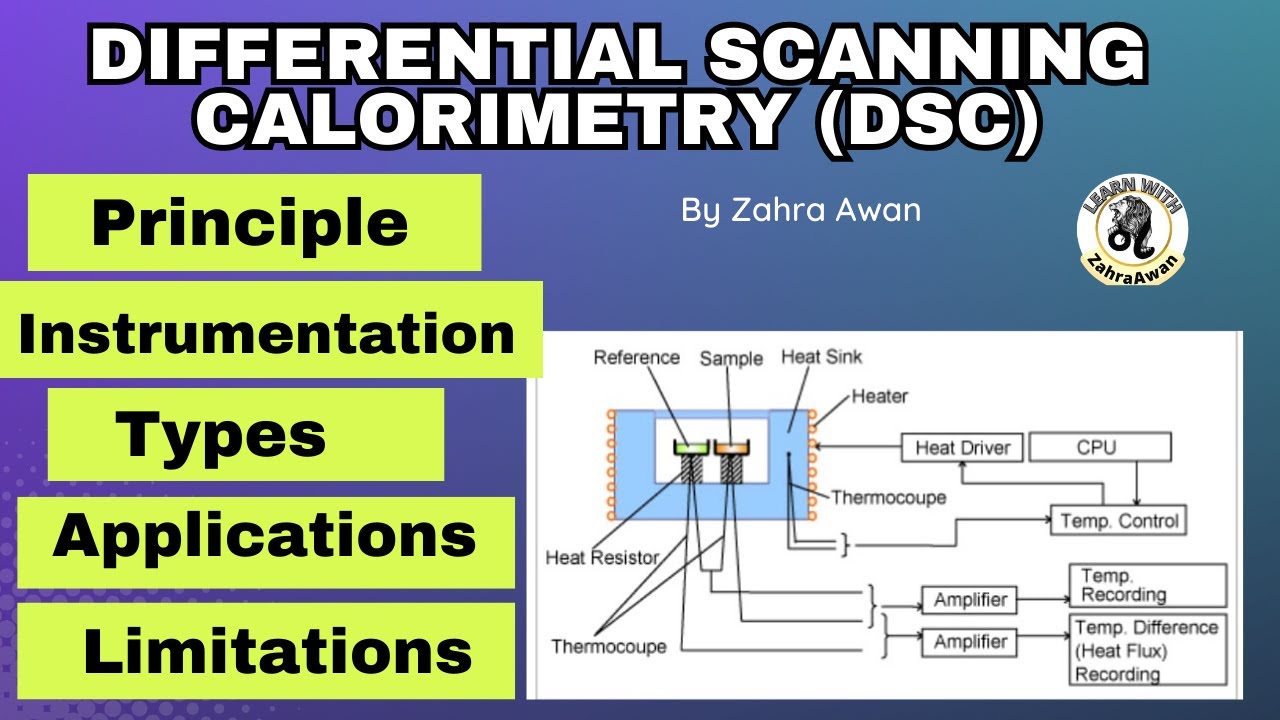
Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc Principle Instrumentation Dsc enables the measurements of the transition such as the glass transition, melting, and crystallization. furthermore, the chemical reaction such as thermal curing, heat history, specific heat capacity, and purity analysis are also measurable. recently, with the development of the highly functional polymeric material, these thermal properties. 4.1 principle. in dsc, the difference in temperature (∆t) between the sample and an inert reference is maintained at zero as they are subjected to controlled heating or cooling. the instrument is provided with a separate heater for the sample and the reference. when a thermal transition occurs in the sample, thermal energy is added to either.

Principle Of Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc Hitachi High Figure 31.2.2 31.2. 2: components of instrument for a differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) experiment. the sample and the reference material are (a) placed in small aluminum pans, each with a separate lid, and then (b) the lid and the pan are crimped together. the sample chamber in (c) allows for applying heat to the sample and the reference. Dielectric thermal analysis. differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is measured as a function of temperature. [1] both the sample and reference are maintained at nearly the same temperature throughout the. 2.2 dta instruments. the basic components of a differential thermal analysis (dta) cell are shown in fig.1. the sample environment consists of a ceramic (or metallic) block to ensure an uniform heat distribution, specimen crucibles and thermocouples (for the sample and reference). metallic blocks are less likely to cause baseline drifts. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is the most important thermal analysis technique used today and the most common thermal analysis instrument found in chemical characterization laboratories. dsc has become an everyday tool in characterization laboratories, but many researchers using this technique have a limited understanding of the true.

Differential Scanning Calorimetry Dsc Ppt Download 2.2 dta instruments. the basic components of a differential thermal analysis (dta) cell are shown in fig.1. the sample environment consists of a ceramic (or metallic) block to ensure an uniform heat distribution, specimen crucibles and thermocouples (for the sample and reference). metallic blocks are less likely to cause baseline drifts. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is the most important thermal analysis technique used today and the most common thermal analysis instrument found in chemical characterization laboratories. dsc has become an everyday tool in characterization laboratories, but many researchers using this technique have a limited understanding of the true. This chapter contains section titled: introduction principles of dsc and types of measurements made practical issues calibration interpretation of data oscillatory temperature profiles. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a thermal analysis technique which involves the measurement of temperature difference between the sample and the reference material as a function of the temperature while sample and reference both are subjected to a controlled temperature program. this technique is especially used for qualitative and.

Differential Scanning Calorimetry Principle Madeleine Jackson This chapter contains section titled: introduction principles of dsc and types of measurements made practical issues calibration interpretation of data oscillatory temperature profiles. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a thermal analysis technique which involves the measurement of temperature difference between the sample and the reference material as a function of the temperature while sample and reference both are subjected to a controlled temperature program. this technique is especially used for qualitative and.

Differential Scanning Calorimetry Principle Oliver Wright

Comments are closed.