Differential Scanning Calorimetry Automated Calorimetry Facility
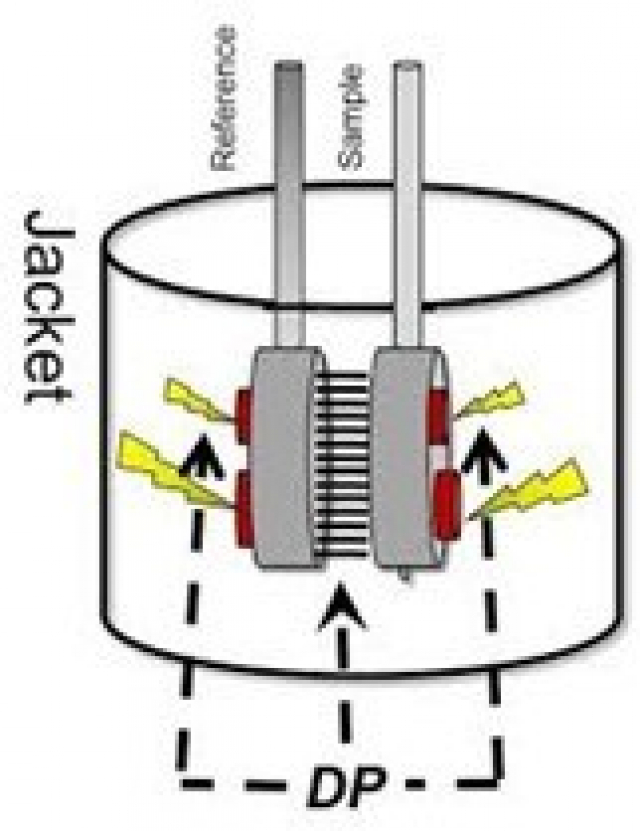
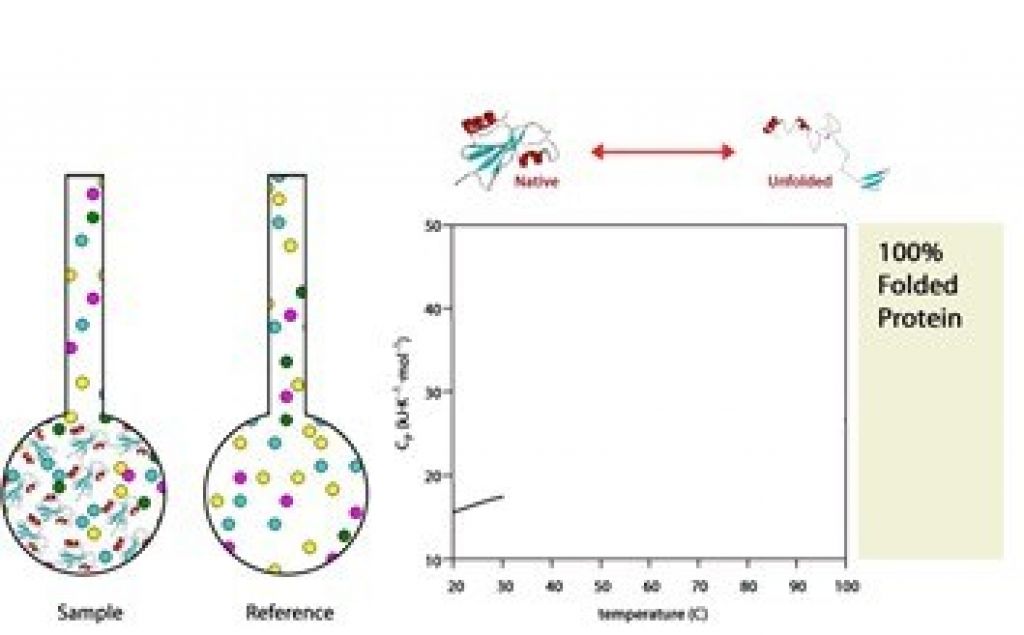
Differential Scanning Calorimetry Automated Calorimetry Facility Differential scanning calorimetry. differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a technique that measures the thermal stability of a macromolecule's tertiary and secondary structure. the raw data obtained in this experiment is a plot of heat capacity difference as a function of temperature, and analysis will yield the macromolecule's t m as well. Principles and design of differential scanning calorimetry experiments differential scanning calorimetry — the basic setup. the dp is the differential power added to maintain Δt~0 between the cells. t m — an indicator of thermal stability. what does the t m value mean? t m corresponds to 50% folded 50% unfolded of a protein.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry Automated Calorimetry Facility The automated biological calorimetry core facility at the pennsylvania state university is a one of a kind fee for service facility in the north east region of the us. this high throughput state of the art capability was envisioned in september 2011 and has been ably serving the needs of the scientific community at penn state. Differential scanning calorimetry (dsc), is a straight forward, non perturbing technique, first developed in the early1960s. this method measures the thermodynamic properties of thermally induced transitions and has been applied to a variety of biological macromolecules such as lipids or proteins.[1,2] examples of these applications have involved conformational states of proteins, dna binding. Dielectric thermal analysis. differential scanning calorimetry (dsc) is a thermoanalytical technique in which the difference in the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of a sample and reference is measured as a function of temperature. [1] both the sample and reference are maintained at nearly the same temperature throughout the. Automated biological calorimetry facility huck institutes for life sciences penn state university 8 althouse lab university park, pa 16802. united states.

Comments are closed.