Different Types Of Inheritance Pattern
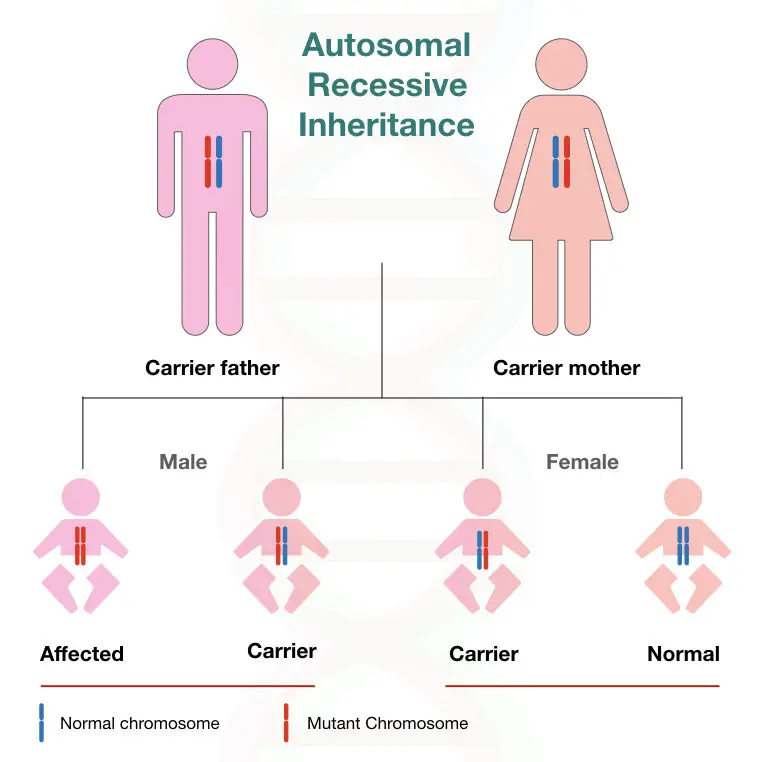
Different Types Of Inheritance Pattern Autosomal recessive inheritance. when a genetic disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, the disorder corresponds to the recessive phenotype. heterozygous individuals will not display symptoms of this disorder, because their unaffected gene will compensate. such an individual is called a carrier. Inheritance patterns differ for genes on sex chromosomes (chromosomes x and y) compared to genes located on autosomes, non sex chromosomes (chromosomes numbers 1 22). this is due to the fact that, in general, females carry two x chromosomes (xx), while males carry one x and one y chromosome (xy). therefore, females carry two copies of each x.
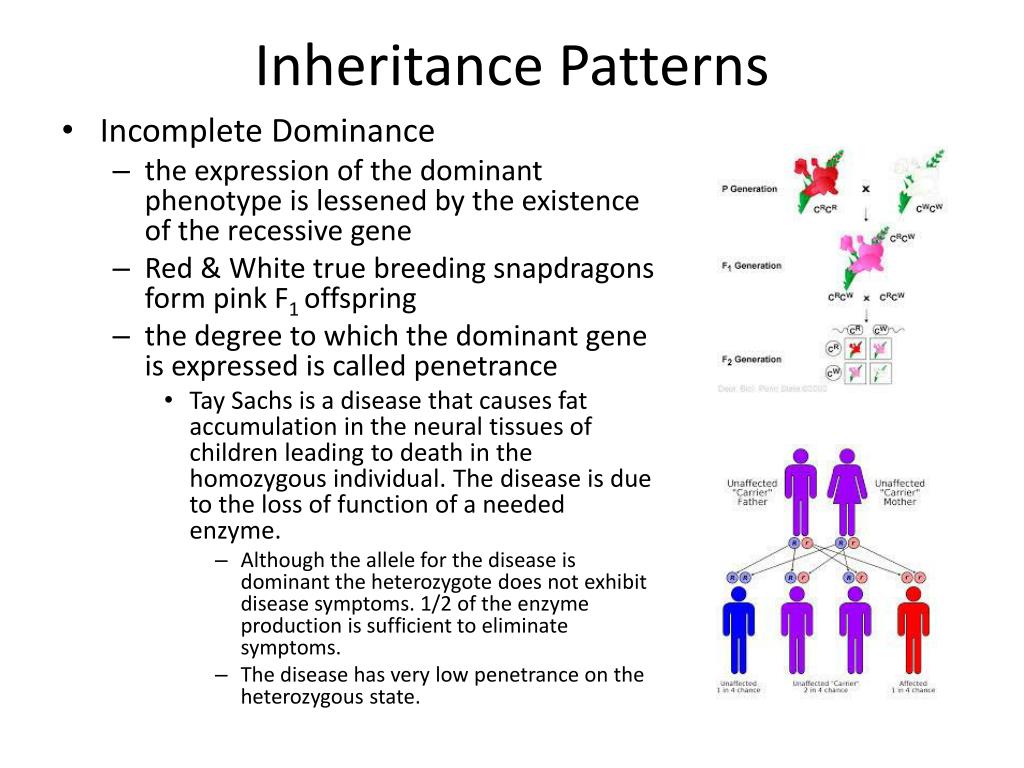
Types Of Inheritance Patterns Both types of the gene have a different inheritance pattern. human sex is decided by the presence or absence of the y chromosome. if a y chromosome is present along with the x chromosome, the embryo develops into a male. A characteristic of x linked inheritance is that fathers cannot pass x linked traits to their sons (no male to male transmission). fragile x syndrome. x linked recessive. x linked recessive disorders are also caused by variants in genes on the x chromosome. in males (who have only one x chromosome), one altered copy of the gene in each cell is. This type of inheritance often follows different patterns than autosomal inheritance and can lead to unique inheritance patterns in certain genetic conditions. while mendelian patterns of inheritance, such as autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive, can be relatively straightforward to understand, non mendelian patterns of inheritance can be more complex. One of the unaffected females mates with a normal man, and they produce two children: one affected male and an unaffected female. this indicates the unaffected mother was a carrier. this pattern of inheritance is typical of an x linked recessive trait. [back to figure 4.3.4] figure 4.3.5 pedigree chart showing the inheritance of a y linked.
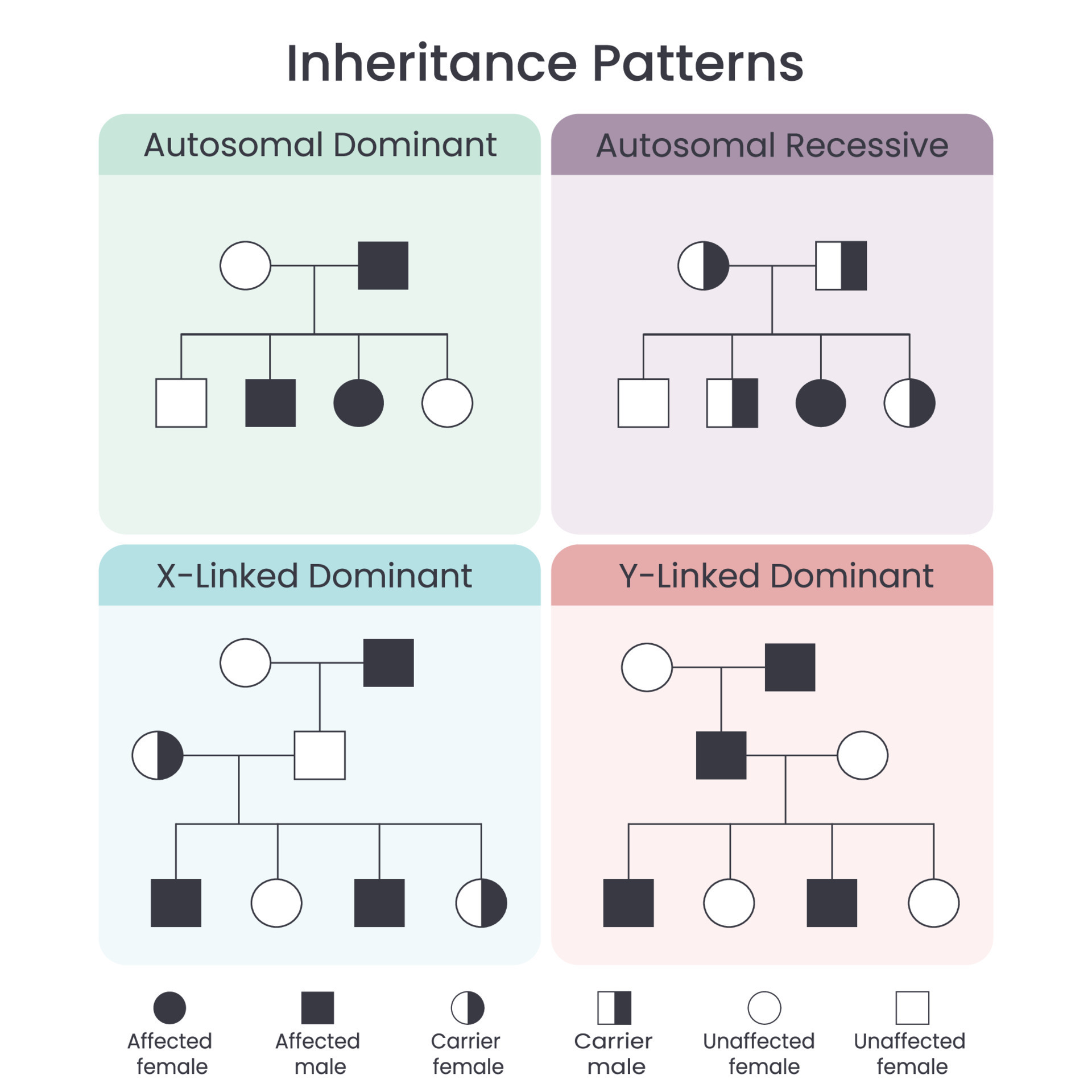
Genetic Inheritance Patterns Scientific Vector Illustration Infographic This type of inheritance often follows different patterns than autosomal inheritance and can lead to unique inheritance patterns in certain genetic conditions. while mendelian patterns of inheritance, such as autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive, can be relatively straightforward to understand, non mendelian patterns of inheritance can be more complex. One of the unaffected females mates with a normal man, and they produce two children: one affected male and an unaffected female. this indicates the unaffected mother was a carrier. this pattern of inheritance is typical of an x linked recessive trait. [back to figure 4.3.4] figure 4.3.5 pedigree chart showing the inheritance of a y linked. This is different from a quantitative trait where alleles at multiple genes are additive. the gene by gene inheritance pattern can also be called epistasis. the take home message on gene by gene interactions is that this phenomenon alters the expected phenotypic ratios of a mendelian dihybrid cross (9:3:3:1) to a different pattern. Mendel's studies of inheritance patterns in pea plants are a solid foundation for our current understanding of single gene diseases in humans. also called mendelian or monogenic diseases, these.

Comments are closed.