Diagram Of Plate Tectonics
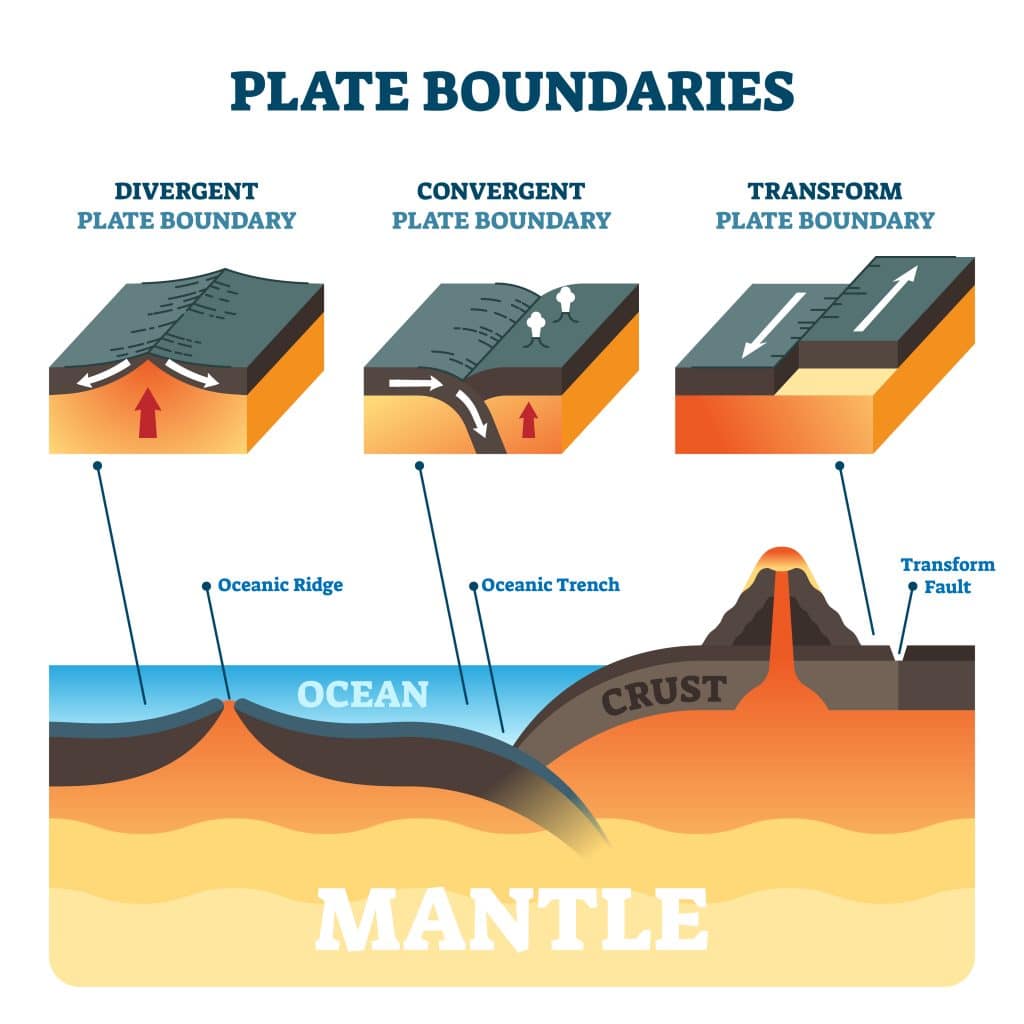
Section 4 The Theory Of Plate Tectonics Nitty Gritty Science Plate tectonics articles, theory, plate diagrams, maps, teaching ideas what is plate tectonics? plate tectonics is a theory about how earth's lithosphere is divided into a series of rigid plates; and, how movements of these plates produce earthquakes, volcanoes, ocean trenches, mountain ranges, and more. 1. major plates. according to the world atlas, there are seven major tectonic plates in all. they are listed below in order of their size. pacific plate – 103,300,000 sq km. north american plate – 75,900,000 sq km. eurasian plate – 67,800,000 sq km. african plate – 61,300,000 sq km. antarctic plate – 60,900,000 sq km.
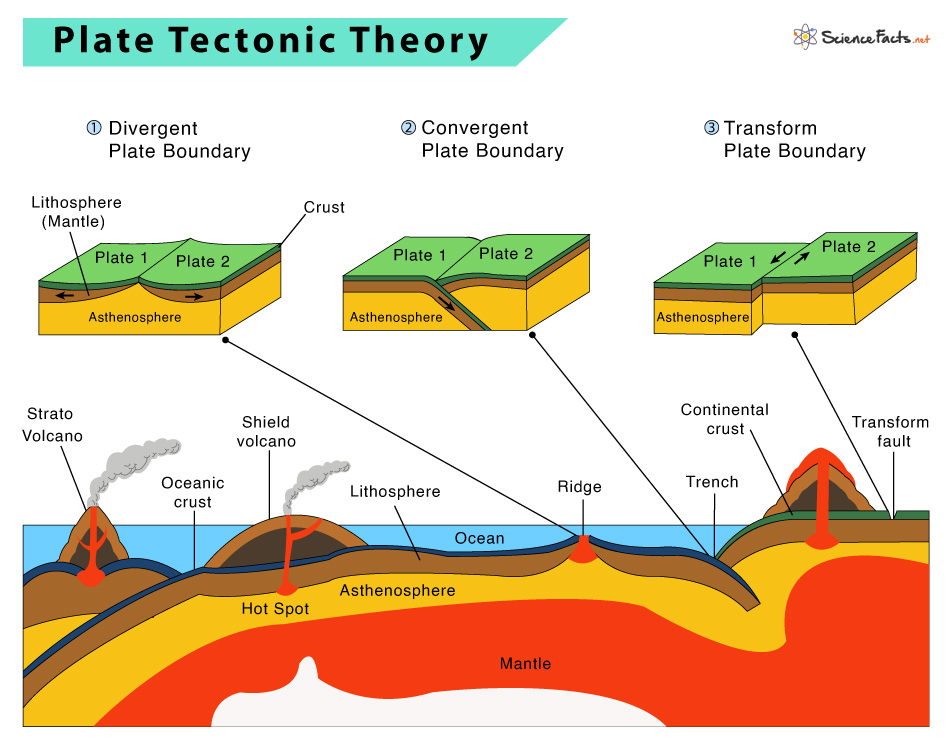
Plate Tectonics Plate Boundaries And Hotspot Explanation Plate tectonics is a scientific theory that explains how major landforms are created as a result of earth’s subterranean movements. the theory, which solidified in the 1960s, transformed the earth sciences by explaining many phenomena, including mountain building events, volcanoes, and earthquakes. in plate tectonics, earth’s outermost. Plate tectonics (from latin tectonicus, from ancient greek τεκτονικός (tektonikós) 'pertaining to building') [ 1 ] is the scientific theory that earth 's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. [ 2 ][ 3 ][ 4 ] the model builds on the concept of continental. In essence, plate tectonic theory is elegantly simple. earth ’s surface layer, 50 to 100 km (30 to 60 miles) thick, is rigid and is composed of a set of large and small plates. together, these plates constitute the lithosphere, from the greek lithos, meaning “ rock.”. the lithosphere rests on and slides over an underlying partially molten. Plates move apart at mid ocean ridges where new seafloor forms. between the two plates is a rift valley. lava flows at the surface cool rapidly to become basalt, but deeper in the crust, magma cools more slowly to form gabbro. so the entire ridge system is made up of igneous rock that is either extrusive or intrusive.
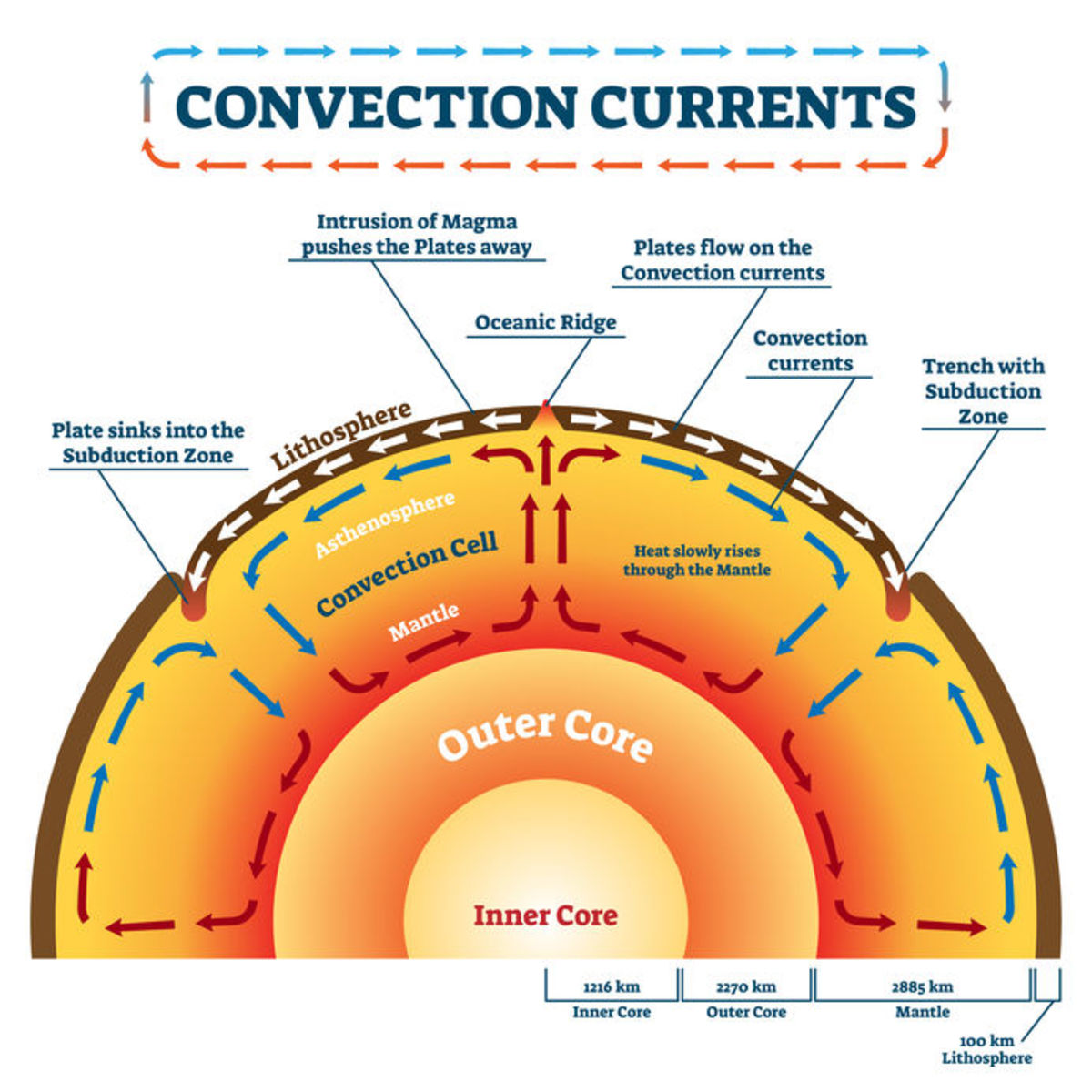
Evolution Of The Theory Of Plate Tectonics Owlcation In essence, plate tectonic theory is elegantly simple. earth ’s surface layer, 50 to 100 km (30 to 60 miles) thick, is rigid and is composed of a set of large and small plates. together, these plates constitute the lithosphere, from the greek lithos, meaning “ rock.”. the lithosphere rests on and slides over an underlying partially molten. Plates move apart at mid ocean ridges where new seafloor forms. between the two plates is a rift valley. lava flows at the surface cool rapidly to become basalt, but deeper in the crust, magma cools more slowly to form gabbro. so the entire ridge system is made up of igneous rock that is either extrusive or intrusive. Plate tectonics refers to the process of plate formation, movement, and destruction. it finds its foundations in two theories, continental drift and sea floor spreading. continental drift describes the movements of continents over the earth's surface. sea floor spreading refers to the creation new oceanic plate material and movement away from. More plate tectonics maps here are two plate tectonics maps which show more detail than the maps above. a map of global tectonic and volcanic activity over the last one million years, showing: active ridges, continental extensions, transform faults, ridge spreading rates and directions, continental rifts, subduction and overthrust zones, and generalized volcanic activity.
Theory Of Plate Tectonics Ck 12 Foundation Plate tectonics refers to the process of plate formation, movement, and destruction. it finds its foundations in two theories, continental drift and sea floor spreading. continental drift describes the movements of continents over the earth's surface. sea floor spreading refers to the creation new oceanic plate material and movement away from. More plate tectonics maps here are two plate tectonics maps which show more detail than the maps above. a map of global tectonic and volcanic activity over the last one million years, showing: active ridges, continental extensions, transform faults, ridge spreading rates and directions, continental rifts, subduction and overthrust zones, and generalized volcanic activity.

Comments are closed.