Diagram Of Earth S Orbit
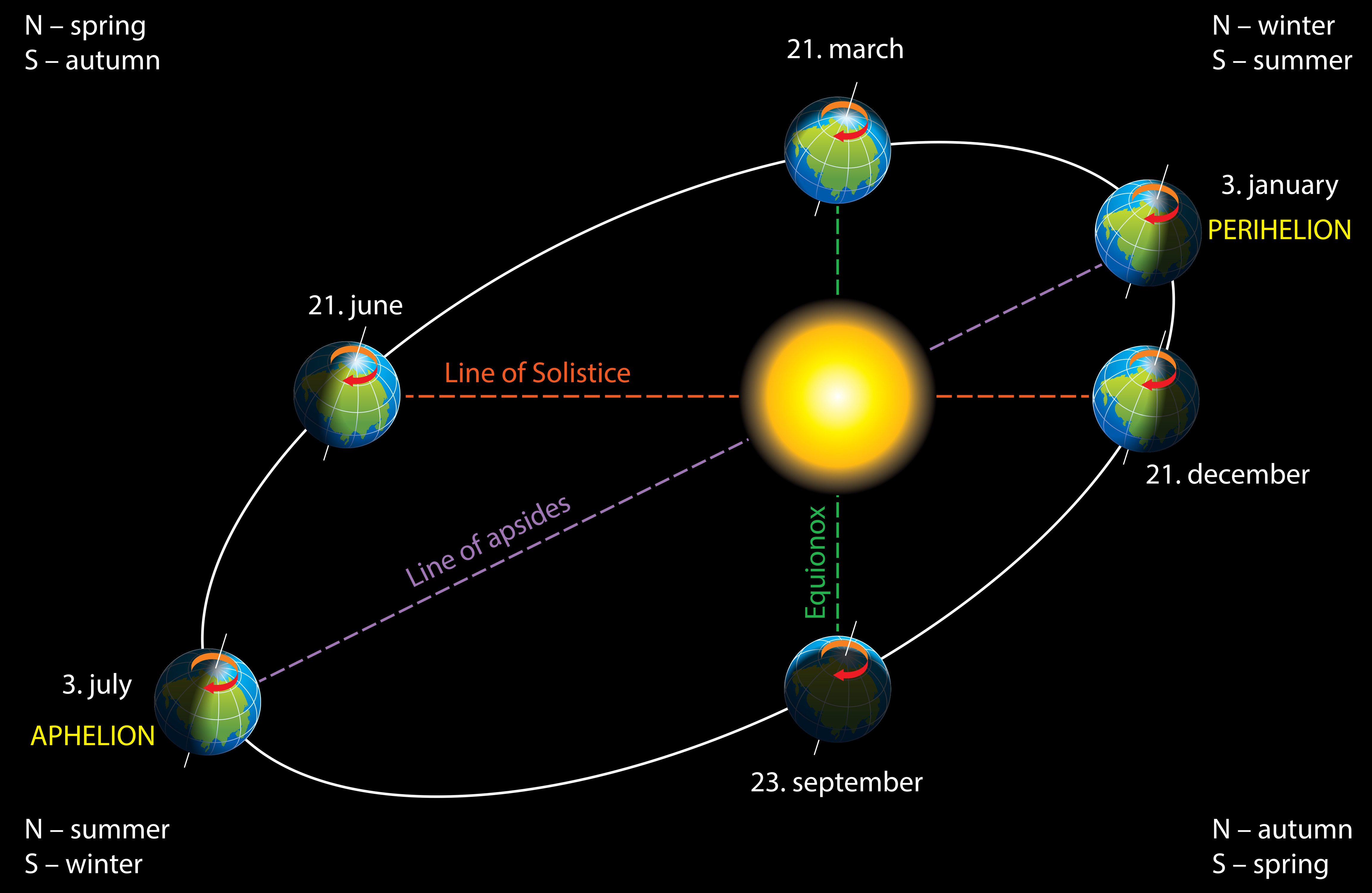
Physics Earth S Orbit Level 1 Activity For Kids Primaryleap Co Uk The following diagram illustrates the positions and relationship between the lines of solstices, equinoxes, and apsides of earth's elliptical orbit. the six earth images are positions along the orbital ellipse, which are sequentially the perihelion (periapsis—nearest point to the sun) on anywhere from january 2 to january 5, the point of. The earth's orbit takes about 365 days, this is also called a year. this means that in 365 days (a year) the earth has gone around the sun. [a] from this we can find that the orbital speed of the earth is about 108,000 kilometres per hour (67,000 mph) through space. the closest distance earth is to the sun, or perihelion, is 146 million km (91.

Earth S Orbit Around The Sun Diagram Stock Image C010 7498 Diagram of the earths orbit around the sun. credit: nasa h. zell first of all, the speed of the earth's orbit around the sun is 108,000 km h, which means that our planet travels 940 million km. Relevant values of the earth in the model distance from the sun: mil. km orbital speed: km s solar energy: w m². solar energy includes all electromagnetic solar radiation which, at a given distance from the sun, falls on an 1 m² area perpendicular to the sun's rays. using mouse you can move in space and rotate the scene. (c) václav Černík. Over long periods of time, the gravitational pull of other members of our solar system slowly change earth’s spin, tilt, and orbit. over approximately 100,000 – 400,000 years, gravitational forces slowly change earth’s orbit between more circular and elliptical shapes, as indicated by the blue and yellow dashed ovals in the figure to the. Then, on july 4 of each year, earth is as far from the sun as it ever gets, at a distance of 152,171,522 kilometers. that point is called "aphelion." every world (including comets and asteroids) in the solar system that primarily orbits the sun has a perihelion point and an aphelion. notice that for earth, the closest point is during northern.

Orientation Of Earth S Tilt In Orbit Over long periods of time, the gravitational pull of other members of our solar system slowly change earth’s spin, tilt, and orbit. over approximately 100,000 – 400,000 years, gravitational forces slowly change earth’s orbit between more circular and elliptical shapes, as indicated by the blue and yellow dashed ovals in the figure to the. Then, on july 4 of each year, earth is as far from the sun as it ever gets, at a distance of 152,171,522 kilometers. that point is called "aphelion." every world (including comets and asteroids) in the solar system that primarily orbits the sun has a perihelion point and an aphelion. notice that for earth, the closest point is during northern. The degree of eccentricity has an effect on our climate, and so, on a time scale of 100,000 years that effect increases and decreases. figure 3.4.1 a representation of the variations in the elliptical nature of earth’s orbit around the sun. the elliptical shapes of the orbits are greatly exaggerated in this diagram. The earth completes one orbit every 365.242199 mean solar days, a fact which goes a long way towards explaining why need an extra calendar day every four years (aka. during a leap year). the.

Comments are closed.