Diagram Of A Fungi
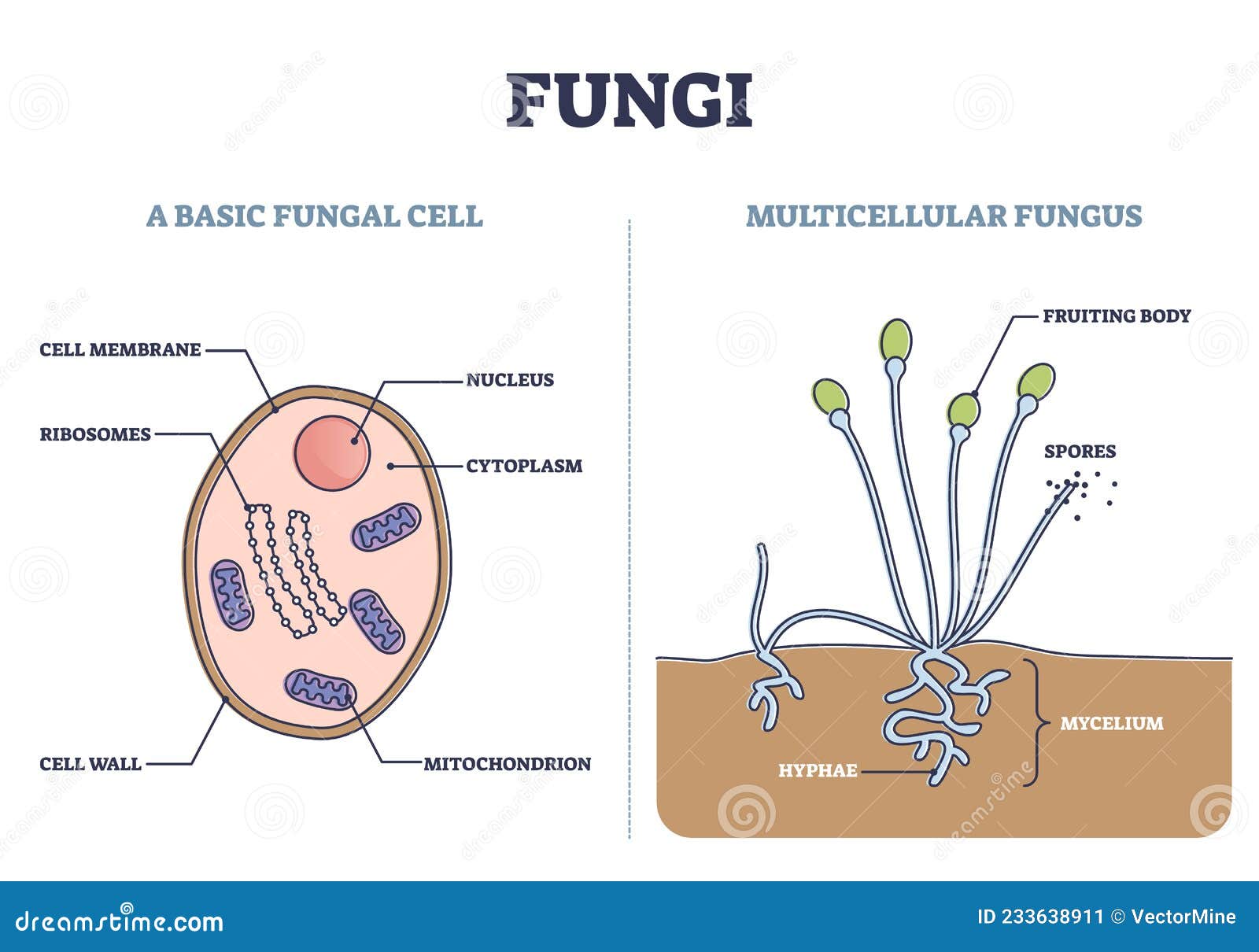
Fungi As Basic Fungal Cell And Multicellular Fungus Structure Outline Fungi thrive in environments that are moist and slightly acidic; they can grow with or without light. figure 24.1b. 1 24.1 b. 1: division of hyphae into separate cells: fungal hyphae may be (a) septated or (b) coenocytic (coeno = “common”; cytic = “cell”) with many nuclei present in a single hypha. Fungus, any of about 144,000 known species of organisms of the kingdom fungi, including yeasts, mildews, molds, and mushrooms. fungi are some of the most widely distributed organisms on earth and are of great environmental and medical importance. learn more about their life cycles, evolution, taxonomy, and features.

Biology вђ Kingdom Fungi Askiitians Fungi, unlike other organisms, possess a unique and intricate cellular structure. at the core of this structure lies the hypha. a hypha (plural: hyphae) is a tubular, branching structure that serves as the foundational unit of fungal growth. imagine the roots of a plant reaching out into the soil, extracting nutrients, and providing the plant. Fungi (singular: fungus) are one of the kingdoms of life in biology, along with animals, plants, protists, bacteria, and archaebacteria. examples of fungi include yeast, mushrooms, toadstools (poisonous mushrooms), and molds. the scientific study of fungi is called mycology. around 150,000 species of fungi are known, but there may be between 2. The basic structural constituent of the cell wall in the zygomycetes and higher fungi (ascomycetes and basidiomycetes) is chitin. it is a polysaccharide based on the nitrogen containing sugar (glucosamine). it is probable that more or less closely associated with chitin in the cell wall are pectic materials, protein, lipids, cellulose, callose. Fungi consist of long thread like structures known as hyphae. these hyphae together form a mesh like structure called mycelium. fungi possess a cell wall which is made up of chitin and polysaccharides. the cell wall comprises a protoplast, which is differentiated into other cell parts such as cell membrane, cytoplasm, cell organelles and nuclei.

Labeled Diagram Of Fungi The basic structural constituent of the cell wall in the zygomycetes and higher fungi (ascomycetes and basidiomycetes) is chitin. it is a polysaccharide based on the nitrogen containing sugar (glucosamine). it is probable that more or less closely associated with chitin in the cell wall are pectic materials, protein, lipids, cellulose, callose. Fungi consist of long thread like structures known as hyphae. these hyphae together form a mesh like structure called mycelium. fungi possess a cell wall which is made up of chitin and polysaccharides. the cell wall comprises a protoplast, which is differentiated into other cell parts such as cell membrane, cytoplasm, cell organelles and nuclei. Some fungi show dimorphism between the two states by following both yeast and mould cell cycle and called “dimorphic fungi”. in this context, we will discuss the structure of fungi by looking into the diagram and morphological features of both yeasts and moulds. content: fungal cell structure. characteristics; ultrastructure; structure of. Fungi definition. fungi (singular: fungus) are a kingdom of usually multicellular eukaryotic organisms that are heterotrophs (cannot make their own food) and have important roles in nutrient cycling in an ecosystem. fungi reproduce both sexually and asexually, and they also have symbiotic associations with plants and bacteria.
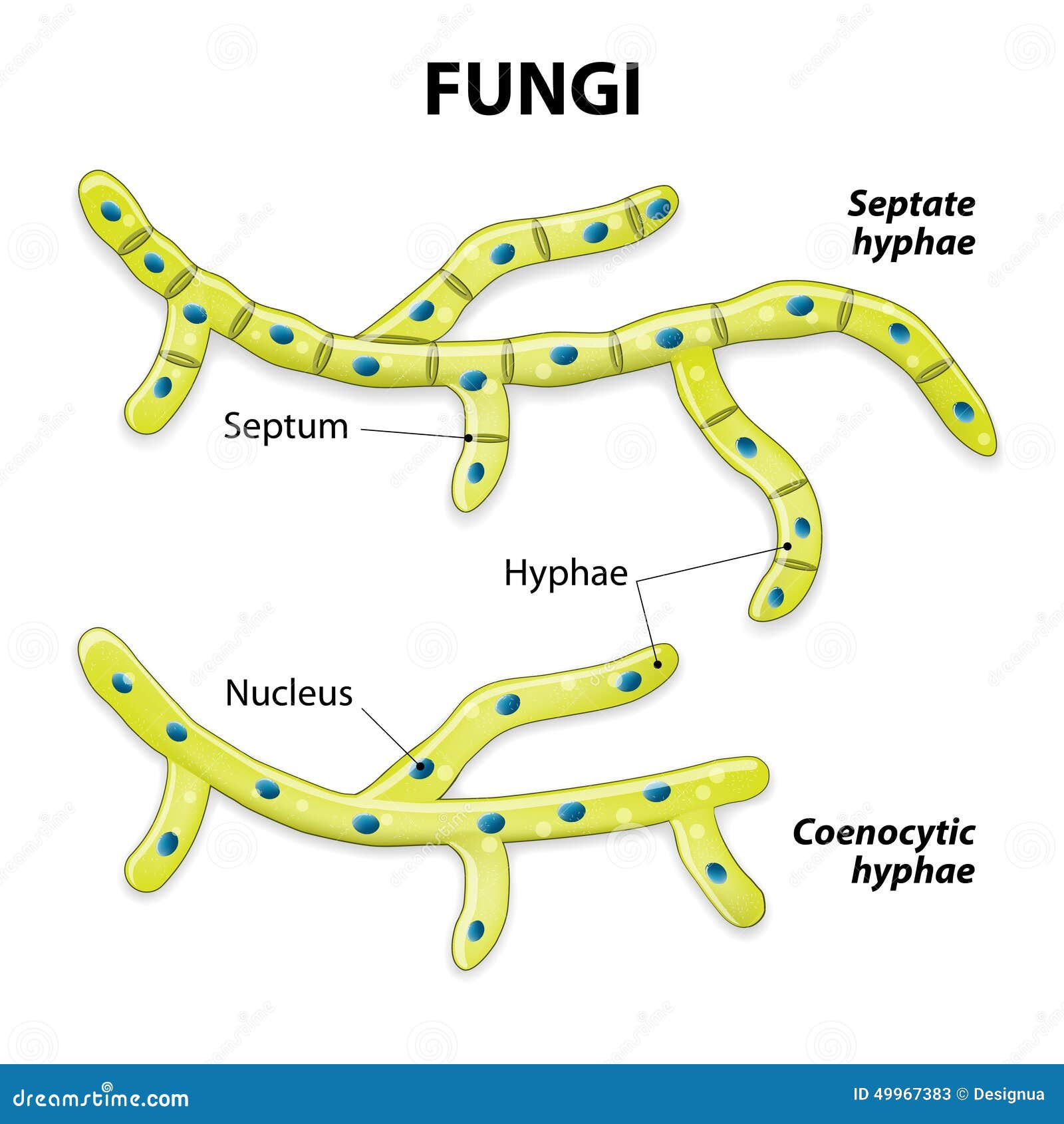
Diagram Of Fungi Cell Some fungi show dimorphism between the two states by following both yeast and mould cell cycle and called “dimorphic fungi”. in this context, we will discuss the structure of fungi by looking into the diagram and morphological features of both yeasts and moulds. content: fungal cell structure. characteristics; ultrastructure; structure of. Fungi definition. fungi (singular: fungus) are a kingdom of usually multicellular eukaryotic organisms that are heterotrophs (cannot make their own food) and have important roles in nutrient cycling in an ecosystem. fungi reproduce both sexually and asexually, and they also have symbiotic associations with plants and bacteria.

Comments are closed.