Deriving The Mean And Variance Of A Continuous Probability Distribution

Deriving The Mean And Variance Of A Continuous Probability Distribution Definition 4.2.1 4.2. 1. if x x is a continuous random variable with pdf f(x) f (x), then the expected value (or mean) of x x is given by. μ = μx = e[x] = ∫−∞∞ x ⋅ f(x)dx. μ = μ x = e [x] = ∫ − ∞ ∞ x ⋅ f (x) d x. the formula for the expected value of a continuous random variable is the continuous analog of the expected. The variance of a probability distribution. in this section i discuss the main variance formula of probability distributions. to see two useful (and insightful) alternative formulas, check out my latest post. from the get go, let me say that the intuition here is very similar to the one for means.

Mean And Variance Of A Continuous Probability Distribution Statistics A discrete random variable is usually integer number. n – the number of proteins in a cell. d‐ number of nucleotides different between two sequences. a continuous random variable is a real number. c=n v – the concentration of proteins in a cell of volume v. percentage d l*100% of different nucleotides in protein sequences of different. Mean & variance derivation to reach well crammed formulae. hypergeometric distribution, poisson distribution. 2. continuous probability distributions. uniform distribution, normal (gaussian. 24.4 mean and variance of sample mean. we'll finally accomplish what we set out to do in this lesson, namely to determine the theoretical mean and variance of the continuous random variable \ (\bar {x}\). in doing so, we'll discover the major implications of the theorem that we learned on the previous page. The normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution that plays a central role in probability theory and statistics. it is often called gaussian distribution, in honor of carl friedrich gauss (1777 1855), an eminent german mathematician who gave important contributions towards a better understanding of the normal distribution.

Continuous Probability Distributions Basic Introduction Youtube 24.4 mean and variance of sample mean. we'll finally accomplish what we set out to do in this lesson, namely to determine the theoretical mean and variance of the continuous random variable \ (\bar {x}\). in doing so, we'll discover the major implications of the theorem that we learned on the previous page. The normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution that plays a central role in probability theory and statistics. it is often called gaussian distribution, in honor of carl friedrich gauss (1777 1855), an eminent german mathematician who gave important contributions towards a better understanding of the normal distribution. The cumulative distribution function f(x) for a continuous rv x is defined for every number x by. f(x) = p(x ≤ x) =. for each x, f(x) is the area under the density curve to the left of x. this is illustrated in figure 4.5, where f(x) increases smoothly as x increases. a pdf and associated cdf. The mean and variance of a continuous random variable can be determined with the help of the probability density function, f(x). mean of continuous random variable. the mean of a continuous random variable can be defined as the weighted average value of the random variable, x. it is also known as the expectation of the continuous random variable.
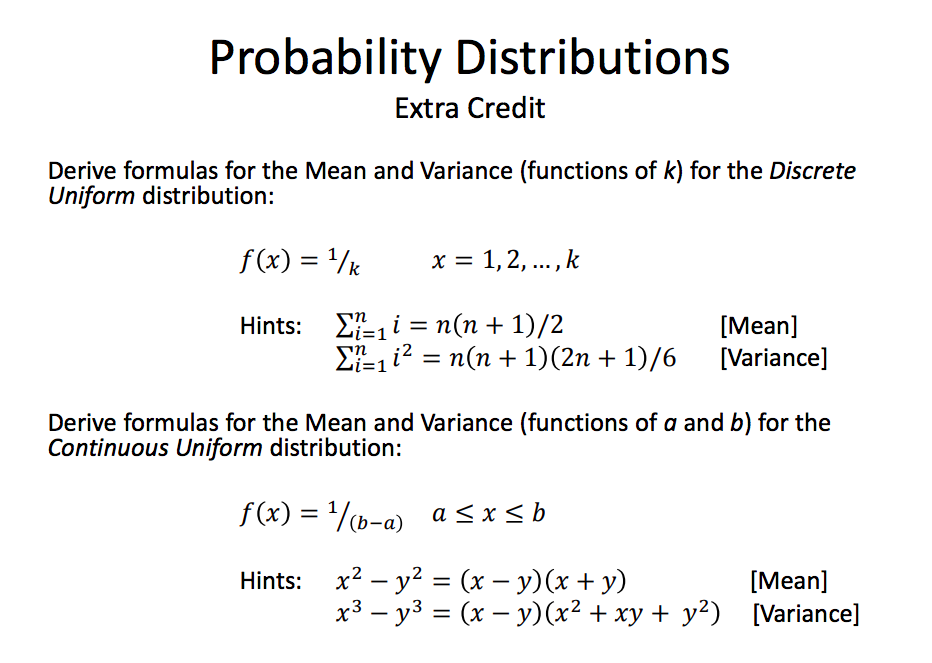
Variance Of Probability Distribution Formula Research Topics The cumulative distribution function f(x) for a continuous rv x is defined for every number x by. f(x) = p(x ≤ x) =. for each x, f(x) is the area under the density curve to the left of x. this is illustrated in figure 4.5, where f(x) increases smoothly as x increases. a pdf and associated cdf. The mean and variance of a continuous random variable can be determined with the help of the probability density function, f(x). mean of continuous random variable. the mean of a continuous random variable can be defined as the weighted average value of the random variable, x. it is also known as the expectation of the continuous random variable.

Mean Variance And Mode Of Continuous Probability Distribution Youtube

Comments are closed.