Dental Plaque Part 1 Ii Plaque As A Biofilm Composition Classification

Dental Plaque Part 1 Ii Plaque As A Biofilm Composition Dental plaque is a soft, sticky deposit that adheres to the tooth surface and other hard surfaces in the oral cavity. it is considered as a root cause of man. Arguably the most thoroughly characterized biofilm matrix polymers in dental plaque are the glucan and fructan polysaccharides that are produced by the action of extracellular glucosyltransferase and fructosyltransferase enzymes on sucrose. 8 these polysaccharides are considered to be important virulence factors in the pathogenesis of dental caries. 9,10 there is also an extensive.
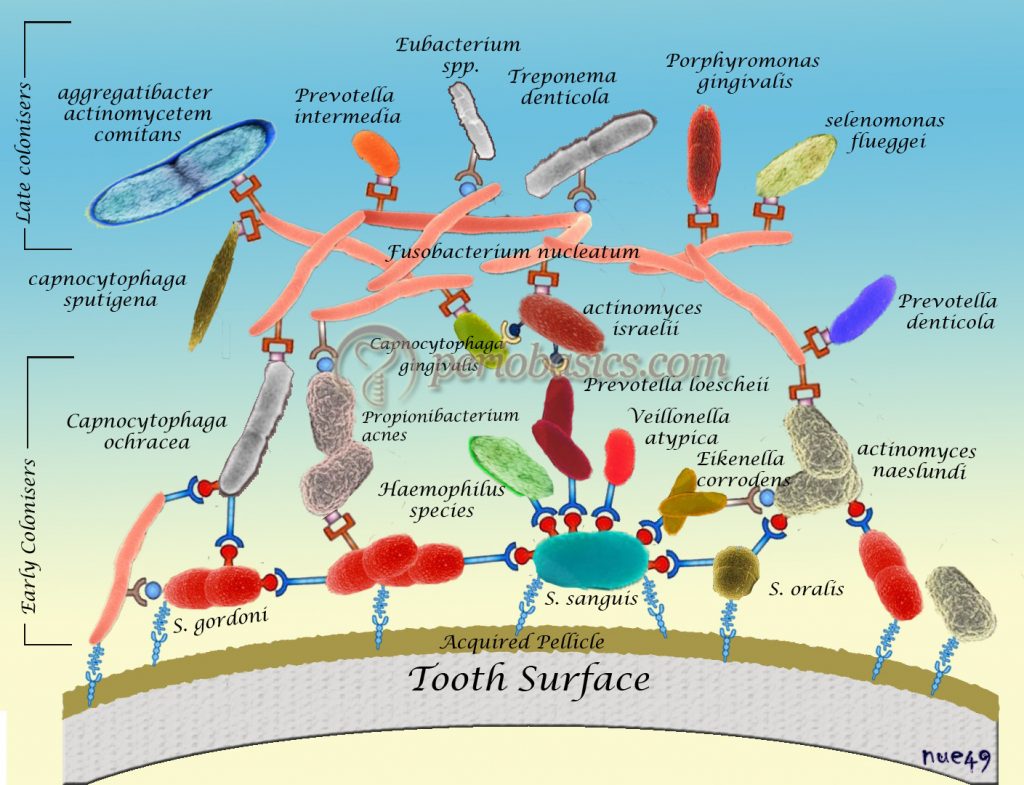
Dental Plaque And Plaque As Biofilm Periobasics Basic Dental plaque. dental plaque is a biofilm of microorganisms (mostly bacteria, but also fungi) that grows on surfaces within the mouth. it is a sticky colorless deposit at first, but when it forms tartar, it is often brown or pale yellow. it is commonly found between the teeth, on the front of teeth, behind teeth, on chewing surfaces, along the. The video focuses on dental plaque as a biofilm, a community of microorganisms on hard, non shedding surfaces like teeth. plaque's composition includes bacteria, yeast, and a matrix of organic and inorganic materials. it can be classified by location, attachment, and health status, with sub gingival plaque linked to periodontal disease. The extracellular matrix is a critical component of microbial biofilms, such as dental plaque, maintaining the spatial arrangement of cells and coordinating cellular functions throughout the structure. the extracellular polymeric substances that comprise the matrix include carbohydrates, nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids, which are frequently. Introduction. dental plaque is the community of microorganisms found on a tooth surface as a biofilm, embedded in a matrix of polymers of host and bacterial origin [1,2].of clinical relevance is the fact that biofilms are less susceptible to antimicrobial agents, while microbial communities can display enhanced pathogenicity (pathogenic synergism) [].

Dental Plaque Part 1 The extracellular matrix is a critical component of microbial biofilms, such as dental plaque, maintaining the spatial arrangement of cells and coordinating cellular functions throughout the structure. the extracellular polymeric substances that comprise the matrix include carbohydrates, nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids, which are frequently. Introduction. dental plaque is the community of microorganisms found on a tooth surface as a biofilm, embedded in a matrix of polymers of host and bacterial origin [1,2].of clinical relevance is the fact that biofilms are less susceptible to antimicrobial agents, while microbial communities can display enhanced pathogenicity (pathogenic synergism) []. Dental plaque is a structurally and functionally organized biofilm. plaque forms in an ordered way and has a diverse microbial composition that, in health, remains relatively stable over time (microbial homeostasis). the predominant species from diseased sites are different from those found in healthy sites, although the putative pathogens can often be detected in low numbers at normal sites. The extracellular matrix is a critical component of microbial biofilms, such as dental plaque, maintaining the spatial arrangement of cells and coordinating cellular functions throughout the structure. the extracellular polymeric substances that comprise the matrix include carbohydrates, nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids, which are frequently.
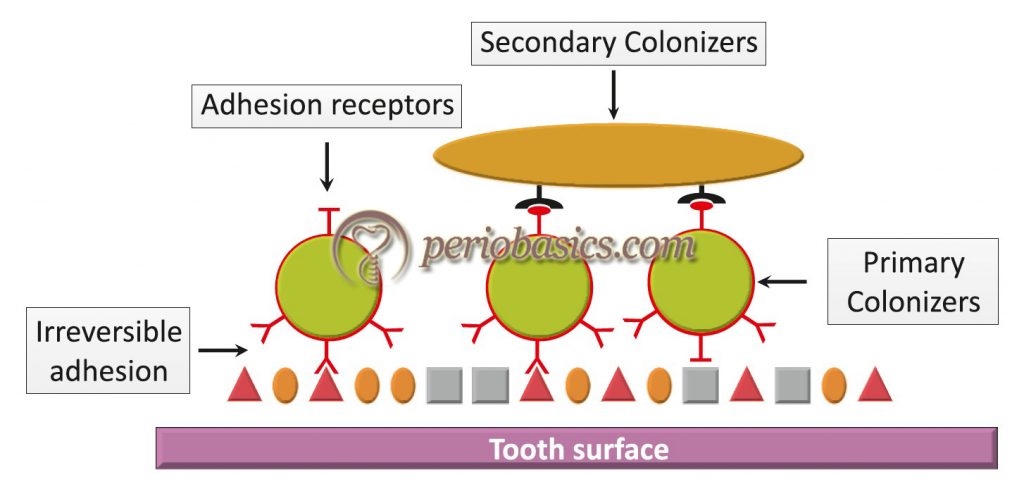
Dental Plaque And Plaque As Biofilm Periobasics Basic Dental plaque is a structurally and functionally organized biofilm. plaque forms in an ordered way and has a diverse microbial composition that, in health, remains relatively stable over time (microbial homeostasis). the predominant species from diseased sites are different from those found in healthy sites, although the putative pathogens can often be detected in low numbers at normal sites. The extracellular matrix is a critical component of microbial biofilms, such as dental plaque, maintaining the spatial arrangement of cells and coordinating cellular functions throughout the structure. the extracellular polymeric substances that comprise the matrix include carbohydrates, nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids, which are frequently.

Dental Plaque Part 2 Biofilm Ppt

Comments are closed.