Density Lab Chemistry
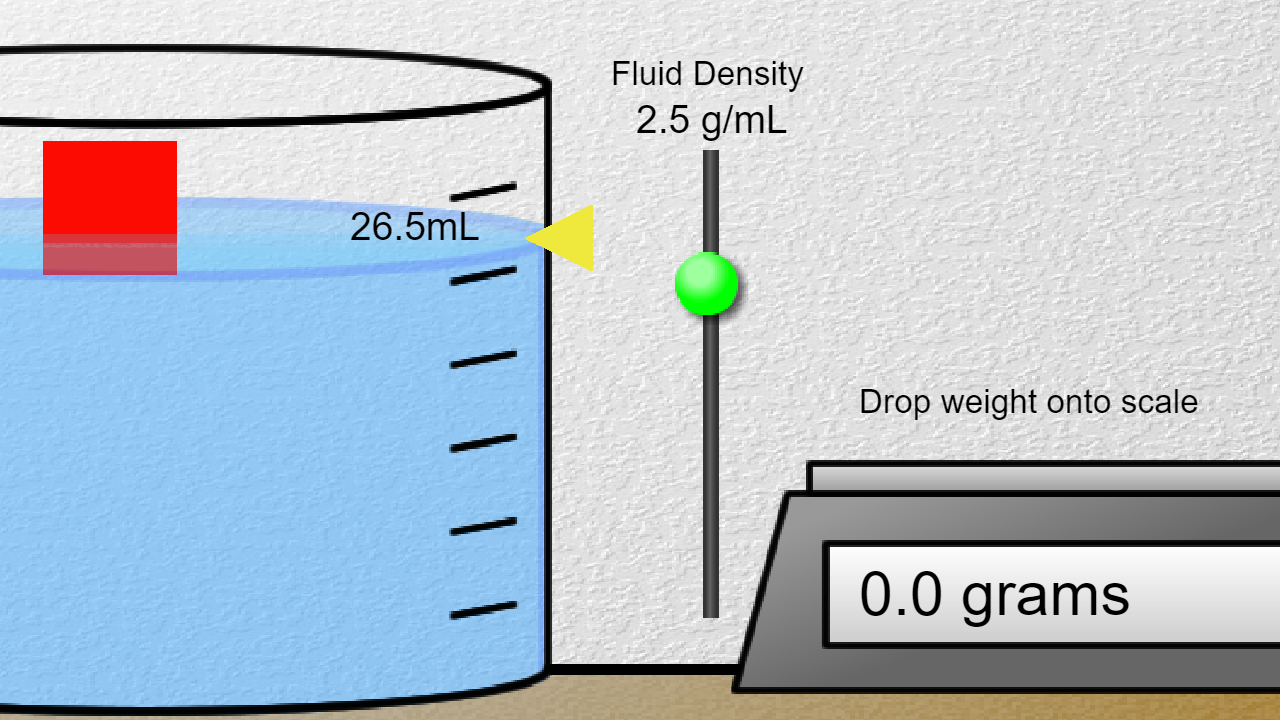
Density Lab Pbs Learningmedia Density is determined by dividing the mass of a substance by its volume: density = mass volume (2.1) (2.1) d e n s i t y = m a s s v o l u m e. the units of density are commonly expressed as g cm 3 for solids, g ml for liquids, and g l for gases. density is also an intensive property of matter. Solution: we can use the density to convert between the mass and the volume. 12.4 𝑔∙ 𝑐 i3 19.3 𝑔 =0.64249 𝑐 i3=0.642 𝑐 i3 note: since both the density and the mass are measured to 3 significant digits, the answer should be rounded to three significant digits as well. in many applications, the volume of a sample can be measured.
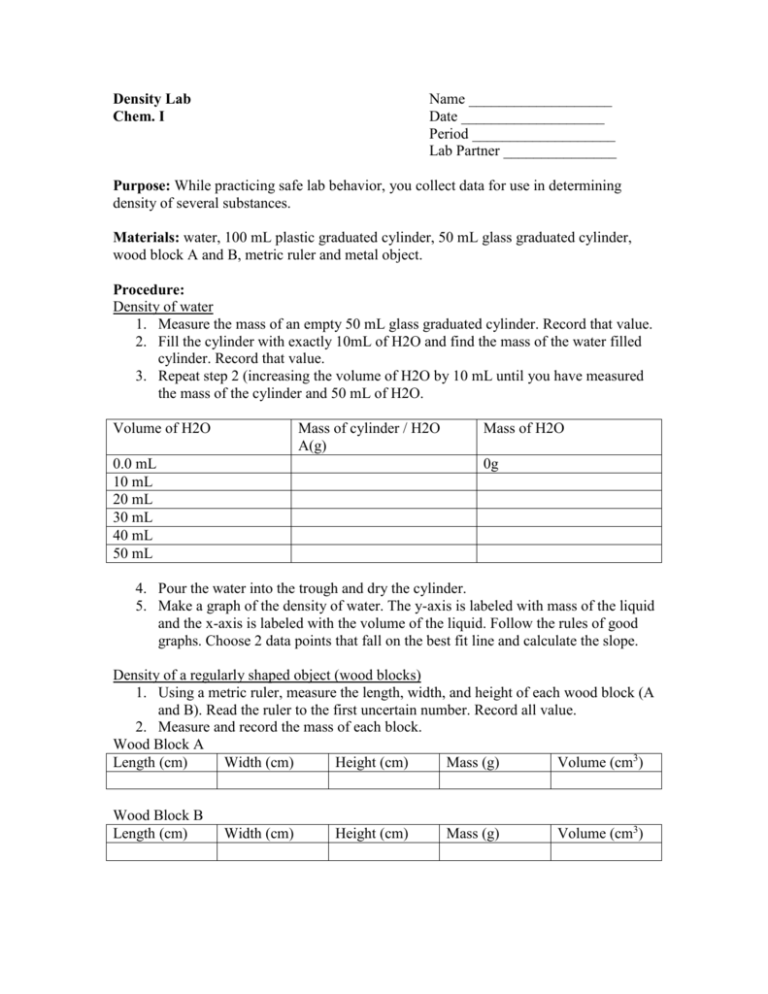
Density Lab Density is a physical property that relates the mass of a substance to its volume. in simple terms, density is defined as the mass per unit volume of a substance, represented by equation 3.2.1: density = mass in grams (g) volume in milliliters (ml) the densities of solids and liquids are expressed as g ml or g cm 3. Why do some materials like wood float in water, and others don’t? interact with blocks of different materials, including a custom option by modifying their mass and volume, to explore the effect on the density and discover the conditions for sinking or floating in water. play detective to determine the material of each block by comparing its density with the values in the table. The general meaning of density is the amount of anything per unit volume. what we conventionally call the "density" is more precisely known as the "mass density". density can be expressed in any combination of mass and volume units; the most commonly seen units are grams per ml (g ml –1, g cm –3), or kilograms per liter. Video 1: virtual chemistry experiment: exploring density part 1 on the science classroom channel (published 9 2 2020) after this introduction, students use the phet simulation, states of matter basic, to observe solids, liquids, and gases at the particulate level (image 1). then, students answer a few analysis questions to deepen their.
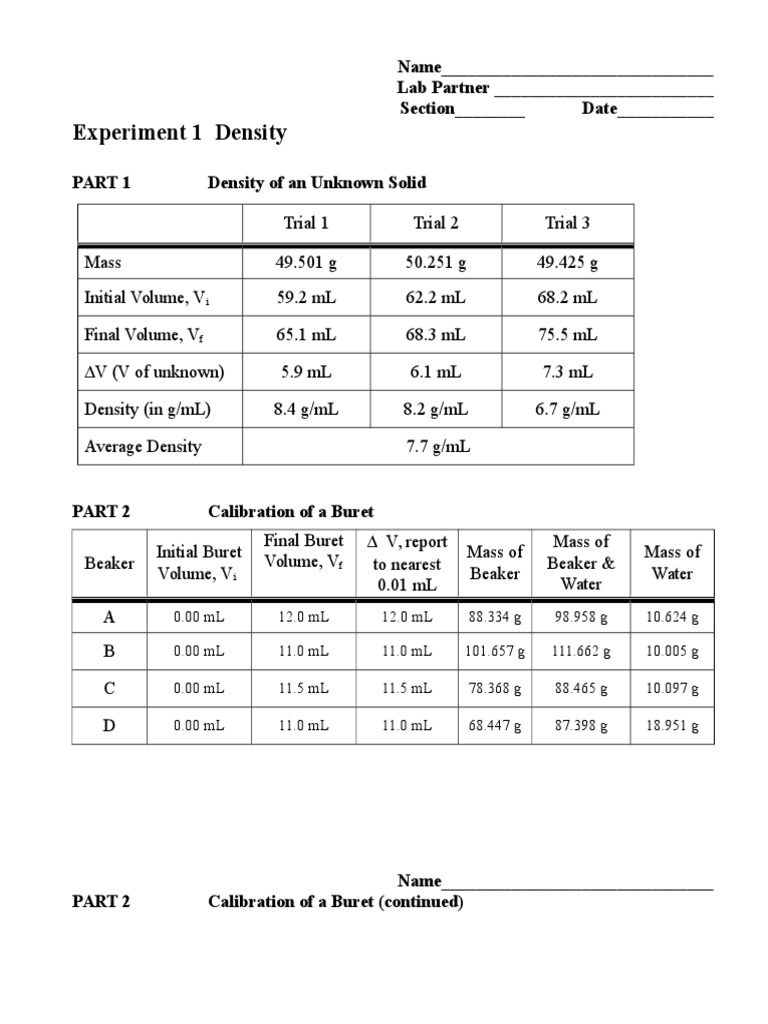
Chemistry Density Lab Results The general meaning of density is the amount of anything per unit volume. what we conventionally call the "density" is more precisely known as the "mass density". density can be expressed in any combination of mass and volume units; the most commonly seen units are grams per ml (g ml –1, g cm –3), or kilograms per liter. Video 1: virtual chemistry experiment: exploring density part 1 on the science classroom channel (published 9 2 2020) after this introduction, students use the phet simulation, states of matter basic, to observe solids, liquids, and gases at the particulate level (image 1). then, students answer a few analysis questions to deepen their. The density of the solid was calculated by dividing its mass by its volume, ρ (g l) = m v. the mass and volume of the liquid sample were measured and its density was calculated in the same manner as the solid. the calculated densities were compared with the known densities of the solid and liquid. Eters cubed (m3), and gallons (gal). density is defined as the ratio of the mass of. an object to the volume it occupies. different materials can have different densities and density. .mass (m)density (ρ) = volume (v)density is an intensive property, meaning it does. t depend on the size of the object. a 1 ml sample of water, for example, ha.
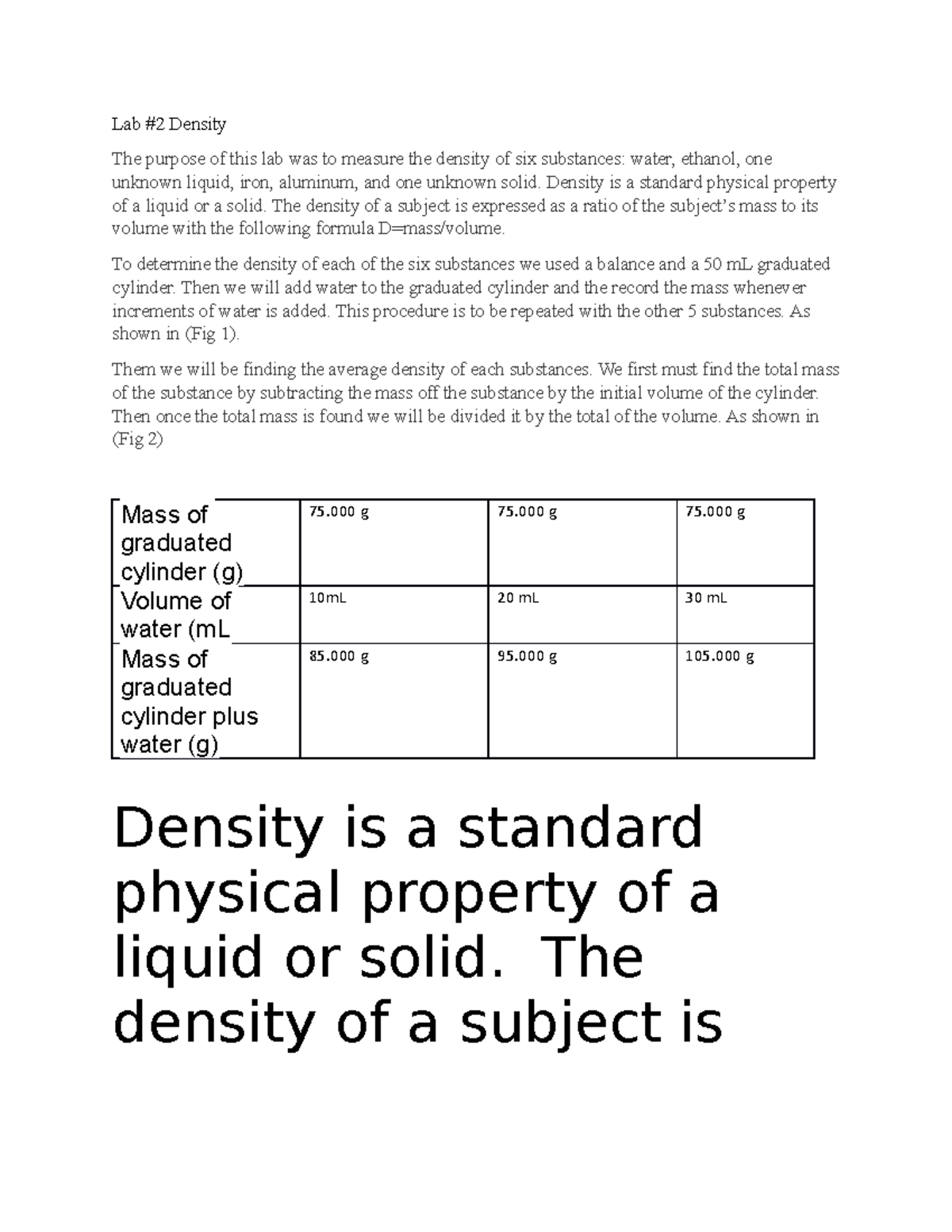
Chemistry 111 Lab 1 Lab 2 Density The Purpose Of This Lab Was To The density of the solid was calculated by dividing its mass by its volume, ρ (g l) = m v. the mass and volume of the liquid sample were measured and its density was calculated in the same manner as the solid. the calculated densities were compared with the known densities of the solid and liquid. Eters cubed (m3), and gallons (gal). density is defined as the ratio of the mass of. an object to the volume it occupies. different materials can have different densities and density. .mass (m)density (ρ) = volume (v)density is an intensive property, meaning it does. t depend on the size of the object. a 1 ml sample of water, for example, ha.
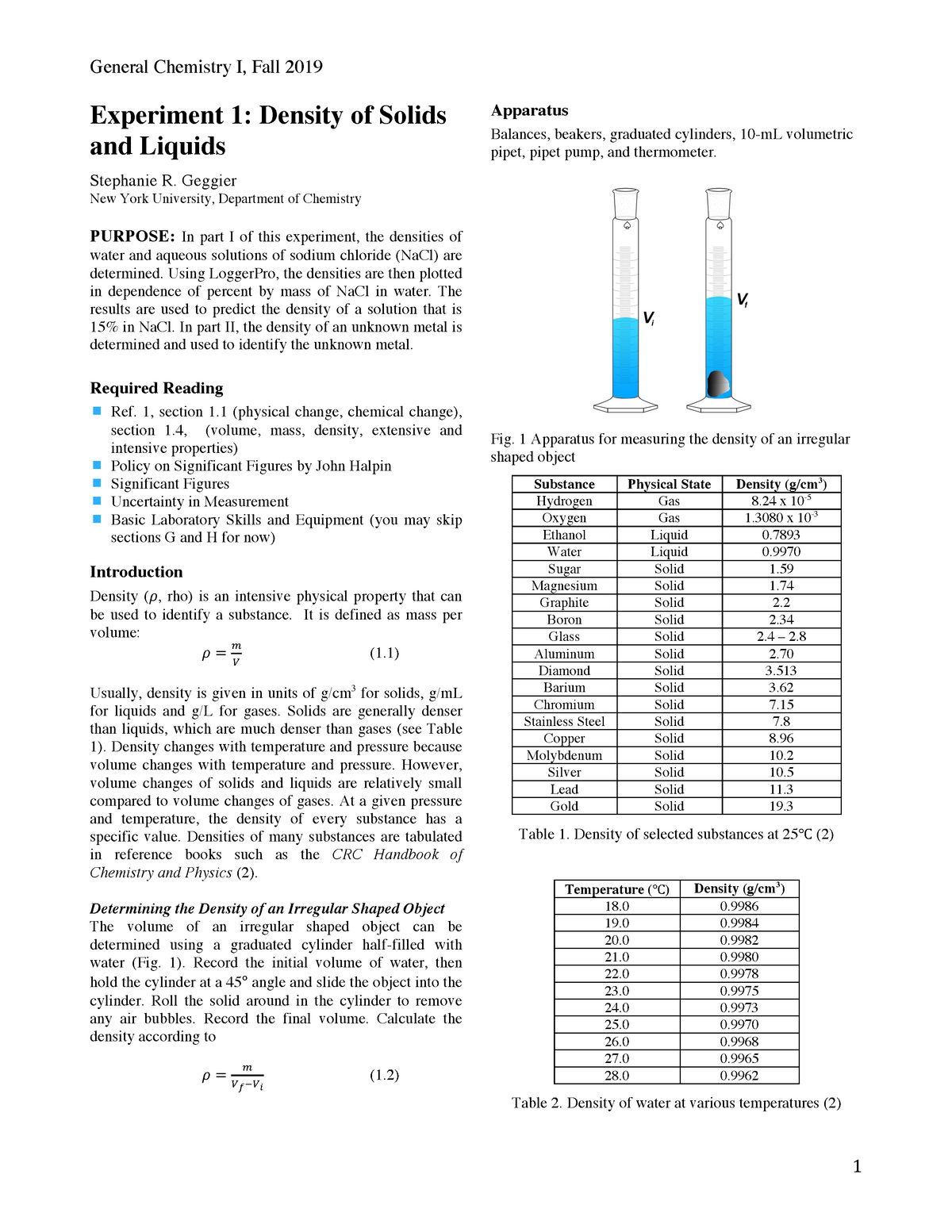
Experiment 1 Density It S The Lab Assignment Experiment 1 Density

Comments are closed.