Demand And Supply At Work In Labor Markets в Economics
What We Know About The 2019 And 2020 Labor Market Comparing Labor Markets for labor have demand and supply curves, just like markets for goods. the law of demand applies in labor markets this way: a higher salary or wage —that is, a higher price in the labor market—leads to a decrease in the quantity of labor demanded by employers, while a lower salary or wage leads to an increase in the quantity of labor demanded. Table 4 shows the differences in supply and demand at different wages. figure 3. a living wage: example of a price floor the original equilibrium in this labor market is a wage of $10 hour and a quantity of 1,200 workers, shown at point e. imposing a wage floor at $12 hour leads to an excess supply of labor.
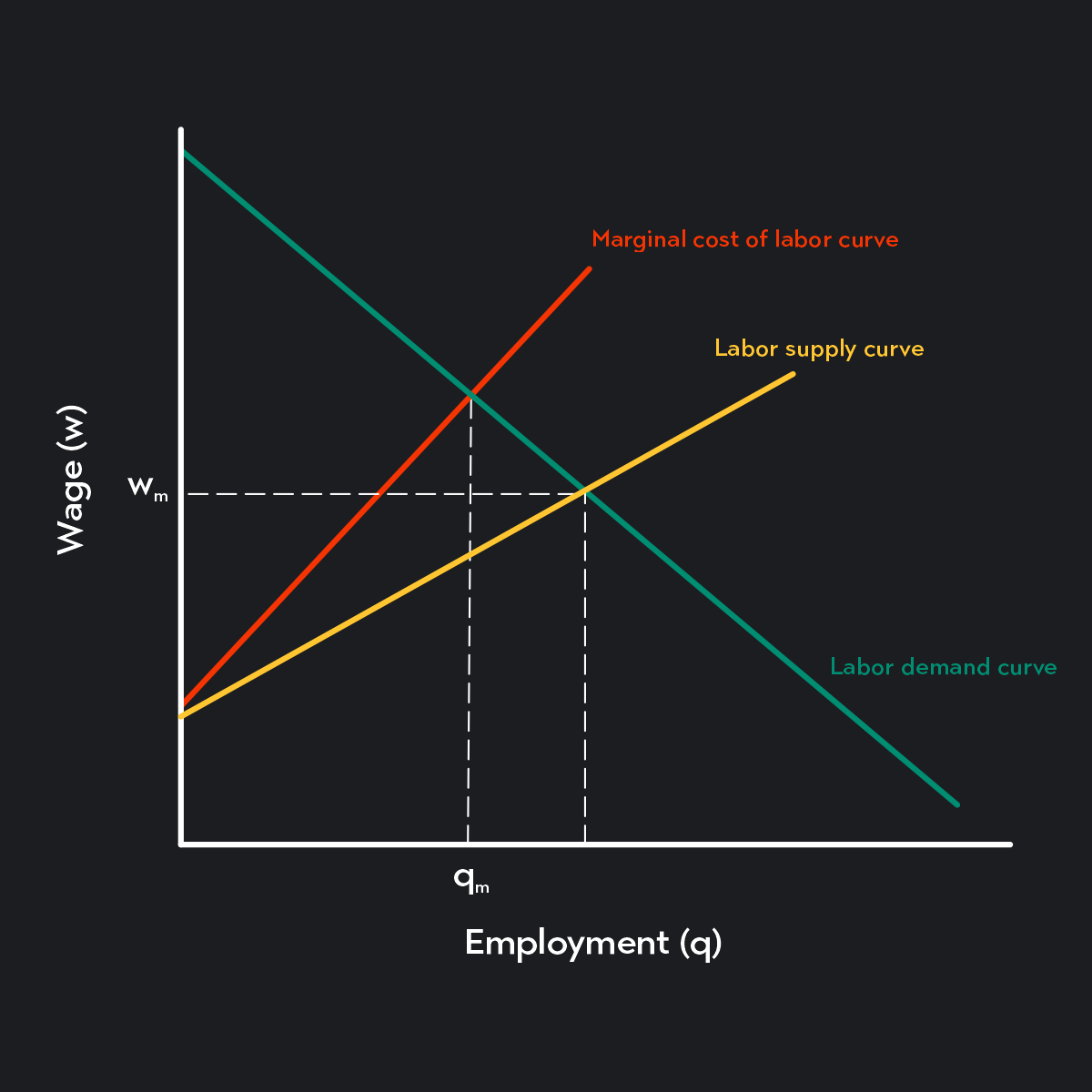
Labor Market Supply Curves Demand Curves Outlier As we have seen, the marginal product of labor could rise because of an increase in the use of other factors of production, an improvement in technology, or an increase in human capital. figure 12.11 changes in the demand for and supply of labor. panel (a) shows an increase in demand for labor; the wage rises to w2 and employment rises to l2. Table 4.10b shows the differences in supply and demand at different wages. figure 4.10b a living wage: example of a price floor. the original equilibrium in this labour market is a wage of $10 hour and a quantity of 1,200 workers, shown at point e. imposing a wage floor at $12 hour leads to an excess supply of labour. Introduction to labor and financial markets; 4.1 demand and supply at work in labor markets; 4.2 demand and supply in financial markets; 4.3 the market system as an efficient mechanism for information; key terms; key concepts and summary; self check questions; review questions; critical thinking questions; problems. Wage determination in competitive labour markets . the industry wage is determined by supply and demand for labour. an individual firm in a perfectly competitive labour market is a wage taker. therefore, its supply curve is elastic. the firm maximises profits where mrp of workers equals the marginal cost of employing them (at q1).

Understanding Shifts In Labor Supply And Labor Demand Video Lesson Introduction to labor and financial markets; 4.1 demand and supply at work in labor markets; 4.2 demand and supply in financial markets; 4.3 the market system as an efficient mechanism for information; key terms; key concepts and summary; self check questions; review questions; critical thinking questions; problems. Wage determination in competitive labour markets . the industry wage is determined by supply and demand for labour. an individual firm in a perfectly competitive labour market is a wage taker. therefore, its supply curve is elastic. the firm maximises profits where mrp of workers equals the marginal cost of employing them (at q1). The bottom line. the labor market is an economic term for the availability of workers and the cost of employment. it plays a major role in the overall economy. the price for labor is largely. Markets for labor have demand and supply curves, just like markets for goods. the law of demand applies in labor markets this way: a higher salary or wage—that is, a higher price in the labor market—leads to a decrease in the quantity of labor demanded by employers, while a lower salary or wage leads to an increase in the quantity of labor demanded.
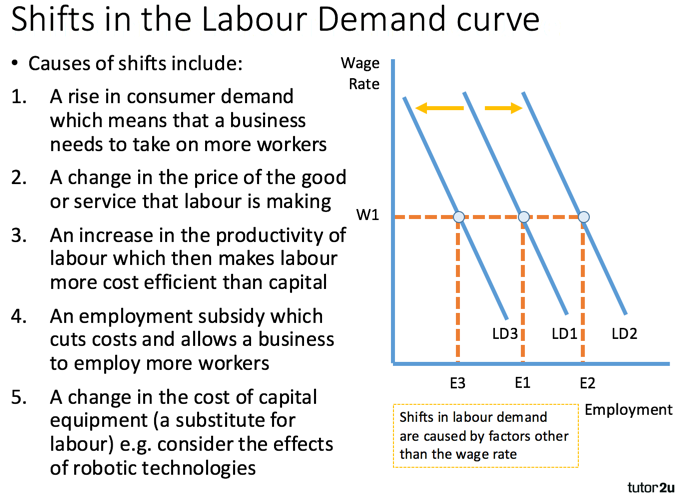
Demand For Labour Labour Markets Economics Tutor2u The bottom line. the labor market is an economic term for the availability of workers and the cost of employment. it plays a major role in the overall economy. the price for labor is largely. Markets for labor have demand and supply curves, just like markets for goods. the law of demand applies in labor markets this way: a higher salary or wage—that is, a higher price in the labor market—leads to a decrease in the quantity of labor demanded by employers, while a lower salary or wage leads to an increase in the quantity of labor demanded.

Comments are closed.