Deformation Of A Single Crystal Lattice Structure
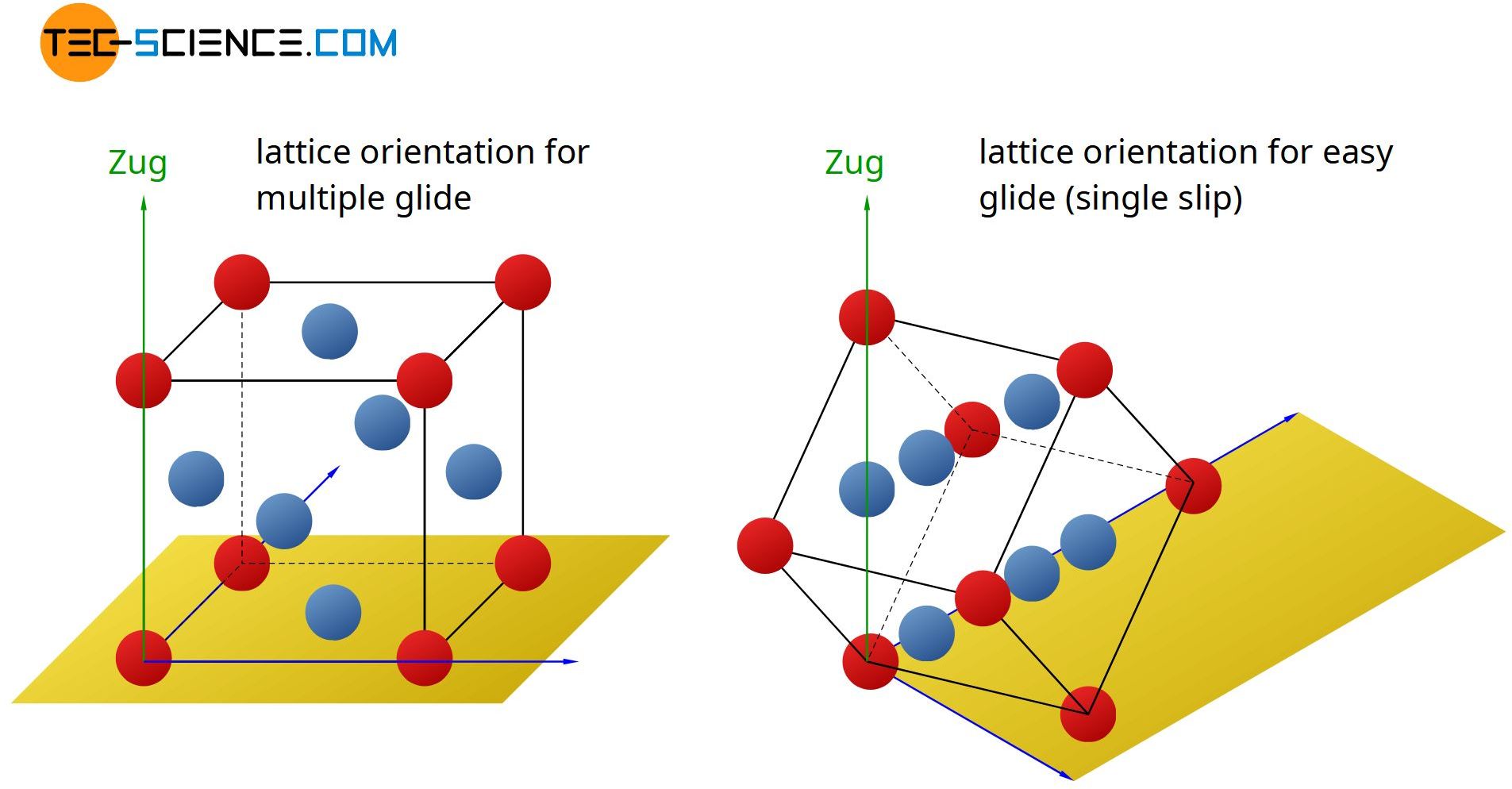
Deformation Of Ideal Crystal Structures Single Crystal Tec Science In this video, the deformation process of specially oriented single crystals is being studied. in the process, ring shaped slip steps are formed. we explain. Introduction. if a material on the atomic level is characterized by a uniform lattice orientation (no grain boundaries), it is also called a single crystal. if such a single crystal is deformed under tension, inclined rings are formed in the deformation region. this can be clearly seen from the copper single crystal shown in the figure below.

Deformation Of A Single Crystal Lattice Structure Youtube Characterization of slip systems. γ tial single crystal has an l1 0 intermetallic structure, which is composed of alternating ti and al atomic layer along the [001] axis, as shown in fig. 1(a. Using dimensional analysis, it can be shown that the fundamental relationship for the flow stress τ τ in stage 2 is: τ = αbg ρ−−√ (7.8.1) (7.8.1) τ = α b g ρ. this is known as the taylor equation. here α is a dimensionless number, g is the shear modulus, b is the burgers vector and ρ is the forest dislocation density of the system. The route to deformation. (a) schematic of a dislocation in a crystal, where the dislocation line is marked with a t. the slip plane, upon which the dislocation moves in the horizontal direction and thus facilitates plastic deformation, is indicated in red. in (b) every other atom in the dislocation line is replaced by an atom (red) from. Deformation mechanisms of single crystal γ tial, prepared either from tial alloy or by direct growth for various orientations have been investigated via transmission electron microscopy (tem) or.

Lattice Structures And Deformation Behaviour A Face Centred Cubic The route to deformation. (a) schematic of a dislocation in a crystal, where the dislocation line is marked with a t. the slip plane, upon which the dislocation moves in the horizontal direction and thus facilitates plastic deformation, is indicated in red. in (b) every other atom in the dislocation line is replaced by an atom (red) from. Deformation mechanisms of single crystal γ tial, prepared either from tial alloy or by direct growth for various orientations have been investigated via transmission electron microscopy (tem) or. The complex 3d lattice deformation is often simplified to changes in the spacing between layers in a multilayer structure composed of (111) planes 13,36. however, it is obvious that the hexagonal. Lattice rotation and crystal slip, dominated by {111}<110> octahedral slip, are the primary mechanisms of room temperature tensile deformation in single crystal superalloys. the varying degrees of involvement of these two mechanisms in samples at different deviation angles are the main reasons for the differences in tensile performance and.

12 Deformation Of A Crystal Structure A Original Lattice The complex 3d lattice deformation is often simplified to changes in the spacing between layers in a multilayer structure composed of (111) planes 13,36. however, it is obvious that the hexagonal. Lattice rotation and crystal slip, dominated by {111}<110> octahedral slip, are the primary mechanisms of room temperature tensile deformation in single crystal superalloys. the varying degrees of involvement of these two mechanisms in samples at different deviation angles are the main reasons for the differences in tensile performance and.

Comments are closed.