Deflationary Gap Macroeconomics

Image Deflationary Gap Png Central Economics Wiki Definition deflationary gap – this is the difference between the full employment level of output and actual output. for example, in a recession, the deflationary gap may be quite substantial, indicative of the high rates of unemployment and underused resources. a deflationary gap is also known as a negative output gap. causes of deflationary gap. Let us learn about inflationary and deflationary gap. inflationary gap: we have so far used the theory of aggregate demand to explain the emergence of dpi in an economy. this theory can now be used to analyse the concept of 'inflationary gap'—a concept introduced first by keynes. this concept may be used to measure the pressure of inflation. if aggregate demand exceeds the aggregate value of.

Deflationary Gap Macroeconomics Typically, a deflationary gap is indicative of underutilized resources, such as labor and capital, leading to higher unemployment rates and lower levels of economic growth. example to understand the concept of a deflationary gap, imagine a country that has the capacity to produce goods and services worth $500 billion in a year (potential gdp. Macroeconomics; what is an inflationary gap? by. will kenton. full bio. when the potential gdp is higher than the real gdp, the gap is instead referred to as a deflationary gap. Deflation is a sustained decrease in the price level of goods and services. inflation, disinflation and deflation refer to increasing or decreasing average price levels of the economy. they usually are calculated as the percentage change in a given price level over a certain period of time—for example, the percentage change from a year earlier. The percentage gap is positive during periods of inflationary gaps and negative during periods of recessionary gaps. over the last 50 years, the economy has seldom departed by more than 5% from its potential output. so the size and duration of the recessionary gap from 2009 to 2011 certainly stand out.
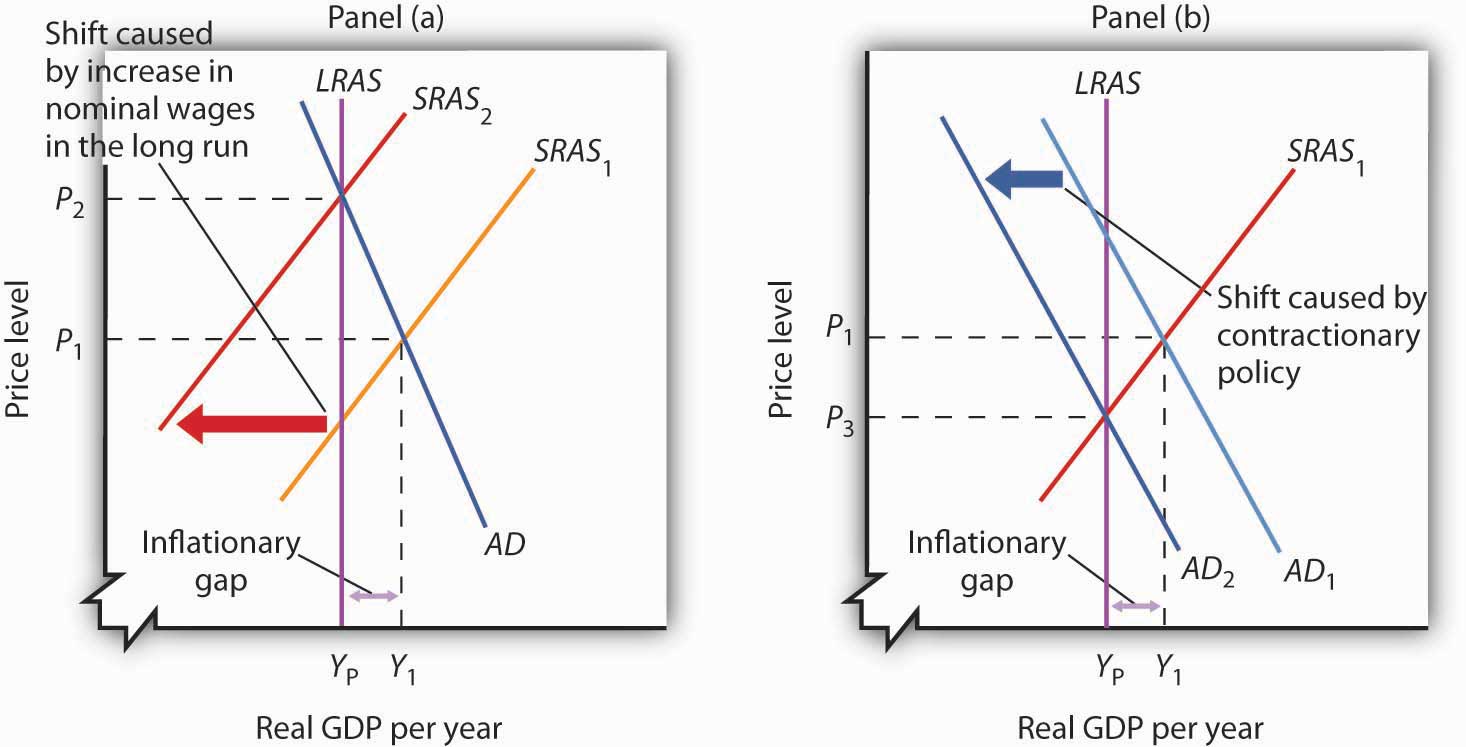
Deflationary Gap Macroeconomics Deflation is a sustained decrease in the price level of goods and services. inflation, disinflation and deflation refer to increasing or decreasing average price levels of the economy. they usually are calculated as the percentage change in a given price level over a certain period of time—for example, the percentage change from a year earlier. The percentage gap is positive during periods of inflationary gaps and negative during periods of recessionary gaps. over the last 50 years, the economy has seldom departed by more than 5% from its potential output. so the size and duration of the recessionary gap from 2009 to 2011 certainly stand out. The major contributor to this deflationary period was the fall in the money supply following catastrophic bank failures. other nations, such as japan in the 1990s, experienced deflation in modern. One of the biggest worries associated with deflation is a deflationary spiral, in which low unemployment and a decreasing price level leads to lower unemployment and an even lower price level.
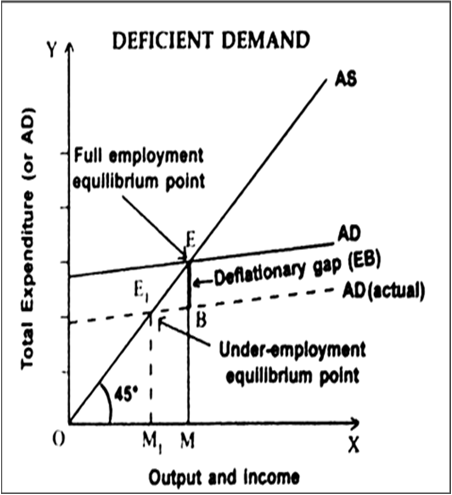
Explain A Concept Of Deflationary Gap With The Help Of A Diagram Ordraw The major contributor to this deflationary period was the fall in the money supply following catastrophic bank failures. other nations, such as japan in the 1990s, experienced deflation in modern. One of the biggest worries associated with deflation is a deflationary spiral, in which low unemployment and a decreasing price level leads to lower unemployment and an even lower price level.
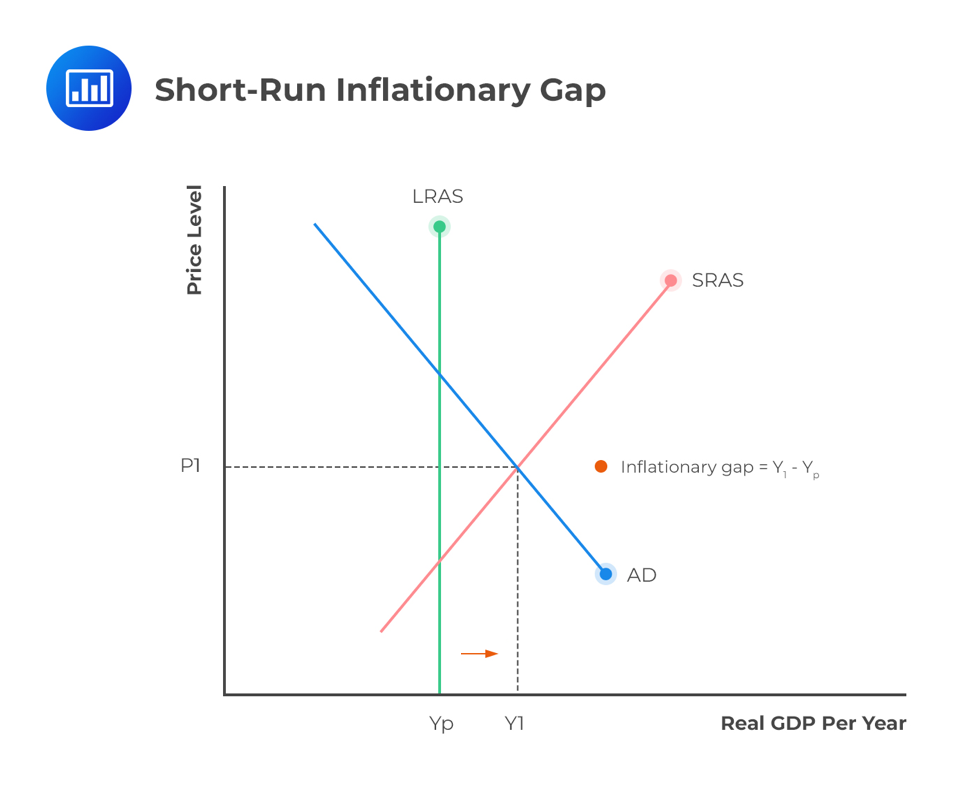
Deflationary Gap Macroeconomics

Comments are closed.