Deconfounding Confounding Part 3 Controlling For Confounding In
Ppt Advanced Data Analysis Methods To Control For Confounding Deconfounding confounding part 3: controlling for confounding in statistical analyses. Deconfounding confounding part 3: controlling for confounding in statistical analyses. alice m richardson. corresponding author. [email protected];.

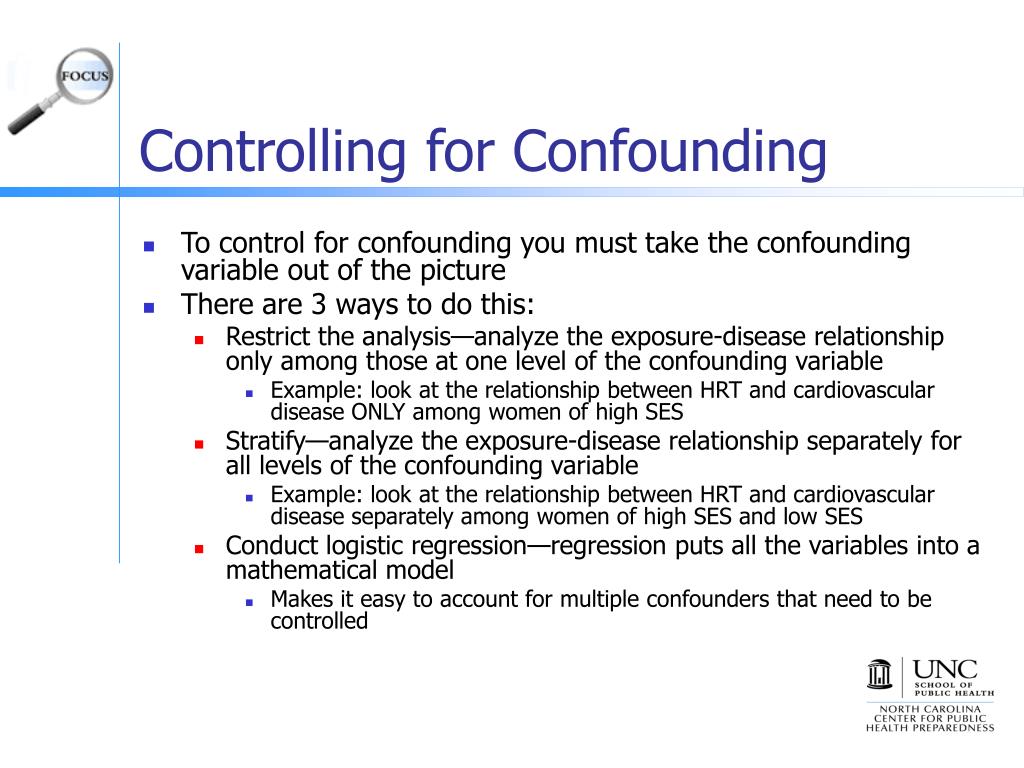
Deconfounding Confounding Part 3 Controlling For Confounding In The traditional concept of confounding was previously introduced in this key research skills series — a confounder is a variable that is associated with both the exposure and outcome of interest without being an intermediate on the causal pathway between them. the traditional concept of confounding was previously introduced in this key research skills series — a confounder is a variable. Deconfounding confounding part 3: controlling for confounding in statistical analyses. 01 richardson deconfounding confounding part 2020.pdf: 333.14 kb: adobe pdf. Deconfounding confounding part 3: controlling for confounding in statistical analyses. august 2020. the medical journal of australia 213 (5) doi: 10.5694 mja2.50737. authors: alice richardson. 8.1 introduction. confounding is a causal concept defined in terms of the data generating model (see figure 7.1 a) as a variable that causally influences the dependent variable and is associated with the independent variable, thereby causing a spurious association. while older definitions of confounding considered it a bias described as a.

Ppt Advanced Data Analysis Methods To Control For Confounding Deconfounding confounding part 3: controlling for confounding in statistical analyses. august 2020. the medical journal of australia 213 (5) doi: 10.5694 mja2.50737. authors: alice richardson. 8.1 introduction. confounding is a causal concept defined in terms of the data generating model (see figure 7.1 a) as a variable that causally influences the dependent variable and is associated with the independent variable, thereby causing a spurious association. while older definitions of confounding considered it a bias described as a. Deconfounding for causal interpretations: the collider bias danger. using deconfounding to cancel the impact of a putative confound z removes any bias incurred by the spurious association between the data x and the prediction target y, when z is associated with both x and y. however, z may be a consequence of both the target and the data. Second, it is designed to control in sample properties, while predictive models are designed for out of sample prediction. the 2 step approach based on applying a classical glm to remove the confounding effect, then a predictive model, may lead to pessimistic results, e.g., below chance prediction [8, 26].

Ppt Confounding Control Standardization Powerpoint Presentation Deconfounding for causal interpretations: the collider bias danger. using deconfounding to cancel the impact of a putative confound z removes any bias incurred by the spurious association between the data x and the prediction target y, when z is associated with both x and y. however, z may be a consequence of both the target and the data. Second, it is designed to control in sample properties, while predictive models are designed for out of sample prediction. the 2 step approach based on applying a classical glm to remove the confounding effect, then a predictive model, may lead to pessimistic results, e.g., below chance prediction [8, 26].

Comments are closed.