Database Life Cycle Database History In An Information System

Database Life Cycle Database History In An Information System The database life cycle (dblc) consists of six phases. these phases include database primary study planning, analysis, detailed system design, (prototyping), implementation and loading, testing and evaluation, operation, maintenance and evolution. in the database primary study, the researcher examines the current systems operations in the. An information system is a system that. provides management of both data and information. an information system is composed of hardware, software (dbms and applications), the database (s), procedures, and people. good decisions are generally based on good information. ultimately, the purpose of an information system is to facilitate good.

Database Life Cycle Database History In An Information System Since maintenance involves the analysis of the changes required, design of a solution, implementation and testing of that solution over the lifetime of a maintained software system, the waterfall life cycle will be repeatedly revisited. database life cycle. we can use the waterfall cycle as the basis for a model of database development that. The 'database life cycle' refers to the series of steps involved in designing a global schema, distributing data across a network, defining local dbms specific schemas, implementing the database, and maintaining it over time. ai generated definition based on: database modeling and design (fifth edition), 2011. about this page. The database life cycle is a set of stages that a database goes through, from initial planning and design to retirement and replacement. while the stages of the database life cycle are generally the same across different database management systems (dbms), the specific tools, methods, and processes used in each stage may differ depending on the dbms. Using these assumptions and figure 13.2.1 13.2. 1, we can see that this diagram represents a model of the activities and their outputs for database development. it is applicable to any class of dbms, not just a relational approach. database application development is the process of obtaining real world requirements, analyzing requirements.
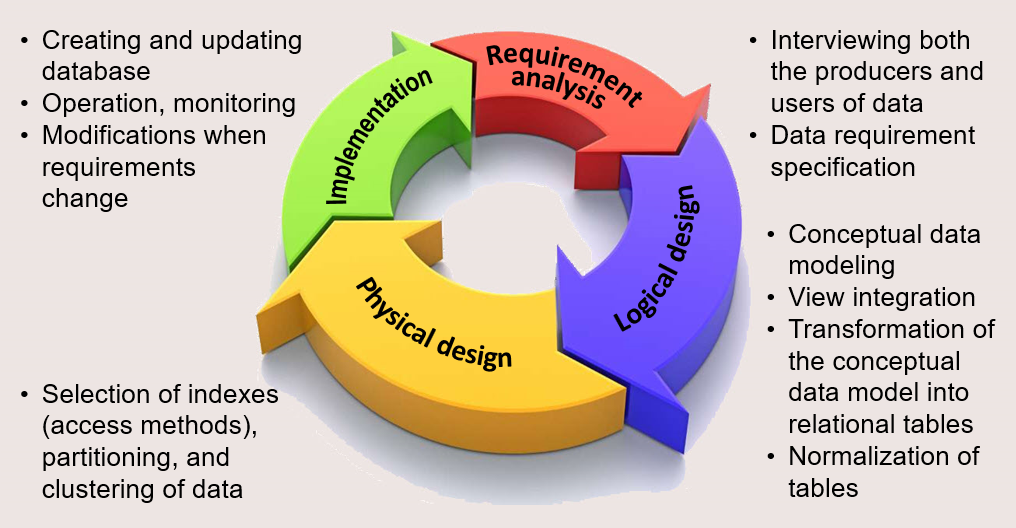
Database Life Cycle Database History In An Information System The database life cycle is a set of stages that a database goes through, from initial planning and design to retirement and replacement. while the stages of the database life cycle are generally the same across different database management systems (dbms), the specific tools, methods, and processes used in each stage may differ depending on the dbms. Using these assumptions and figure 13.2.1 13.2. 1, we can see that this diagram represents a model of the activities and their outputs for database development. it is applicable to any class of dbms, not just a relational approach. database application development is the process of obtaining real world requirements, analyzing requirements. This is the final stage of the database system life cycle, where we create and maintain the database. we can briefly describe it as follows: implementation: creation of tables in the database using data definition language (ddl) and updating, performing queries, and configuring indexes and constraints with data manipulation language (dml). the. The stages of systems development basically mirror the stages of a database lifecycle but are a superset. whereas database design deals with designing the system to store the data, systems design is also concerned with the processes that will impact on the data. ← database design: overview. ↑ database design ↑. database design phase 1.

Comments are closed.