Cooling Curve Diagram Explanation

Heating And Cooling Curves вђ Overview Examples Expii By removing the time axis from the curves and replacing it with composition, the cooling curves indicate the temperatures of the solidus and liquidus for a given composition. this allows the solidus and liquidus to be plotted to produce the phase diagram: this page titled 12.5: interpretation of cooling curves is shared under a cc by nc sa. A cooling curve is a line graph that represents the change of phase of matter, typically from a gas to a solid or a liquid to a solid. the independent variable (x axis) is time and the dependent variable (y axis) is temperature. [1] below is an example of a cooling curve used in castings. the initial point of the graph is the starting.
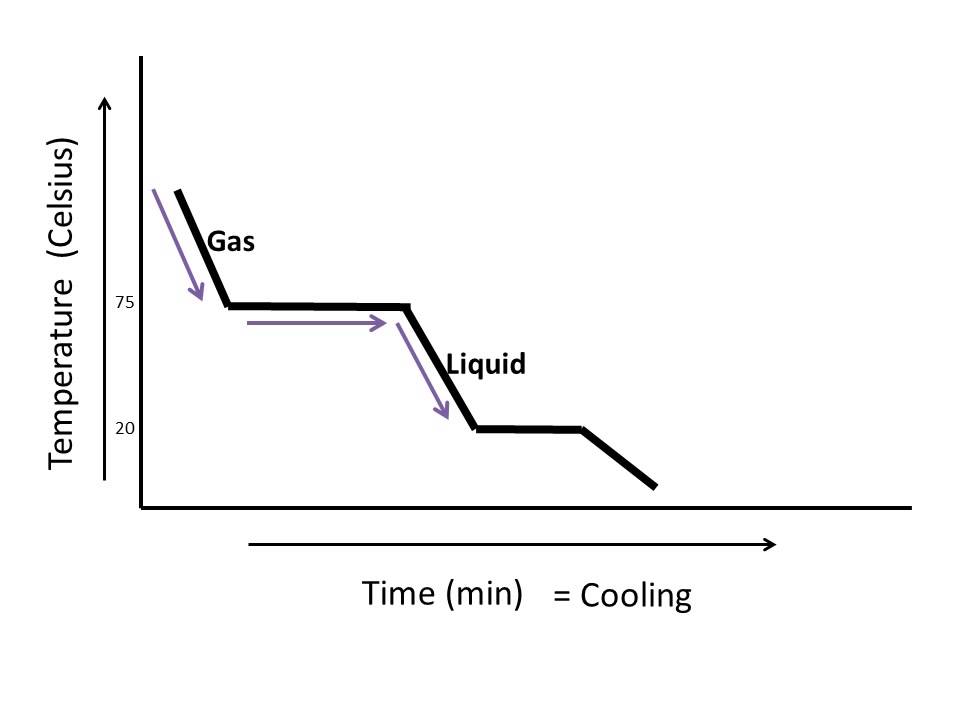
How To Read A Cooling Curve Youtube A quick note about cooling curves. let's say we wanted to go from steam to ice. we would use a cooling curve. the cooling curve is a mirror image of the heating curve. so, it will start at a high temperature and have downward diagonals. the diagonals alternate with plateaus. the flat lines are the enthalpy of condensation and freezing. remember. A cooling curve for a sample that begins at the temperature and composition given by point a is shown in figure 8.10.1b 8.10. 1 b. figure 8.10.1 8.10. 1: (a) cooling of a two component system from liquid to solid. (b) cooresponding cooling curve for this process. as the sample cools from point a, the temperature will decrease at a rate. By removing the time axis from the curves and replacing it with composition, the cooling curves indicate the temperatures of the solidus and liquidus for a given composition. this allows the solidus and liquidus to be plotted to produce the phase diagram: this page titled 4.2.5: interpretation of cooling curves is shared under a cc by nc sa. The heating curve for carbon dioxide would have only one plateau, at the sublimation temperature of co 2 . the entire experiment could be run in reverse. steam above 100°c could be steadily cooled down to 100°c, at which point it would condense to liquid water. the water could then be cooled to 0°c, at which point continued cooling would.

Heating And Cooling Curves By removing the time axis from the curves and replacing it with composition, the cooling curves indicate the temperatures of the solidus and liquidus for a given composition. this allows the solidus and liquidus to be plotted to produce the phase diagram: this page titled 4.2.5: interpretation of cooling curves is shared under a cc by nc sa. The heating curve for carbon dioxide would have only one plateau, at the sublimation temperature of co 2 . the entire experiment could be run in reverse. steam above 100°c could be steadily cooled down to 100°c, at which point it would condense to liquid water. the water could then be cooled to 0°c, at which point continued cooling would. A cooling curve of a substance is a graph of the variation of the temperature with time as it is allowed to cool. the gradient of the cooling curve is related to the heat capacity, the thermal conductivity of the substance, and the external temperature. the more heat is required to change the temperature of the substance, the slower it cools. Interpretation of cooling curves. the melting temperature of any pure material (a one component system) at constant pressure is a single unique temperature. the liquid and solid phases exist together in equilibrium only at this temperature. when cooled, the temperature of the molten material will steadily decrease until the melting point is.

Digging Into Phase Diagrams Cooling Curves Physical Chemistry A cooling curve of a substance is a graph of the variation of the temperature with time as it is allowed to cool. the gradient of the cooling curve is related to the heat capacity, the thermal conductivity of the substance, and the external temperature. the more heat is required to change the temperature of the substance, the slower it cools. Interpretation of cooling curves. the melting temperature of any pure material (a one component system) at constant pressure is a single unique temperature. the liquid and solid phases exist together in equilibrium only at this temperature. when cooled, the temperature of the molten material will steadily decrease until the melting point is.

Cooling Curve Spm Chemistry

Comments are closed.