Convection Cell
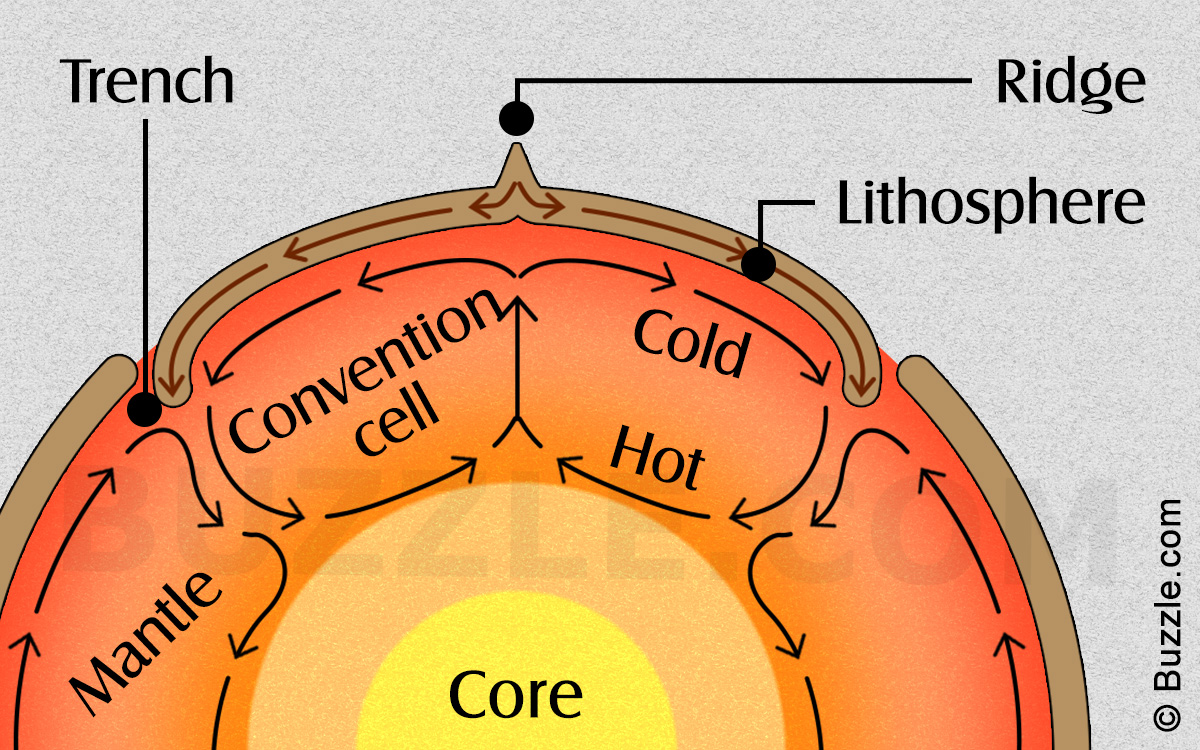
What Are Convection Cells And How Do They Work Science Struck A convection cell is a phenomenon of rising and falling currents in a fluid due to density differences caused by heating or cooling. learn how convection cells form clouds, thunderstorms, solar granules and more with examples and references. Convection cells are circular movements of fluids or gases caused by heat variations. learn how convection cells work in the earth's mantle and atmosphere, and how they affect plate tectonics, landforms, winds and climate.
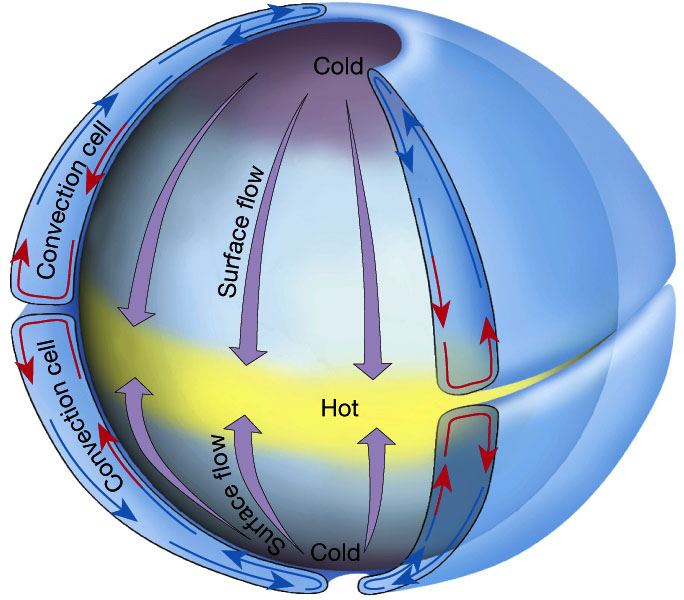
Convection Cell Convection is fluid flow due to density differences and gravity. learn about natural convection, thermal convection, granular convection and convective heat transfer, with illustrations and applications. How do convection cells form? convection cells fluid is warmed by the heat source and is pushed away. the fluid then begins to lose heat, and inevitably cools. this cooler, denser matter is forced back toward the initial heat source by the flow of newly heated matter. a system of motion forms, called a convection cell. Convection that occurs naturally is called natural convection or free convection. if a fluid is circulated using a fan or a pump, it's called forced convection. the cell formed by convection currents is called a convection cell or bénard cell. The convection cells created by rising air at the equator and sinking air at 30 o are referred to as hadley cells, of which there is one in each hemisphere. the cold air that descends at the poles moves over the earth’s surface towards the equator, and by about 60 o latitude it begins to rise, creating a polar cell between 60 o and 90 o .
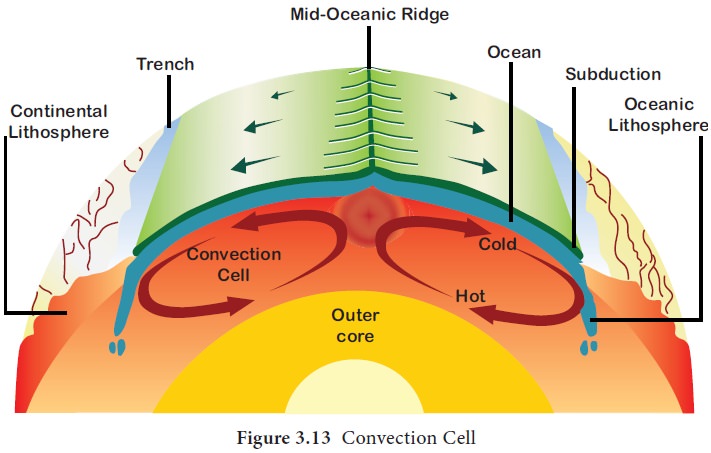
Convection Cell Lithosphere Endogenic Processes Geography Convection that occurs naturally is called natural convection or free convection. if a fluid is circulated using a fan or a pump, it's called forced convection. the cell formed by convection currents is called a convection cell or bénard cell. The convection cells created by rising air at the equator and sinking air at 30 o are referred to as hadley cells, of which there is one in each hemisphere. the cold air that descends at the poles moves over the earth’s surface towards the equator, and by about 60 o latitude it begins to rise, creating a polar cell between 60 o and 90 o . Convection cells are circular patterns of air or water movement caused by the uneven heating and cooling of a substance. hot air or water rises, creating an area of low pressure, while cooler air or water sinks, creating an area of high pressure. Convection is the process of heat transfer by movement of a heated fluid. learn about natural and forced convection, convection currents, and convection cells in the atmosphere and other fluids.
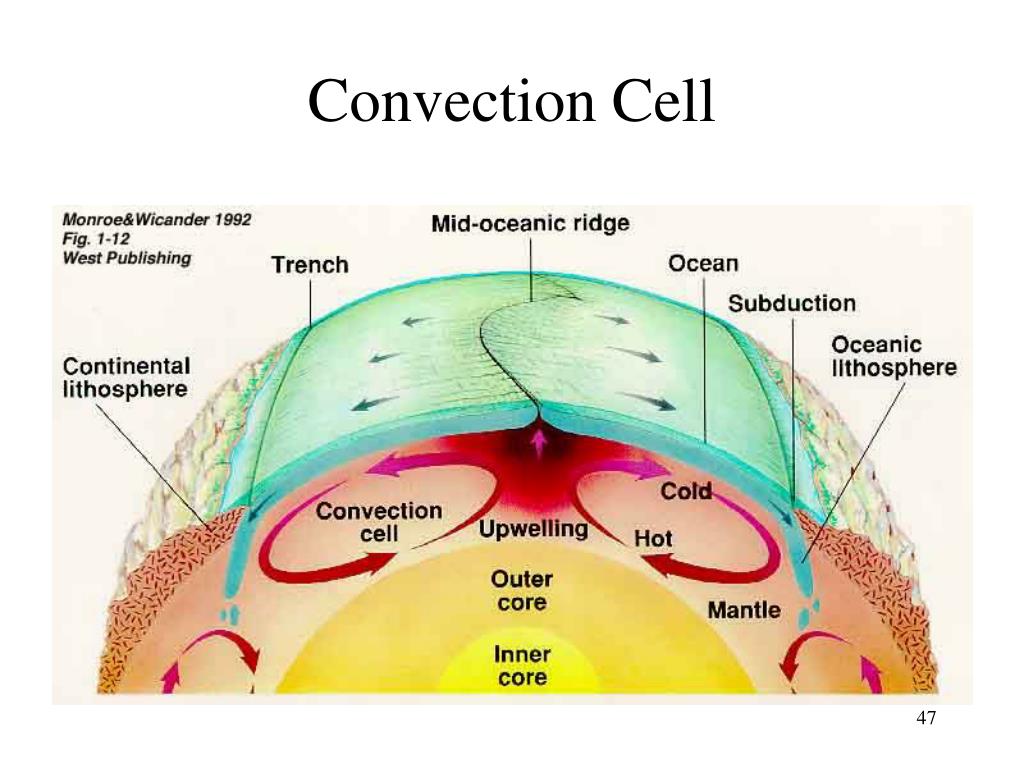
Ppt Structure Of The Earth Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Convection cells are circular patterns of air or water movement caused by the uneven heating and cooling of a substance. hot air or water rises, creating an area of low pressure, while cooler air or water sinks, creating an area of high pressure. Convection is the process of heat transfer by movement of a heated fluid. learn about natural and forced convection, convection currents, and convection cells in the atmosphere and other fluids.

Convection

Comments are closed.