Continuous Cooling Transformation Diagrams
Use A Continuous Cooling Transformation Diagram For A Chegg Definition: stability of phases during continuous cooling of austenite. there are two types of cct diagrams. i) plot of (for each type of transformation) transformation start, specific fraction of transformation and transformation finish temperature against transformation time on each cooling curve. A continuous cooling transformation (cct) phase diagram is often used when heat treating steel. [ 1 ] these diagrams are used to represent which types of phase changes will occur in a material as it is cooled at different rates. these diagrams are often more useful than time temperature transformation diagrams because it is more convenient to.

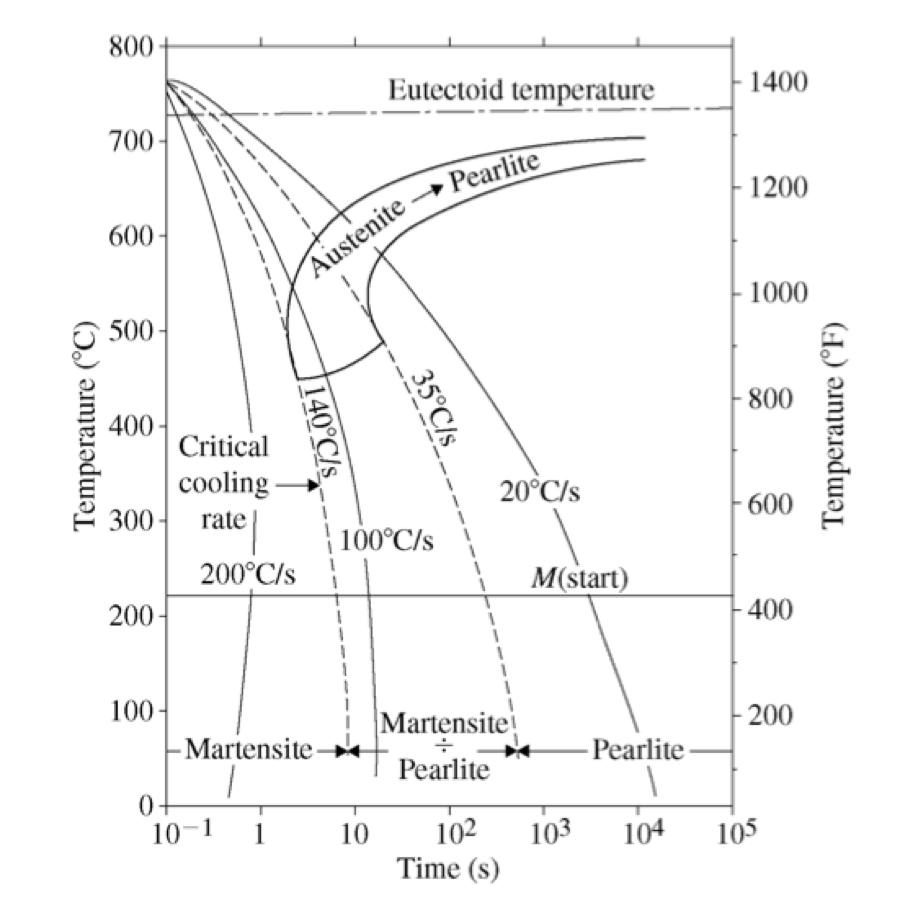
Continuous Cooling Transformation Diagram Download Scientific Diagram A continuous cooling transformation (cct) diagram is a useful tool that can be used with a thermal model for microstructure design and manufacturing process control. however, traditional cct diagrams are developed based on slow and monotonic cooling processes such as furnace cooling and air cooling, which are greatly different from the. Continuous cooling transformation (cct) diagrams are widely used when heat treating steels and represent which type of phase will occur in a material as it is cooled at different cooling rates. cct diagrams are constructed on the basis of dilatometry measurements on relatively small testing samples (cylindrical shape with diameter of 4mm and length of 11 mm in this study). the main aim of this. 1. introduction. to evaluate the performance of structural steels, understanding its microstructure after processing is crucial. the continuous cooling transformation (cct) diagram of a steel plays an important role in providing information on the steel microstructure, as the information includes the start temperatures of phase transformation during cooling, as well as hardness. In the present work, continuous cooling transformation (cct) of coarse grained heat affected zone (cghaz) and simulation of charpy sized impact specimens were performed using a gleeble 3800 thermomechanical simulator. results obtained from the dilation studies show significant effect of cooling rates on microstructure and low temperature (–20 °c) charpy impact toughness. phase.

Comments are closed.