Consumers That Eat Both Plants And Animals Are Called
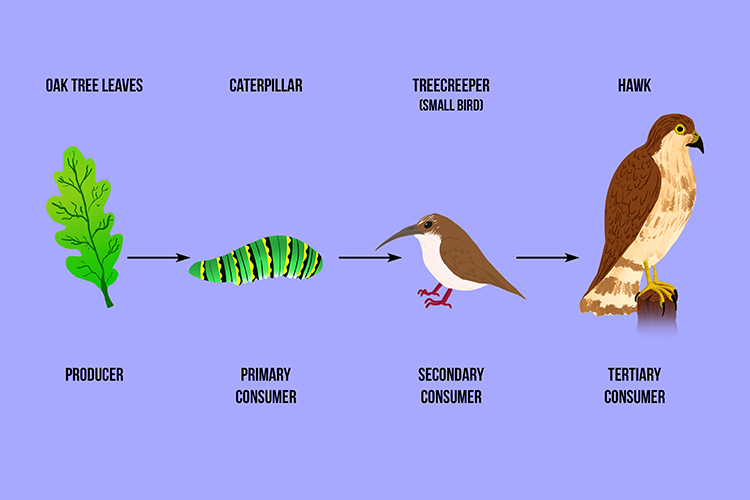
A Tertiary Consumer Eats Secondary Animals In The Food Chain Some secondary consumers eat both plants and animals. they are called omnivores, from the latin words that mean “eats everything.” a raccoon is an example of an omnivore; it eats plant matter such as berries and acorns, but it also catches crayfish, frogs, fish, and other small animals. ecosystems can also have tertiary consumers. A consumer in a food chain is a living creature that eats organisms from a different population. a consumer is a heterotroph and a producer is an autotroph. like sea angels, they take in organic moles by consuming other organisms, so they are commonly called consumers. heterotrophs can be classified by what they usually eat as herbivores.
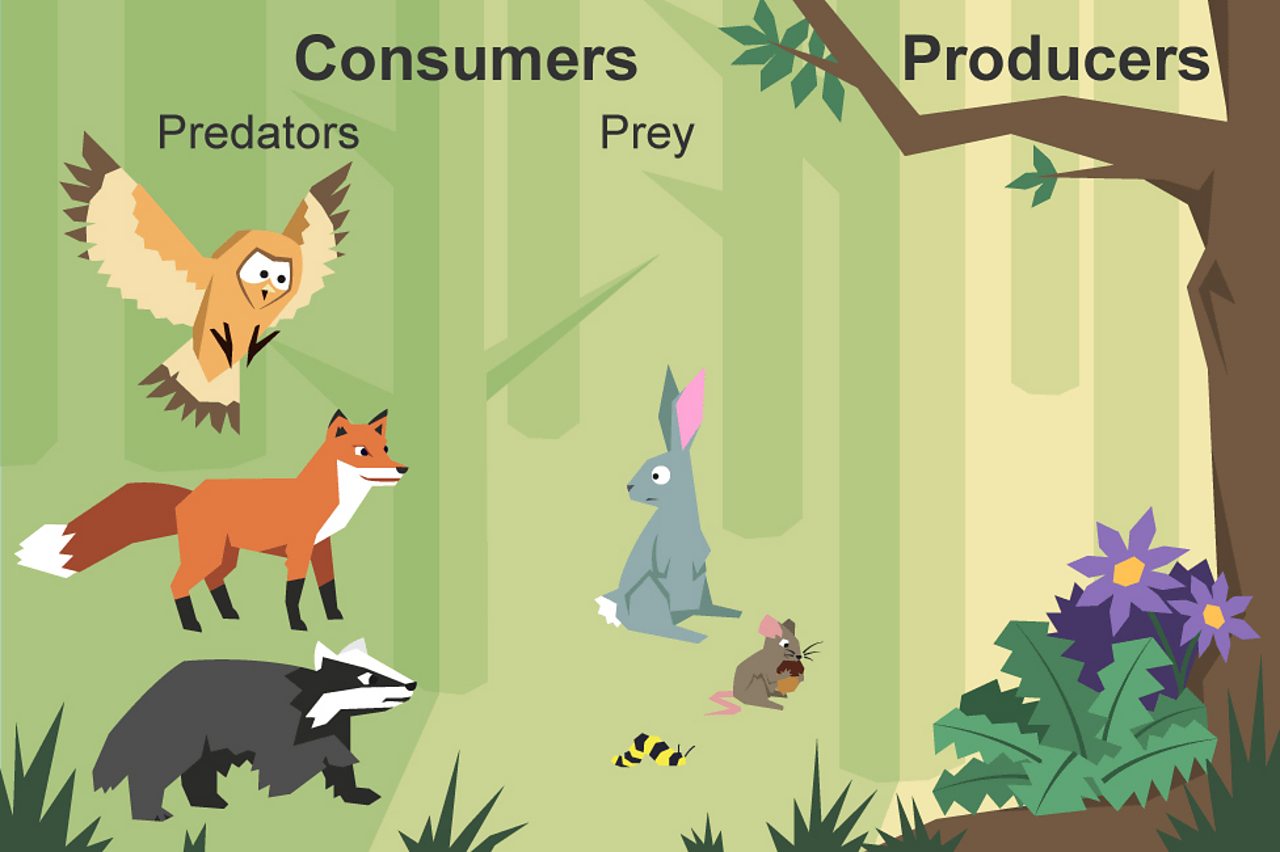
What Is A Food Chain Bbc Bitesize Top predators, also called apex predators, eat other consumers. higher level consumers (i.e., secondary, tertiary, and above) can be carnivores (animals that eat other animals) or omnivores (animals that eat both plants and animals). omnivores, like people, consume many types of foods. people eat plants, such as vegetables and fruits. Secondary consumer definition. secondary consumers are organisms that eat primary consumers for energy. primary consumers are always herbivores, or organisms that only eat autotrophic plants. however, secondary consumers can either be carnivores or omnivores. carnivores only eat other animals, and omnivores eat both plant and animal matter. Herbivores are unable to make their own energy and are known as consumers. as herbivores only ever eat producers, they are primary consumers in the second trophic level of the food chain. omnivores – animals which eat both plants and other animals – are also consumers. the animals they eat do not produce their own energy, and are therefore. Consumers the next trophic levels are made up of animals that eat producers. these organisms are called consumers. consumers can be carnivores (animals that eat other animals) or omnivores (animals that eat both plants and animals). omnivores, like people, consume many types of foods. people eat plants, such as vegetables and fruits. we also.

Consumers That Eat Both Plants And Animals Food Chain Facts For Kids Herbivores are unable to make their own energy and are known as consumers. as herbivores only ever eat producers, they are primary consumers in the second trophic level of the food chain. omnivores – animals which eat both plants and other animals – are also consumers. the animals they eat do not produce their own energy, and are therefore. Consumers the next trophic levels are made up of animals that eat producers. these organisms are called consumers. consumers can be carnivores (animals that eat other animals) or omnivores (animals that eat both plants and animals). omnivores, like people, consume many types of foods. people eat plants, such as vegetables and fruits. we also. A consumer is a living thing that eats other plants and animals. food chain basics: the first consumer in the chain is also called the primary consumer. the thrushes who eat both insects. Food chains. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally decomposers. these levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics.

Comments are closed.