Consumer Surplus Price Floor
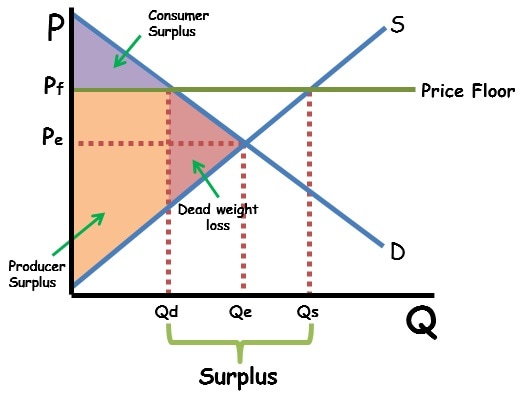
What Is Economic Surplus And Deadweight Loss Reviewecon Consumer surplus will only increase as long as the benefit from the lower price exceeds the costs from the resulting shortage. consumer surplus always decreases when a binding price floor is instituted in a market above the equilibrium price. the total economic surplus equals the sum of the consumer and producer surpluses. Learn how price floors can reduce consumer surplus and create deadweight loss in a market. consumer surplus is the area above the market price and below the demand curve, and deadweight loss is the area of social surplus that is lost due to inefficiency.

How To Calculate Consumer Surplus Producer Surplus With A Price Floor Consumer and producer surpluses are shown as the area where consumers would have been willing to pay a higher price for a good or the price where producers would have been willing to sell a good. in the sample market shown in the graph, equilibrium price is $10 and equilibrium quantity is 3 units. the consumer surplus area is highlighted above. Figure 3.22 european wheat prices: a price floor example the intersection of demand (d) and supply (s) would be at the equilibrium point e 0. however, a price floor set at pf holds the price above e 0 and prevents it from falling. the result of the price floor is that the quantity supplied qs exceeds the quantity demanded qd. As a result, the new consumer surplus is t v, while the new producer surplus is x. (b) the original equilibrium is $8 at a quantity of 1,800. consumer surplus is g h j, and producer surplus is i k. a price floor is imposed at $12, which means that quantity demanded falls to 1,400. as a result, the new consumer surplus is g, and the new. A price floor is a regulation that prevents buying and selling a good or service below a specified price. price floors are often implemented with one or more of the following goals in mind: to push the price of a good or service above the market price. to reduce the demand for goods or services thought to be harmful.

Price Ceiling And Price Floor Gemanalyst As a result, the new consumer surplus is t v, while the new producer surplus is x. (b) the original equilibrium is $8 at a quantity of 1,800. consumer surplus is g h j, and producer surplus is i k. a price floor is imposed at $12, which means that quantity demanded falls to 1,400. as a result, the new consumer surplus is g, and the new. A price floor is a regulation that prevents buying and selling a good or service below a specified price. price floors are often implemented with one or more of the following goals in mind: to push the price of a good or service above the market price. to reduce the demand for goods or services thought to be harmful. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. if you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. Fig 4.15 shows a price floor example using a string of struggling movie theatres, all in the same city. the current equilibrium is $8 per movie ticket, with 1,800 people attending movies. the original consumer surplus is a b d, and original the producer surplus is c e.
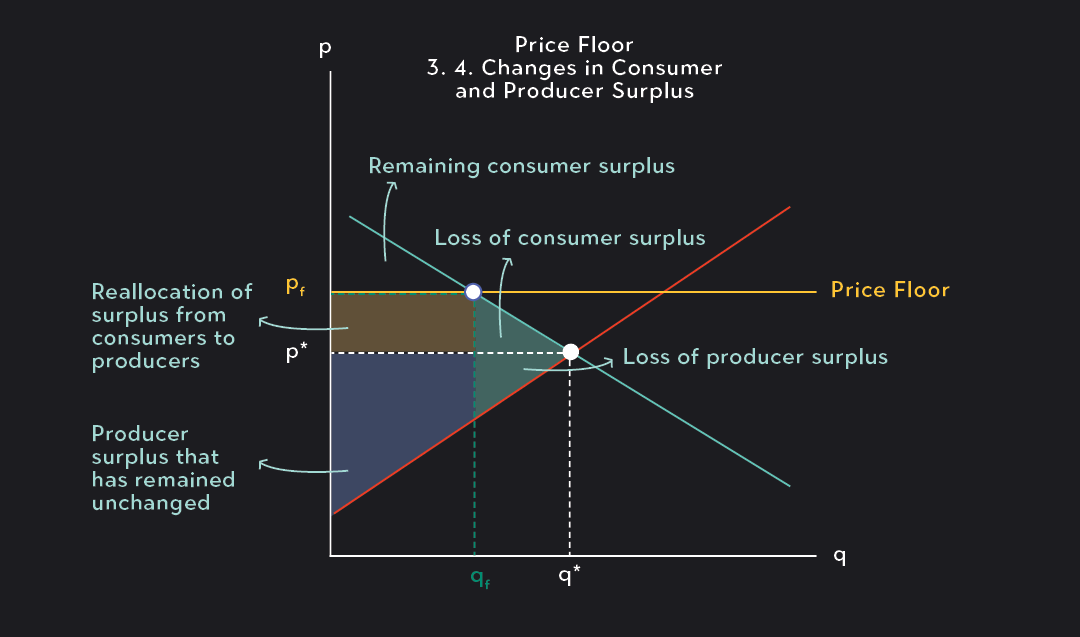
Price Ceiling Surplus If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. if you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. Fig 4.15 shows a price floor example using a string of struggling movie theatres, all in the same city. the current equilibrium is $8 per movie ticket, with 1,800 people attending movies. the original consumer surplus is a b d, and original the producer surplus is c e.
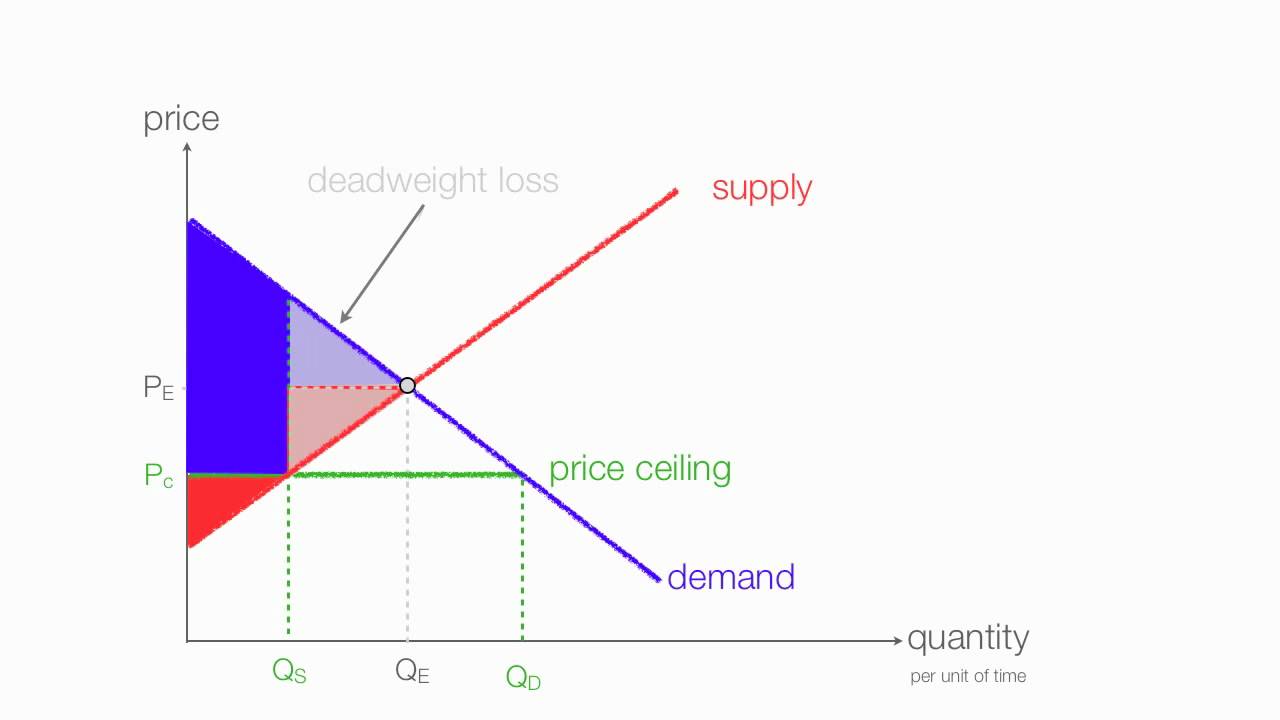
How To Calculate Changes In Consumer And Producer Surplus With Price

Comments are closed.