Circular Flow Model Economics Microeconomics Macroeconomics Honors
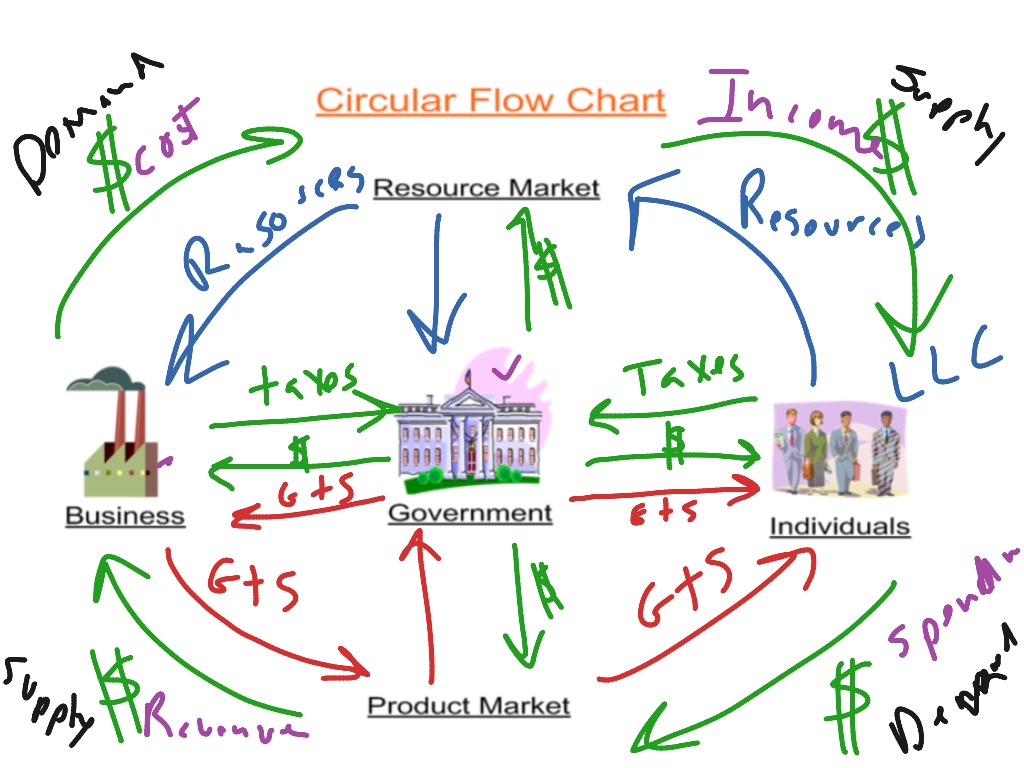
Circular Flow Model Economics Microeconomics Macroeconomics Honors The circular flow model is a conceptual framework that illustrates the interdependent relationships between the key participants in an economy households, firms, and the government and the flow of economic resources, goods and services, and money between them. it provides a simplified representation of the continuous cycle of economic activity and the interconnectedness of various sectors. The circular flow model is a conceptual framework in economics that illustrates how the economy operates as a circular process involving the exchange of money and resources between households and firms. it depicts the interdependence and continuous interactions between these two key economic agents.
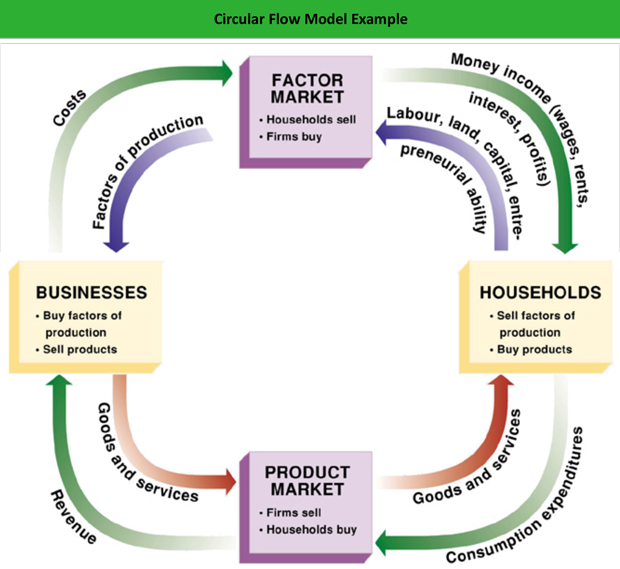
In The Circular Flow Diagram The economy can be thought of as two cycles moving in opposite directions. in one direction, we see goods and services flowing from individuals to businesses and back again. this represents the idea that, as laborers, we go to work to make things or provide services that people want. in the opposite direction, we see money flowing from businesses to households and back again. this represents. 2.2 circular flow model a good model to start within economics is the circular flow diagram (fig 2.1).it pictures the economy as consisting of two groups—households and firms—that interact in two markets: the goods and services market in which firms sell and households buy and the labour market in which households sell labour to business firms or other employees. Circular flow model. in economics, a good model to start with is the circular flow diagram, shown below. it pictures the economy as consisting of two groups—households and firms—that interact in two markets: the goods and services market in which firms sell and households buy and the labor market in which households sell labor to business firms or other employees. The circular flow diagram (fig 2.1) pictures the economy as consisting of two groups—households and firms—that interact in two markets: the goods and services market, in which firms sell and households buy and the labour market, in which households sell, labour to business firms or other employees. the direction of the arrows shows that in.

Circular Flow Diagram Microeconomics Circular flow model. in economics, a good model to start with is the circular flow diagram, shown below. it pictures the economy as consisting of two groups—households and firms—that interact in two markets: the goods and services market in which firms sell and households buy and the labor market in which households sell labor to business firms or other employees. The circular flow diagram (fig 2.1) pictures the economy as consisting of two groups—households and firms—that interact in two markets: the goods and services market, in which firms sell and households buy and the labour market, in which households sell, labour to business firms or other employees. the direction of the arrows shows that in. The circular flow model uses one of the most well known diagrams in economics to illustrate how income, expenditure, products, and inputs circulate through an economy. it is one of the first concepts that will be introduced to students of macroeconomics. it is a fairly basic model, but it does give an important overview of how all the important. Circular flow model. the circular flow model is a visual representation of how money, goods, and services move throughout an economy between different economic agents. it highlights the interactions between households, firms, and the government, illustrating how resources and income circulate in a continuous loop, thereby forming the backbone.

Comments are closed.