Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pathophysiology Wikidoc Vrogue Co
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pathophysiology Wikidoc Vrogue Co Overview. carpal tunnel syndrome (cts) is known as a common pathology in hand. most common diagnosis of cts is idiopathic but it is accepted that the median nerve neuropathy could be caused due to the chronic increased pressure within the carpal tunnel. but the exact pathophysiology of this pressure increase is not well known yet. Anatomy. main article: carpal tunnel. the median nerve passes through the carpal tunnel, a canal in the wrist that is surrounded by bone on three sides, and a fibrous sheath (the flexor retinaculum) on the fourth. nine tendons — the flexor tendons of the hand—pass through this canal. [3] the median nerve can be compressed by a decrease in.

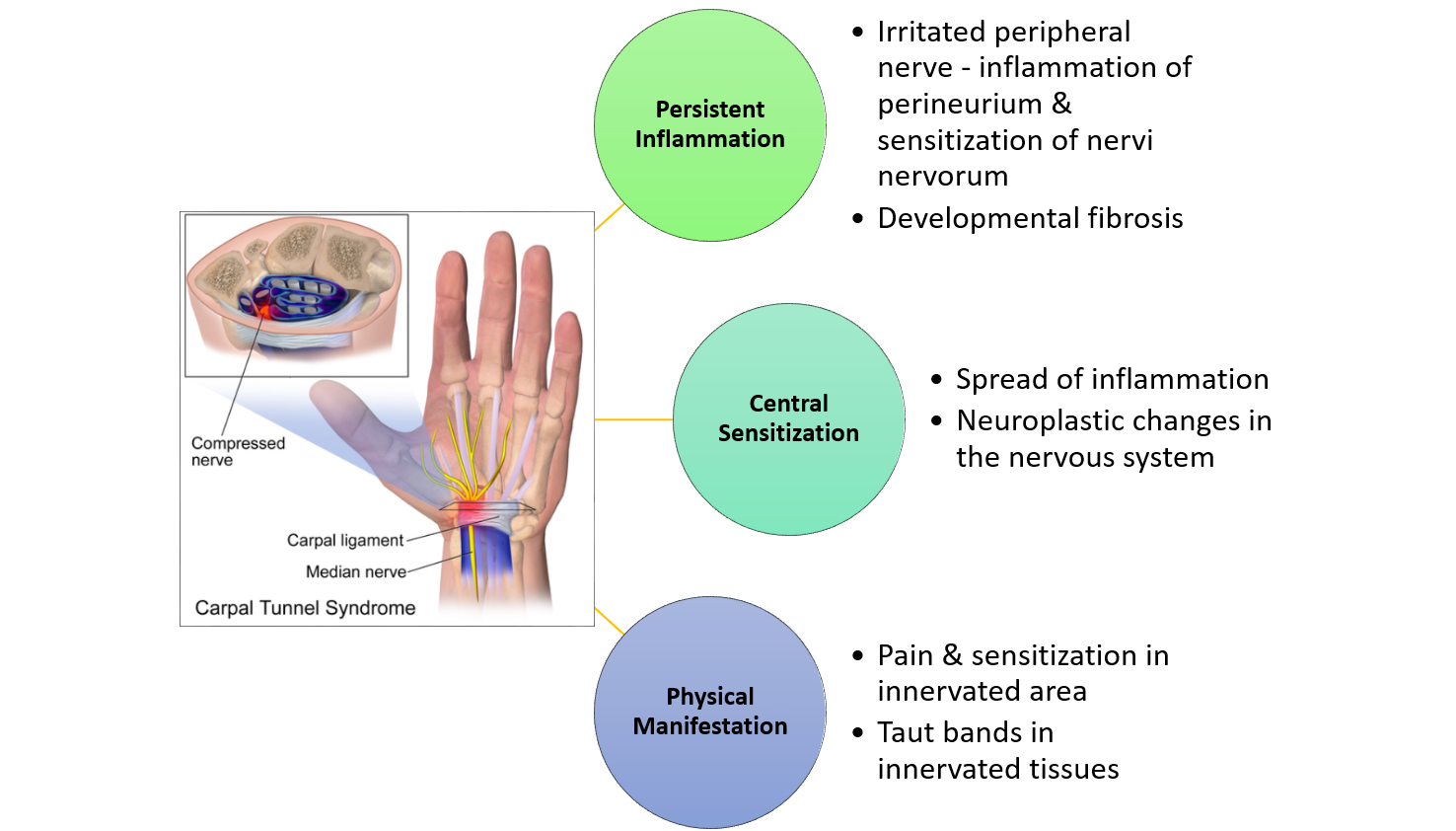
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pathophysiology Wikidoc Vrogue Co Pathophysiology of carpal tunnel syndrome illustrating the compression of the median nerve within the carpal tunnel space. this image is available under the creative commons cc by nc license and permits non commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium provided the original work is properly cited [ 11 ]. Carpal tunnel syndrome (cts) or median neuropathy at the wrist is a medical condition in which the median nerve is compressed at the wrist, leading to pain, paresthesias, and muscle weakness in the forearm and hand. [1] a form of compressive neuropathy, cts is more common in women than it is in men, and, though it can occur at any age, has a. Carpal tunnel syndrome (cts) occurs when the median nerve is compressed as it traverses the carpal tunnel. the primary factor contributing to the onset of cts is the elevated pressure within the carpal tunnel. the typical initial signs of cts include pain, numbness, and paresthesias, which affect the first 3 digits and the lateral half of the fourth digit.[1] symptoms of cts can exhibit. The carpal tunnel is an osteofibrous outlet, which lies between the flexor retinaculum (fr) and the carpal bones. the roof of this tunnel is the fibrous transverse carpal ligament, which is the intermediate part of the fr. nine flexor tendons, and their sheath, and the median nerve pass through the tunnel where the nerve enters the tunnel in.

Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pathophysiology Wikidoc Carpal tunnel syndrome (cts) occurs when the median nerve is compressed as it traverses the carpal tunnel. the primary factor contributing to the onset of cts is the elevated pressure within the carpal tunnel. the typical initial signs of cts include pain, numbness, and paresthesias, which affect the first 3 digits and the lateral half of the fourth digit.[1] symptoms of cts can exhibit. The carpal tunnel is an osteofibrous outlet, which lies between the flexor retinaculum (fr) and the carpal bones. the roof of this tunnel is the fibrous transverse carpal ligament, which is the intermediate part of the fr. nine flexor tendons, and their sheath, and the median nerve pass through the tunnel where the nerve enters the tunnel in. In carpal tunnel syndrome (cts), the median nerve is compressed at the level of the carpal tunnel in the wrist. this entrapment manifests as unpleasant symptoms, such as burning, tingling, or numbness in the palm that extends to the fingers. as the disease progresses, afflicted individuals also repo …. Carpal tunnel syndrome (cts) occurs when the median nerve becomes compressed as it passes through the wrist within the carpal tunnel, resulting in pain, tingling, weakness, or numbness in the hand.

Comments are closed.