Carbohydrates Part 1 Simple Sugars And Fischer Projections

Carbohydrates Part 1 Simple Sugars And Fischer Projections Quizalize It's the night before the big game! you're carbo loading! wait, what are carbs? did you know that sugar is a carbohydrate? you didn't?! well, you'd better wa. Exercise 25.3.1 25.3. 1. draw 'zigzag' structures (using the solid dash wedge convention to show stereochemistry) for the four sugars in the figure below. label all stereocenters r or s. answer. the wedge and dash notations we have been using are effective for drawing three dimensional configurations on a two dimensional surface,, but can be.

Carbohydrates R,s stereochemical designations (section 5.5) can be assigned to the chirality center in a fischer projection by following three steps, as shown in worked example 25.1. step 1 rank the four substituents in the usual way ( section 5.5 ). Following the lead of emil fischer, we can use a representation – the “fischer projection formula” (figure 13.4): put the c atoms in a vertical row; the c atoms are numbered from top to bottom. bonds in the vertical orientation are assumed to be bending back behind the page, and bonds in the horizontal orientation are assumed to be. Most natural sugars are d and most natural amino acids are l . one method for determining whether a molecule is d or l by looking at the fischer projection of a molecule. if the oh ( nh 2 for amino acids) on the bottom most chiral center is on the right hand side of the fischer projection, the molecule is “ d “. The usefulness of this notation to fischer, in his carbohydrate studies, is evident in the following diagram. there are eight stereoisomers of 2,3,4,5 tetrahydroxypentanal, a group of compounds referred to as the aldopentoses. since there are three chiral centers in this constitution, we should expect a maximum of 2 3 stereoisomers.
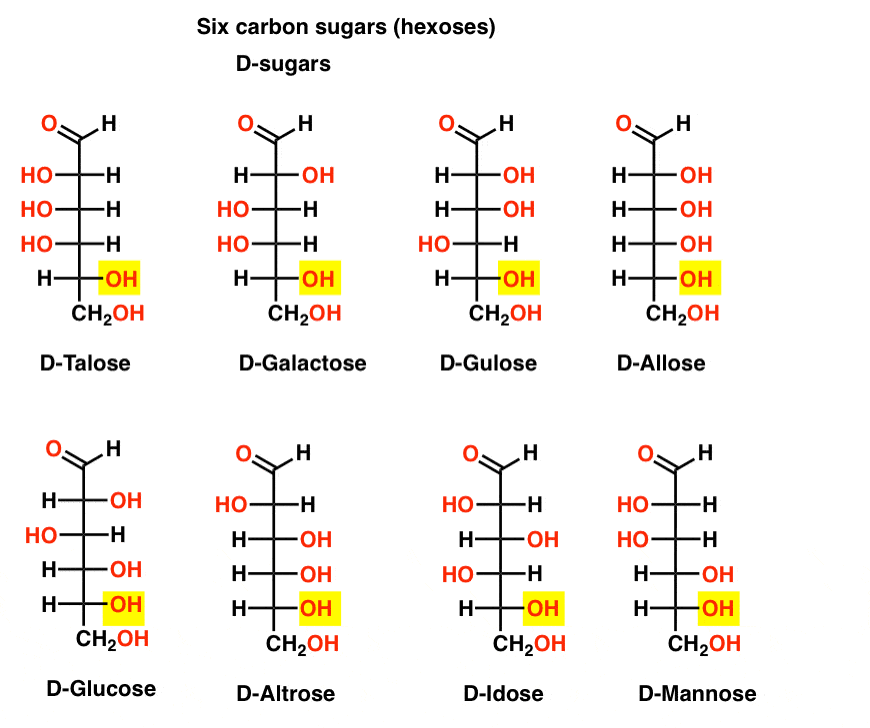
D And L Notation For Sugars вђ Master Organic Chemistry Most natural sugars are d and most natural amino acids are l . one method for determining whether a molecule is d or l by looking at the fischer projection of a molecule. if the oh ( nh 2 for amino acids) on the bottom most chiral center is on the right hand side of the fischer projection, the molecule is “ d “. The usefulness of this notation to fischer, in his carbohydrate studies, is evident in the following diagram. there are eight stereoisomers of 2,3,4,5 tetrahydroxypentanal, a group of compounds referred to as the aldopentoses. since there are three chiral centers in this constitution, we should expect a maximum of 2 3 stereoisomers. 4. recognize whether a sugar is a reducing or a nonreducing sugar. 5. discuss the use of the benedict's reagent to measure the level of glucose in urine. draw and name the common, simple carbohydrates using structural formulas and fischer projection formulas. 6. given the linear structure of a monosaccharide, draw the haworth. The term carbohydrate is used to refer to a broad class of polyhydroxylated aldehydes and ketones commonly called sugars. carbohydrates are also known as saccharides. the general formula for a carbohydrate is approximated as cnh2non. the number of carbons in the carbohydrate chain is also given special nomenclature. 3 carbons – triose.
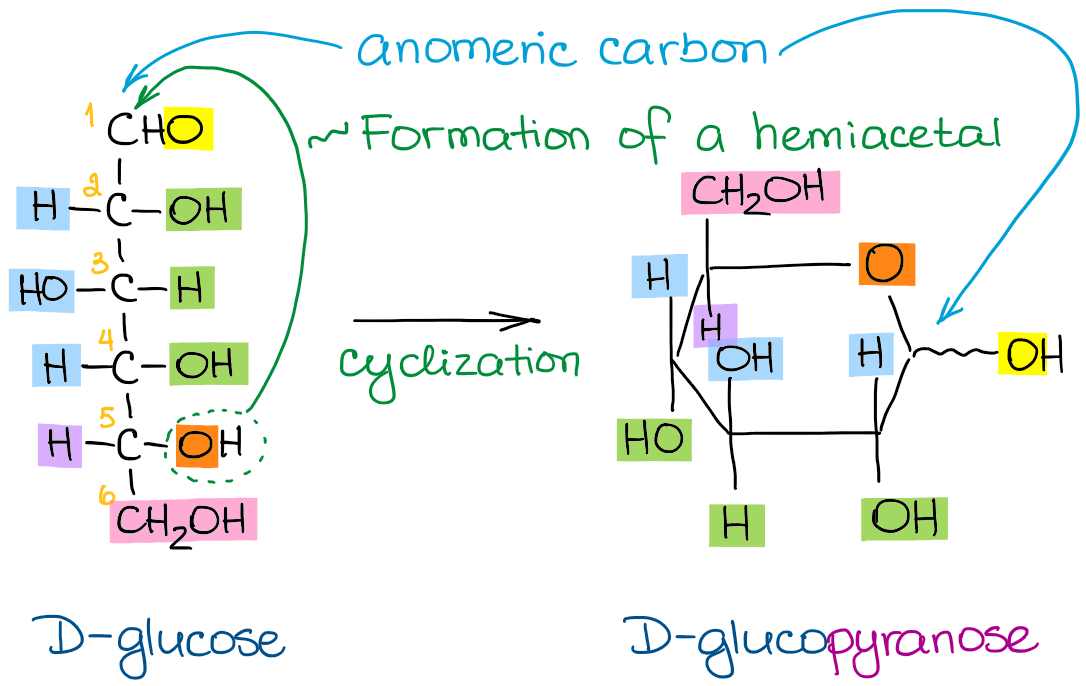
Converting Between Fischer Haworth And Chair Forms Of Carbohydrates 4. recognize whether a sugar is a reducing or a nonreducing sugar. 5. discuss the use of the benedict's reagent to measure the level of glucose in urine. draw and name the common, simple carbohydrates using structural formulas and fischer projection formulas. 6. given the linear structure of a monosaccharide, draw the haworth. The term carbohydrate is used to refer to a broad class of polyhydroxylated aldehydes and ketones commonly called sugars. carbohydrates are also known as saccharides. the general formula for a carbohydrate is approximated as cnh2non. the number of carbons in the carbohydrate chain is also given special nomenclature. 3 carbons – triose.

Comments are closed.