Calculate The Missing Sides Of A Triangle Using Pythagoras Theorem
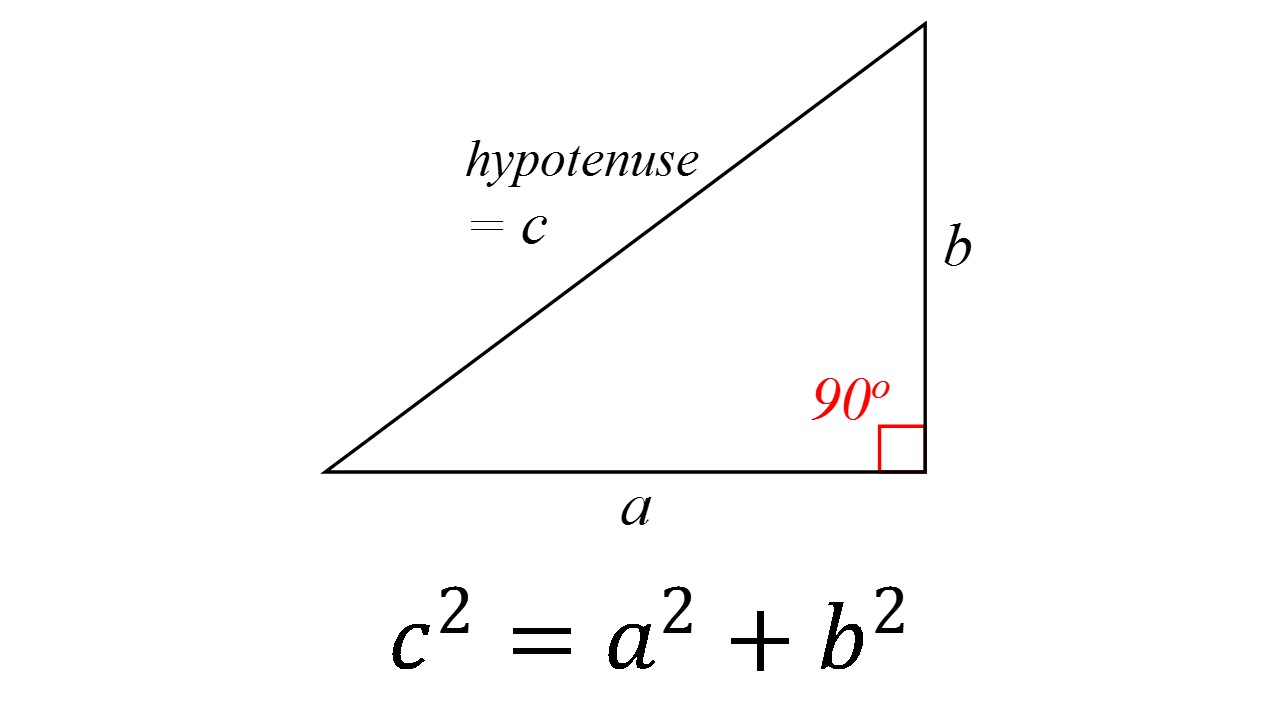
How Do You Use The Pythagorean Theorem To Determine If The Following The pythagorean theorem states that the sum of the squared sides of a right triangle equals the length of the hypotenuse squared. you might recognize this theorem in the form of the pythagorean equation: a2 b2 = c2 a 2 b 2 = c 2. if you know the length of any 2 sides of a right triangle you can use the pythagorean equation formula to find. The pythagorean theorem calculator is one of the most accessible tools you will come across, despite the name being scary. all you need is any two of the three sides of a right triangle, and you are all set. let's take a look at the steps to use our pythagorean theorem calculator. input leg a of the right triangle. next, input leg b of the.
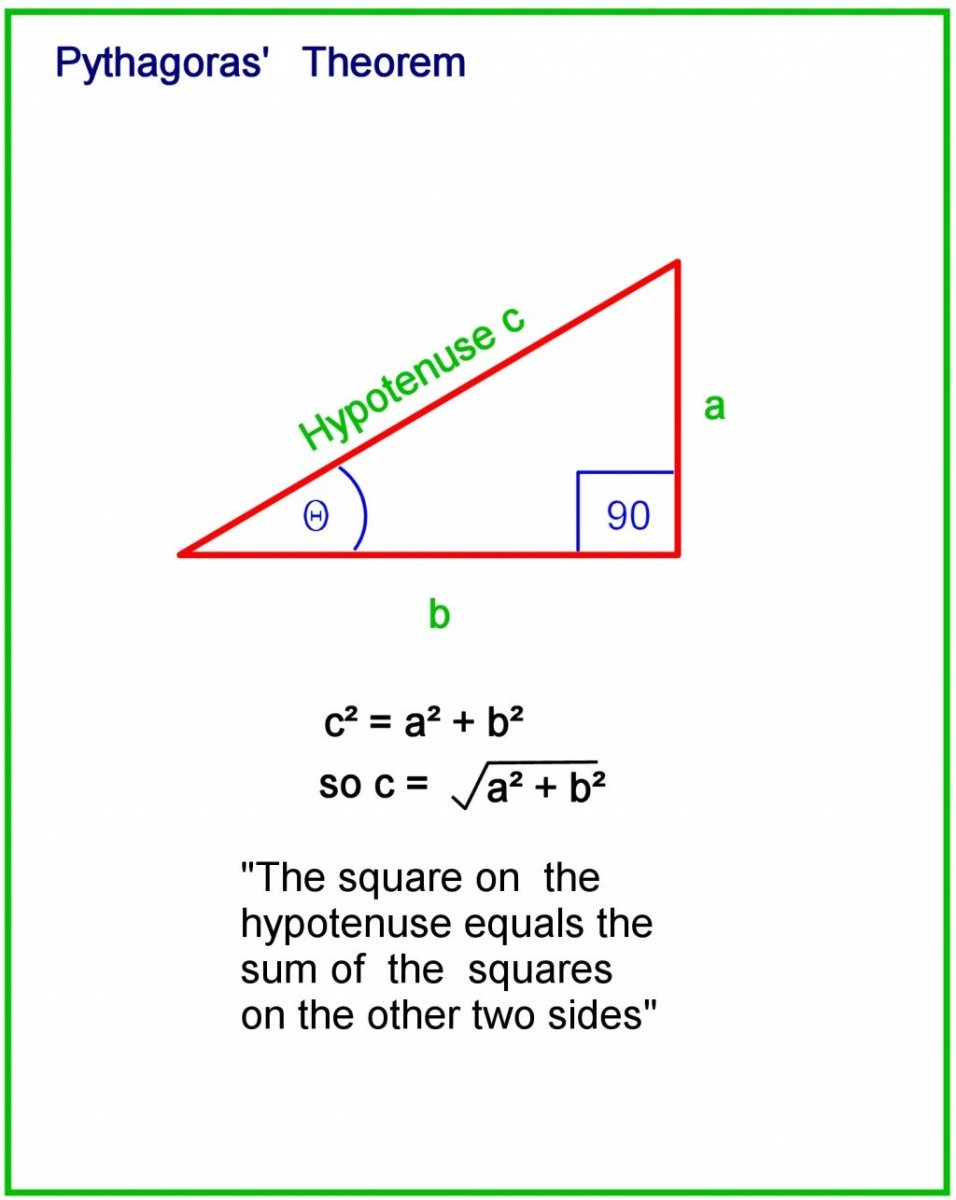
How To Calculate The Sides And Angles Of Triangles Using Pythagoras A 2 b 2 = c 2. this is known as the pythagorean equation, named after the ancient greek thinker pythagoras. this relationship is useful because if two sides of a right triangle are known, the pythagorean theorem can be used to determine the length of the third side. referencing the above diagram, if. a = 3 and b = 4. Step 1: enter the values of any two angles and any one side of a triangle below for which you want to find the length of the remaining two sides. the pythagorean theorem calculator finds the length of the remaining two sides of a given triangle using sine law or definitions of trigonometric functions. if a given triangle is a right angle. The calculator is designed specifically to operate within this principle. to use the tool, one must input the known lengths of two sides of the triangle (either the base, perpendicular, or hypotenuse), and the calculator will compute the missing third side's length. when using this calculator to determine the side length of a right angled. Pythagorean theorem calculator. enter the lengths of any two sides of a right triangle to find the unknown side using pythagorean theorem equation i.e. \ (a^2 b^2=c^2\). solve for: side b. hypotenuse c. units: no. of decimal places: a = c² b². calculate.
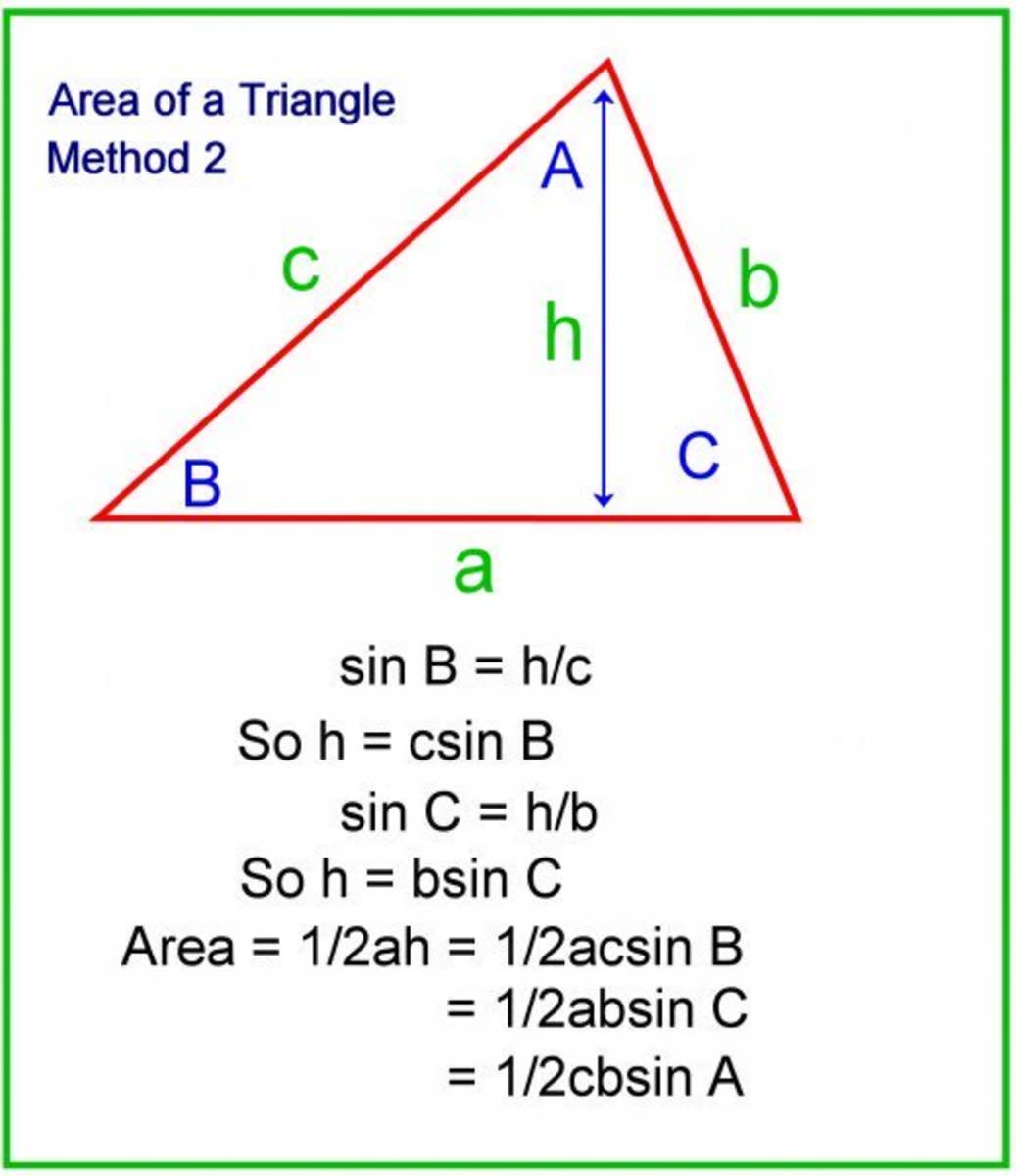
How To Calculate The Sides And Angles Of Triangles Using Pythagoras The calculator is designed specifically to operate within this principle. to use the tool, one must input the known lengths of two sides of the triangle (either the base, perpendicular, or hypotenuse), and the calculator will compute the missing third side's length. when using this calculator to determine the side length of a right angled. Pythagorean theorem calculator. enter the lengths of any two sides of a right triangle to find the unknown side using pythagorean theorem equation i.e. \ (a^2 b^2=c^2\). solve for: side b. hypotenuse c. units: no. of decimal places: a = c² b². calculate. A pythagoras triangle is any right triangle. pythagoras triangle satisfies the pythagorean theorem, which allows calculating the length of the third side of an angle knowing the value of the other two. the pyhtagoras theorem in a triangle states that: h² = c₁² c₂², where: h is the hypotenuse; and; c₁ and c₂ are the catheti. The length of the sides of these new triangles can be defined using the pythagorean theorem as follows: 1 ac² 1 bc² = 1 cd². note, ac, bc, and cd represent the length of the line segments connecting the respective vertices. this can be rewritten to more simply express the height of a right triangle: 1 a² 1 b² = 1 h².

Calculate The Missing Sides Of A Triangle Using Pythagoras Theorem A pythagoras triangle is any right triangle. pythagoras triangle satisfies the pythagorean theorem, which allows calculating the length of the third side of an angle knowing the value of the other two. the pyhtagoras theorem in a triangle states that: h² = c₁² c₂², where: h is the hypotenuse; and; c₁ and c₂ are the catheti. The length of the sides of these new triangles can be defined using the pythagorean theorem as follows: 1 ac² 1 bc² = 1 cd². note, ac, bc, and cd represent the length of the line segments connecting the respective vertices. this can be rewritten to more simply express the height of a right triangle: 1 a² 1 b² = 1 h².

Comments are closed.