Boiling Point Of Organic Compounds

Boiling Point Of Organic Compounds Youtube 4.3 boiling points. page id. for general purposes it is useful to consider temperature to be a measure of the kinetic energy of all the atoms and molecules in a given system. as temperature is increased, there is a corresponding increase in the vigor of translational and rotation motions of all molecules, as well as the vibrations of atoms and. The last compound, an isomer of octane, is nearly spherical and has an exceptionally high melting point (only 6º below the boiling point). contributors william reusch, professor emeritus ( michigan state u. ), virtual textbook of organic chemistry.

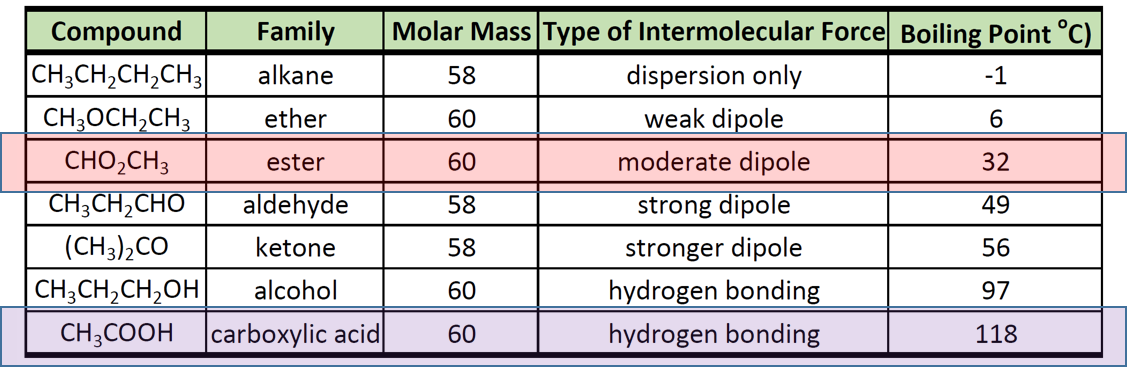
Pdf Normal Boiling Points For Organic Compounds Correlation And Aldehyde, ketone are highly polar due to permanent dipole dipole attraction. thus its boiling point is relatively higher than alkane, haloalkanes, ether, ester, and amine. alcohol, carboxylic acid and amide have strong hydrogen bonding. thus their boiling point is the largest. the boiling point of organic molecules increases in the order:. Learn how intermolecular interactions such as dipole dipole, hydrogen bonding, and van der waals forces affect the boiling and melting points of organic compounds. see examples of common organic solvents and isomers with different physical properties. Boiling points increase as the number of carbons is increased. branching decreases boiling point. let’s have a closer look:. table of contents. trend #1: the relative strength of the four intermolecular forces. trend #2 – for molecules with a given functional group, boiling point increases with increasing molecular weight. Learn how noncovalent interactions, size, shape, and polarity affect the melting and boiling points of organic molecules. see examples, trends, and exercises for different types of organic compounds.
Ch105 Chapter 9 вђ Organic Compounds Of Oxygen вђ Chemistry Boiling points increase as the number of carbons is increased. branching decreases boiling point. let’s have a closer look:. table of contents. trend #1: the relative strength of the four intermolecular forces. trend #2 – for molecules with a given functional group, boiling point increases with increasing molecular weight. Learn how noncovalent interactions, size, shape, and polarity affect the melting and boiling points of organic molecules. see examples, trends, and exercises for different types of organic compounds. This organic chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into boiling point of organic compounds such as straight chain alkanes, branched alkanes,. Organic chemistry with a biological emphasis by tim soderberg (university of minnesota, morris) 2.11: intermolecular forces and relative boiling points (bp) is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by libretexts. the relative strength of the intermolecular forces (imfs) can be used to predict the relative boiling.

3 Trends That Affect Boiling Points вђ Master Organic Chemistry This organic chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into boiling point of organic compounds such as straight chain alkanes, branched alkanes,. Organic chemistry with a biological emphasis by tim soderberg (university of minnesota, morris) 2.11: intermolecular forces and relative boiling points (bp) is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by libretexts. the relative strength of the intermolecular forces (imfs) can be used to predict the relative boiling.

Comments are closed.