Biotic Factors Great Barrier Reef

What Are Biotic Factors In The Great Barrier Reef Printable Templates The reef covers an area over 300,000 square kilometers and includes a wide range of ocean depth, and it contains such biodiversity as to make it one of the most complex ecosystems on earth. much like any other ecosystem on earth, the great barrier reef relies on biotic and abiotic components to keep it functional and stable. The great barrier reef, which extends for over 2,300 kilometers (1429 miles) along the northeastern coast of australia, is home to over 9,000 known species. there are likely many more—new discoveries are frequently being made, including a new species of branching coral discovered in 2017. this richness and uniqueness make the reef crucial for.

The Great Barrier Reef The great barrier reef is the largest living structure on earth. it provides habitat for nearly 9,000 species of marine life—and that’s just the (relatively) easy to count ones! the reef’s rich biodiversity helps it to maintain a stable and healthy coral reef system. another way to look at biodiversity is from the perspective of the. The great barrier reef (gbr) is a diverse ecosystem extending for more than 2,300 km along australia’s northeast coast. it is recognised internationally as being of outstanding universal value (united nations educational, scientific and cultural organisation, 1981; lucas et al., 1997; gbrmpa, 2014a). its diversity includes but is not. One recent study on the great barrier reef [gbr] found that coral dwelling damselfishes occupying bleached or dead coral hosts were more susceptible to predation than the same species occupying healthy coral colonies (coker et al. 2009). as discussed above, live coral provides a direct food source for some fishes. As pressures on the great barrier reef intensify, there is a growing need to consolidate and communicate the existing scientific knowledge about this globally important coastal environment. the great barrier reef: biology, environment and management is the second edition of an edited collection of 32 chapters written by 48 leading coastal and marine experts. the editors have done a good job of.
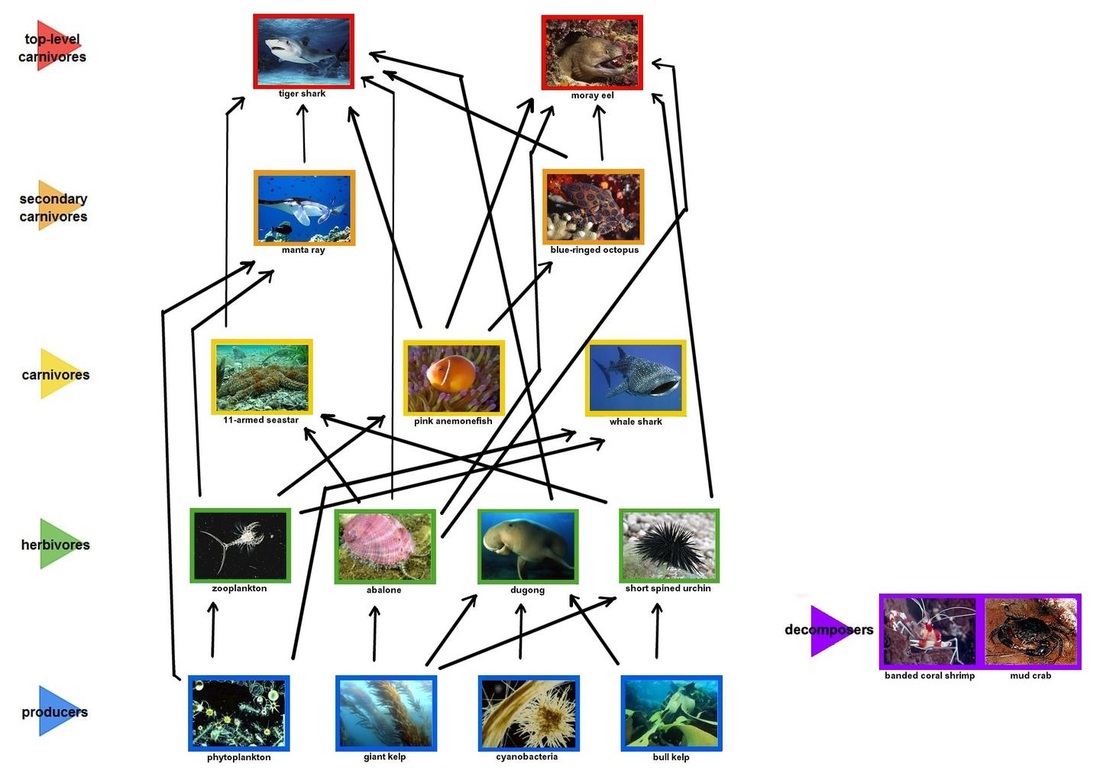
Biotic Factors Great Barrier Reef One recent study on the great barrier reef [gbr] found that coral dwelling damselfishes occupying bleached or dead coral hosts were more susceptible to predation than the same species occupying healthy coral colonies (coker et al. 2009). as discussed above, live coral provides a direct food source for some fishes. As pressures on the great barrier reef intensify, there is a growing need to consolidate and communicate the existing scientific knowledge about this globally important coastal environment. the great barrier reef: biology, environment and management is the second edition of an edited collection of 32 chapters written by 48 leading coastal and marine experts. the editors have done a good job of. Great barrier reef, world’s largest coral reef complex, located in the pacific ocean off northeastern australia. it extends for more than 1,250 miles (2,000 km) in a northwest southeast direction, and its width ranges from 37 to 155 miles (60 to 250 km). it has an area of some 135,000 square miles (350,000 square km). In the northern section of australia’s great barrier reef, halimeda algal bioherms occupy >6,000 km2 of the inter reef seabed, more than twice the area of adjacent shallow coral reefs.

Biotic Factors Great Barrier Reef Great barrier reef, world’s largest coral reef complex, located in the pacific ocean off northeastern australia. it extends for more than 1,250 miles (2,000 km) in a northwest southeast direction, and its width ranges from 37 to 155 miles (60 to 250 km). it has an area of some 135,000 square miles (350,000 square km). In the northern section of australia’s great barrier reef, halimeda algal bioherms occupy >6,000 km2 of the inter reef seabed, more than twice the area of adjacent shallow coral reefs.

Comments are closed.