Biodegradable Polymers And Composites Recent Development And

Biodegradable Polymers And Composites Recent Development And The first section provides an introductory overview of biodegradable polymers and their composites. the second section focuses on the most prominent polymers used in the industry. furthermore, the fabrication techniques, along with their property and application relationships are provided with an emphasis on mechanical reinforcements and the biomedical field. Polylactide (pla)—glass fiber composites have high electrical resistivity (2.5 × 10 22 –4.9 × 10 22) µohm.cm as shown in fig. 2b.melting temperature of biodegradable polymers is variant.

Biodegradable Polymers Blends And Composites Biodegradable polymers and composites: recent development and challenges. reduce the issue of plastic waste and eventually lead to a circular economy. ram k. gupta, national institute for. Abstract. biodegradable polymers are highly sought after as they have the potential to reduce the issue of plastic waste and eventually lead to a circular economy. yet, conciliating eco. Biodegradable polymers are highly sought after as they have the potential to reduce the issue of plastic waste and eventually lead to a circular economy. yet, conciliating eco‐friendliness with competitive properties is often challenging. polymerization and processing techniques have been developed and optimized to improve such factors. some of the common polymerization methods to obtain. In recent times, considerable research works are being performed in developing completely biodegradable materials (green composites) by combining biodegradable polymer matrix with biofibers [18]. biodegradable polymers can be broadly classified into two types based on the source, bio and synthetic polymers [19].
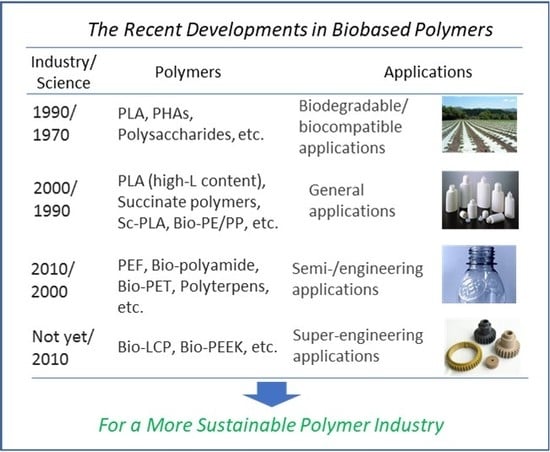
Polymers Free Full Text The Recent Developments In Biobased Biodegradable polymers are highly sought after as they have the potential to reduce the issue of plastic waste and eventually lead to a circular economy. yet, conciliating eco‐friendliness with competitive properties is often challenging. polymerization and processing techniques have been developed and optimized to improve such factors. some of the common polymerization methods to obtain. In recent times, considerable research works are being performed in developing completely biodegradable materials (green composites) by combining biodegradable polymer matrix with biofibers [18]. biodegradable polymers can be broadly classified into two types based on the source, bio and synthetic polymers [19]. Polylactide (pla)—glass fiber composites have high elec trical resistivity (2.5×10 22–4.9×10 ) µohm.cm as shown in fig. 2b. melting temperature of biodegradable polymers is. Natural biodegradable polymers are an important class of biodegradable polymers. the basic features of natural biodegradable polymers are that they are easily available and derived from natural sources and relatively inexpensive e.g., polysaccharides, lignin, chitosan, starch, cellulose, guar gum, collagen, albumin, etc. [62] as shown in fig. 7.

Schematic Representation Of Diverse Biodegradable Polymers And Their Polylactide (pla)—glass fiber composites have high elec trical resistivity (2.5×10 22–4.9×10 ) µohm.cm as shown in fig. 2b. melting temperature of biodegradable polymers is. Natural biodegradable polymers are an important class of biodegradable polymers. the basic features of natural biodegradable polymers are that they are easily available and derived from natural sources and relatively inexpensive e.g., polysaccharides, lignin, chitosan, starch, cellulose, guar gum, collagen, albumin, etc. [62] as shown in fig. 7.

Comments are closed.