Binomial Probability Manual And Calculator Steps Youtube

Binomial Probability Manual And Calculator Steps Youtube This video demonstrates the calculation of a probability using a binomial probability distribution. the first 2:45 shows the formula and how to apply the var. Learn how to use the binomial probability theorem to calculate probabilities in this free math video tutorial by mario's math tutoring. we go through a coupl.

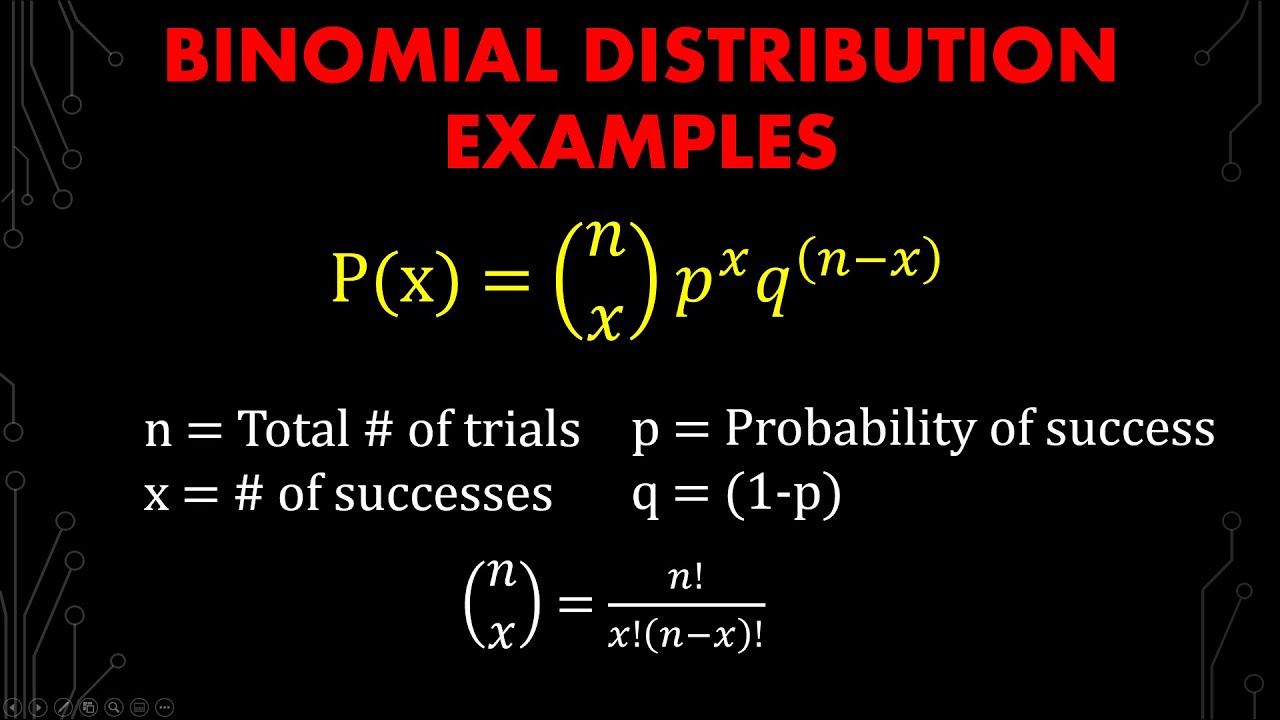
Binomial Distribution Calculation Tricks Using Scientific Calculator Learn how to solve any binomial distribution problem in statistics! in this tutorial, we first explain the concept behind the binomial distribution at a hig. Solution: the mean of the binomial distribution is interpreted as the mean number of successes for the distribution. to find the mean, use the formula μ = n ⋅ p where n is the number of trials and p is the probability of success on a single trial. substituting values for this problem, we have μ = 6 ⋅ 0.65 multiplying the expression we. Let's run these values through our calculator: input values: enter 10 for the number of trials (n), 5 for the number of successful outcomes (x), and 0.5 for the probability of success (p). review: the calculator promptly computes the binomial probability, providing the likelihood of getting exactly 5 heads in 10 flips. The binomial distribution formula is: b (x; n, p) = ncx * px * (1 – p)n – x where: b = binomial probability. n c x = combinations formula n c x = n! (x! (n – x)!) x = total number of “successes”. p = probability of a success on a single attempt. n = number of attempts or trials. note: the binomial distribution formula can also be.

Binomial Probability Step By Step Examples Youtube Let's run these values through our calculator: input values: enter 10 for the number of trials (n), 5 for the number of successful outcomes (x), and 0.5 for the probability of success (p). review: the calculator promptly computes the binomial probability, providing the likelihood of getting exactly 5 heads in 10 flips. The binomial distribution formula is: b (x; n, p) = ncx * px * (1 – p)n – x where: b = binomial probability. n c x = combinations formula n c x = n! (x! (n – x)!) x = total number of “successes”. p = probability of a success on a single attempt. n = number of attempts or trials. note: the binomial distribution formula can also be. Use the binomial probability formula to calculate the probability of success (p) for all possible values of r you are interested in. sum the values of p for all r within the range of interest. for example, the probability of getting two or fewer successes when flipping a coin four times (p = 0.5 and n = 4) would be:. In statistics, a binomial distribution is a probability distribution of the number of successes in a sequence of independent experiments or trials. the result of each experiment must be dichotomous, which means the result must be a yes no, success fail, heads tails, true false, or similar outcome. unlike a normal distribution, a binomial.

Binomial Probability Distribution On The Calculator Youtube Use the binomial probability formula to calculate the probability of success (p) for all possible values of r you are interested in. sum the values of p for all r within the range of interest. for example, the probability of getting two or fewer successes when flipping a coin four times (p = 0.5 and n = 4) would be:. In statistics, a binomial distribution is a probability distribution of the number of successes in a sequence of independent experiments or trials. the result of each experiment must be dichotomous, which means the result must be a yes no, success fail, heads tails, true false, or similar outcome. unlike a normal distribution, a binomial.
How To Calculate Binomial Distribution The Easy Way Youtube

Comments are closed.