Basic Taxonomy 6 Kingdoms Of Life Classification

The 6 Kingdoms Of Life Simple Explanation For Kids Wehavekids An overview of the characteristics of the six kingdoms of classification. all life on earth can be classified into one of these groups.these 6 kingdoms of li. By. regina bailey. updated on may 19, 2024. all organisms are traditionally classified into three domains and further subdivided into one of six kingdoms of life: archaebacteria, eubacteria, protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia. in other words, kingdoms are the second highest taxonomic rank. the three domains are bacteria, archaea, and eukaryota.

Basic Taxonomy 6 Kingdoms Of Life Classification Youtube Under the three domains are six kingdoms in taxonomy: animalia, contains general animals and is the largest kingdom with over 1 000 000 species. plantae, contains all plants on earth. protista, the third kingdom, was introduced by the german biologist ernst haeckel in 1866 to classify micro organisms which are neither animals nor plants. since. The 5 kingdoms of life are animalia, plantae, fungi, protista, and monera. when there are 6 kingdoms, monera breaks into eubacteria and archaebacteria. in biology, a kingdom of life is a taxonomy rank that is below domain and above phylum. in other words, it is a broad classification of organisms according to their characteristics. A domain contains one or more kingdoms. intermediate minor rankings are not shown. in biology, a kingdom is the second highest taxonomic rank, just below domain. kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla (singular phylum). traditionally, some textbooks from the united states and canada used a system of six kingdoms (animalia. Kingdoms of life. the diversity of the life of earth is bewildering. from microorganisms to trees to animals to fungi, life has evolved through time down countless pathways to provide us with the present day contingent of species. many scientists have devoted their lives to the giant task of classifying each organism into taxonomic groups.
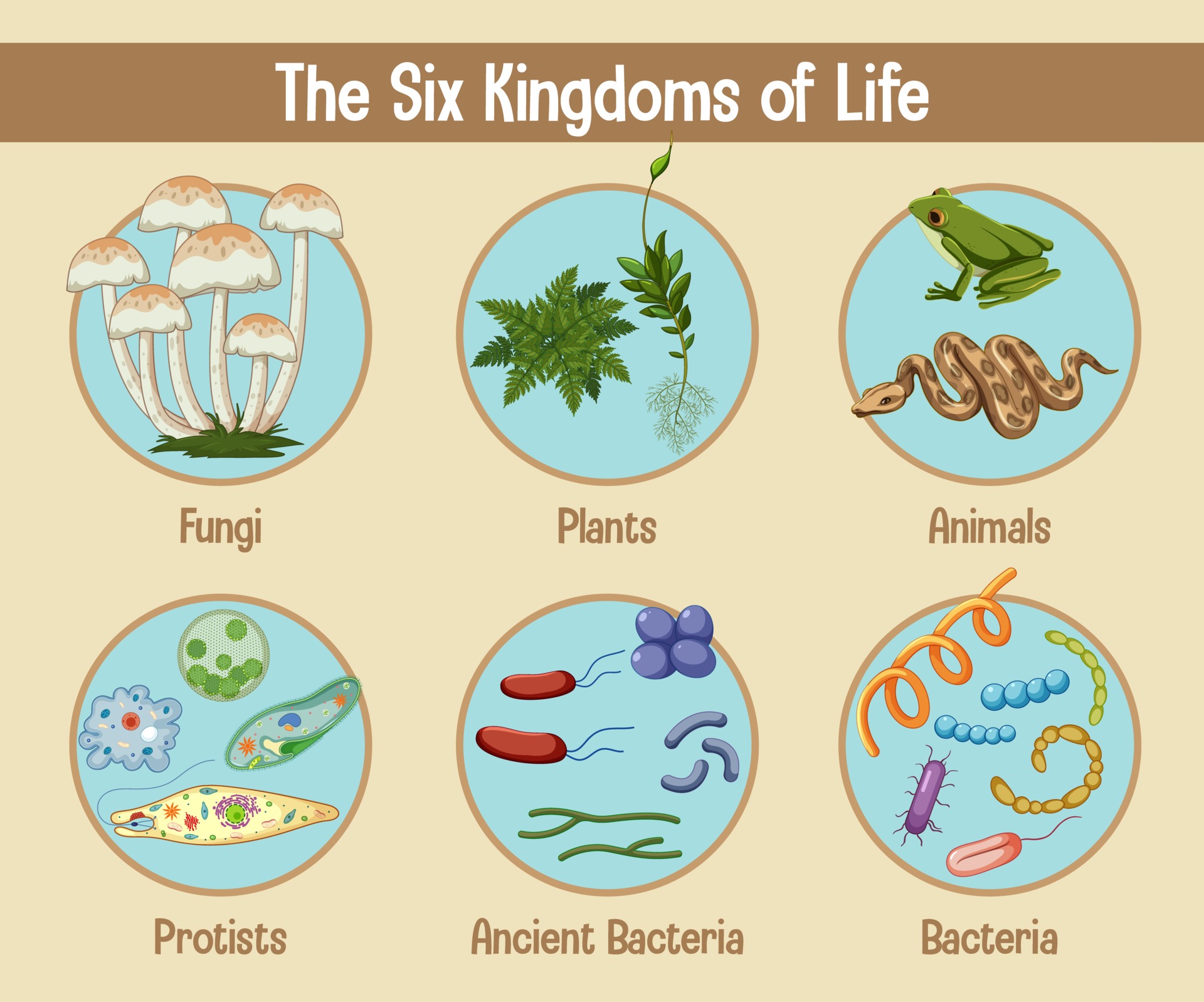
Science Poster Of Six Kingdoms Of Life 2906732 Vector Art At Vecteezy A domain contains one or more kingdoms. intermediate minor rankings are not shown. in biology, a kingdom is the second highest taxonomic rank, just below domain. kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla (singular phylum). traditionally, some textbooks from the united states and canada used a system of six kingdoms (animalia. Kingdoms of life. the diversity of the life of earth is bewildering. from microorganisms to trees to animals to fungi, life has evolved through time down countless pathways to provide us with the present day contingent of species. many scientists have devoted their lives to the giant task of classifying each organism into taxonomic groups. In 1990, many scientists agreed that kingdom monera should be divided into eubacteria and archaea, making six kingdoms. today, the exact way that kingdoms should be divided is still a matter of disagreement among some biologists. in the past, classification was made on the basis of appearance and similar body parts. For example, after the common beginning of all life, scientists divide organisms into three large categories called a domain: bacteria, archaea, and eukarya. within each domain is a second category called a kingdom. after kingdoms, the subsequent categories of increasing specificity are: phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species (figure 1).
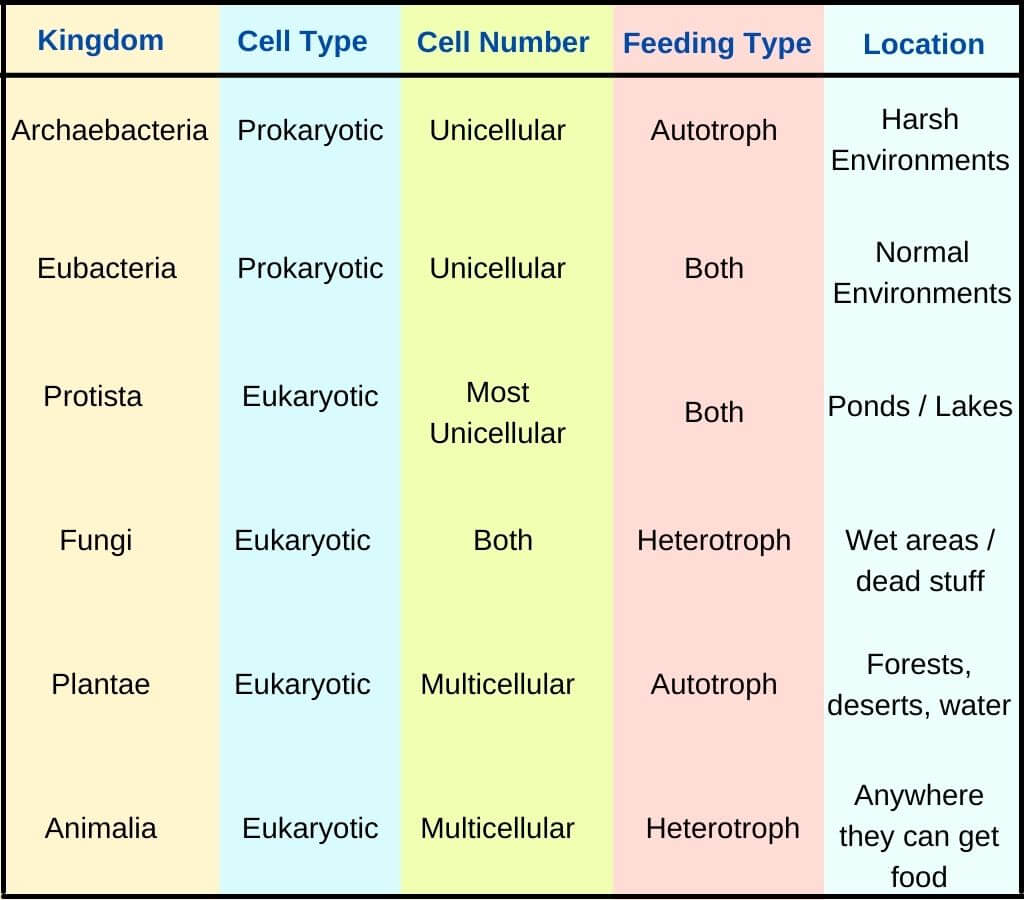
A Simple Explanation Of The 6 Kingdoms Of Life In 1990, many scientists agreed that kingdom monera should be divided into eubacteria and archaea, making six kingdoms. today, the exact way that kingdoms should be divided is still a matter of disagreement among some biologists. in the past, classification was made on the basis of appearance and similar body parts. For example, after the common beginning of all life, scientists divide organisms into three large categories called a domain: bacteria, archaea, and eukarya. within each domain is a second category called a kingdom. after kingdoms, the subsequent categories of increasing specificity are: phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species (figure 1).
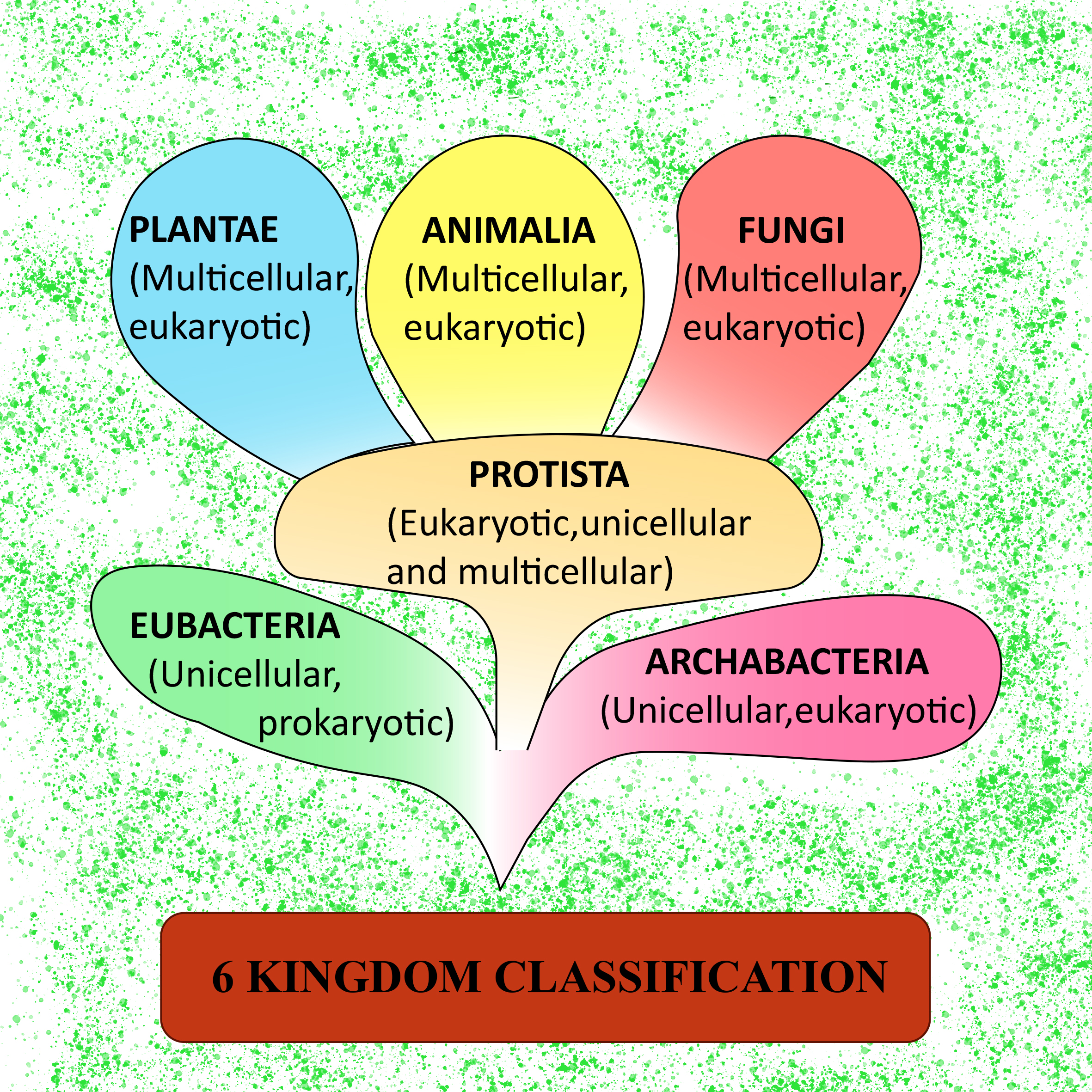
6 Kingdoms Chart

Comments are closed.