Bar Charts And Bar Graphs Explained
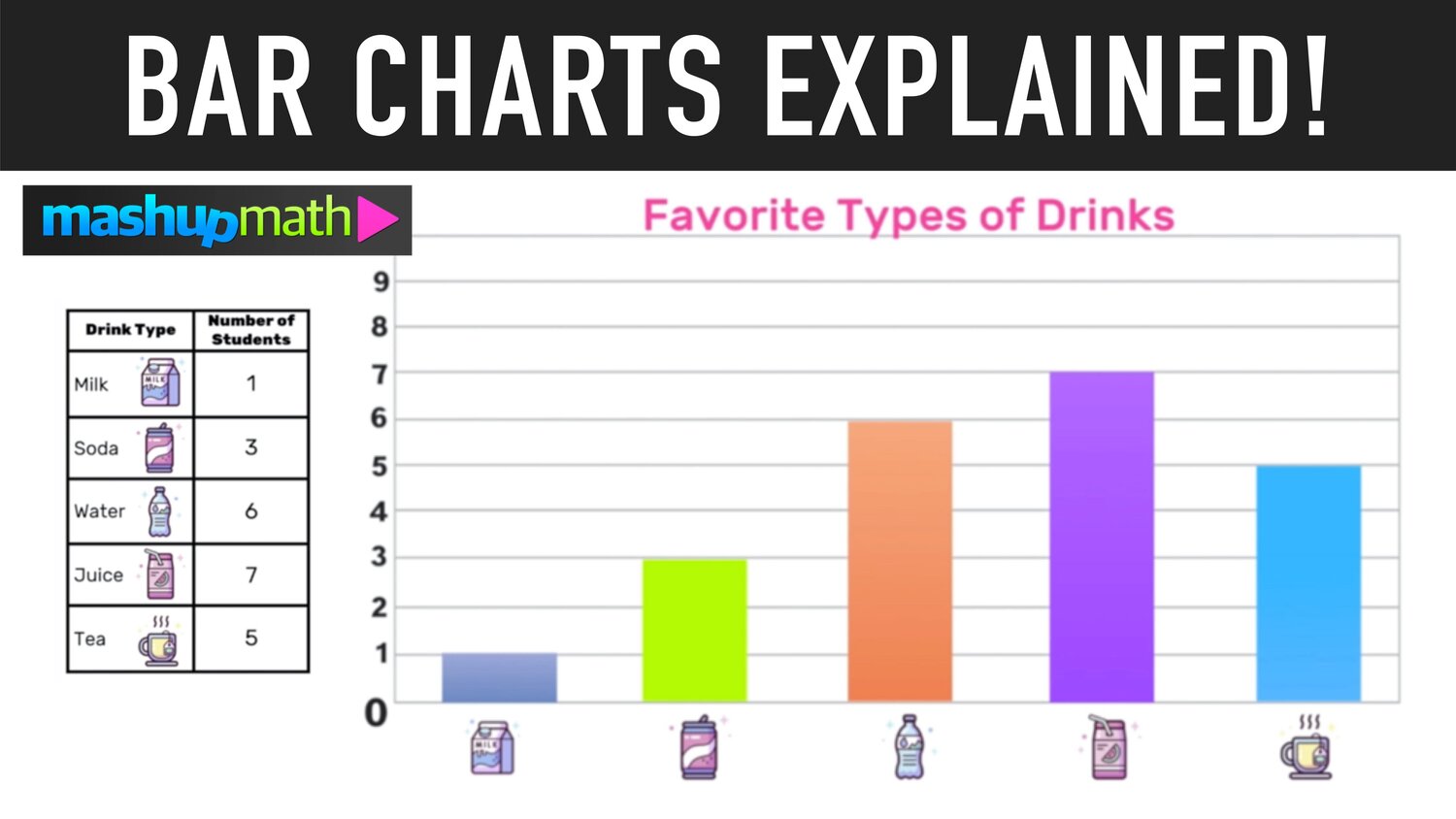
Bar Charts And Bar Graphs Explained вђ Mashup Math Bar charts: using, examples, and interpreting. use bar charts to compare categories when you have at least one categorical or discrete variable. each bar represents a summary value for one discrete level, where longer bars indicate higher values. types of summary values include counts, sums, means, and standard deviations. Create a bar graph that represents the data chart for a student survey of favorite types of drinks. the first step to making a bar graph is to give the bar graph a title. for this example, you can title the graph favorite types of drinks. the next step is to label the vertical and horizontal axes. for the vertical axis, you must choose.
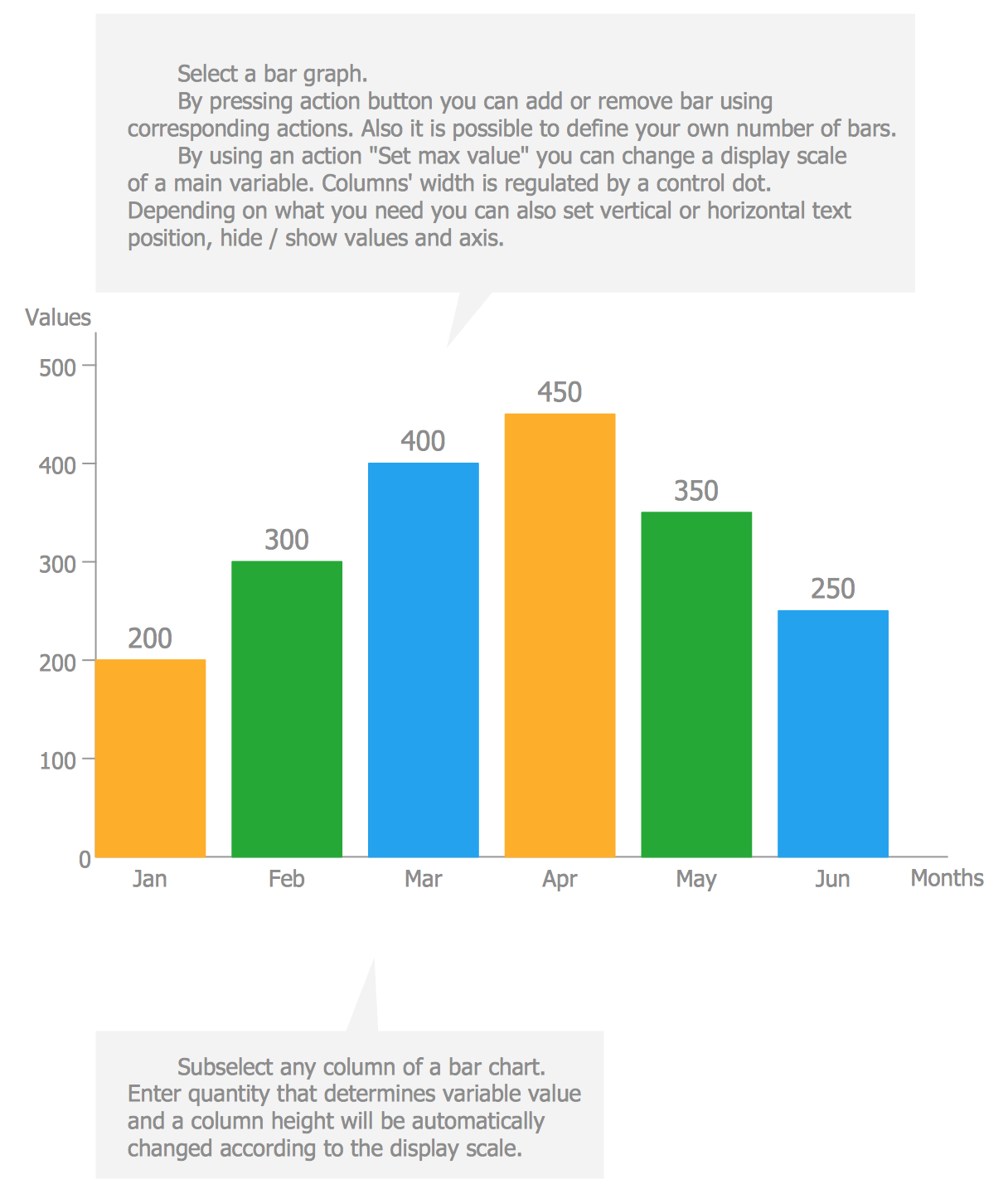
Basic Bar Graphs Solution Conceptdraw In this lesson, you will learn how to read, plot, and create bar charts and bar graphs. free practice worksheet: mashupmath blog create a b. A bar graph, also called a bar chart, represents data graphically in the form of bars. the height of the bars corresponds to the data they represent. like all graphs, bar graphs are also presented on a coordinate plane having an x axis and a y axis. parts. the different parts of a bar graph are: title; bars; categories; x axis; x axis label; y. A bar chart (aka bar graph, column chart) plots numeric values for levels of a categorical feature as bars. levels are plotted on one chart axis, and values are plotted on the other axis. each categorical value claims one bar, and the length of each bar corresponds to the bar’s value. bars are plotted on a common baseline to allow for easy. Step 1: open the file you want to work with in spss or type the data into a new worksheet. step 2: click “graphs,” then click “legacy dialogs” and then click “bar” to open the bar charts dialog box. step 3: click on an image for the type of bar graph you want (simple, clustered (a.k.a. grouped), or stacked) and then click the.

Bar Graph Bar Chart Cuemath A bar chart (aka bar graph, column chart) plots numeric values for levels of a categorical feature as bars. levels are plotted on one chart axis, and values are plotted on the other axis. each categorical value claims one bar, and the length of each bar corresponds to the bar’s value. bars are plotted on a common baseline to allow for easy. Step 1: open the file you want to work with in spss or type the data into a new worksheet. step 2: click “graphs,” then click “legacy dialogs” and then click “bar” to open the bar charts dialog box. step 3: click on an image for the type of bar graph you want (simple, clustered (a.k.a. grouped), or stacked) and then click the. In a vertical bar chart, the x axis serves as the beginning point for the bars. vertical bar charts are typically the default and a basic option. you might also see this type of graph called a column chart. horizontal. opposite from a vertical bar chart, the horizontal bar chart has the starting point for the bars on the y axis. Bar charts show the frequency counts of values for the different levels of a categorical or nominal variable. sometimes, bar charts show other statistics, such as percentages. figure 1 is an example of a bar chart for responses to a survey question. figure 1: bar chart displaying frequency counts for survey data.
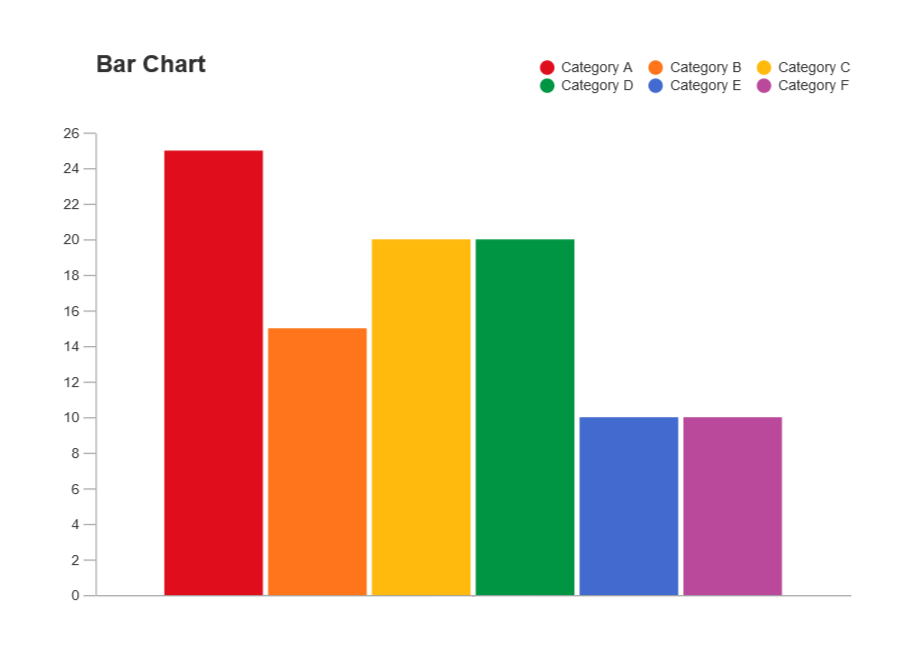
Bar Graph Learn About Bar Charts And Bar Diagrams In a vertical bar chart, the x axis serves as the beginning point for the bars. vertical bar charts are typically the default and a basic option. you might also see this type of graph called a column chart. horizontal. opposite from a vertical bar chart, the horizontal bar chart has the starting point for the bars on the y axis. Bar charts show the frequency counts of values for the different levels of a categorical or nominal variable. sometimes, bar charts show other statistics, such as percentages. figure 1 is an example of a bar chart for responses to a survey question. figure 1: bar chart displaying frequency counts for survey data.
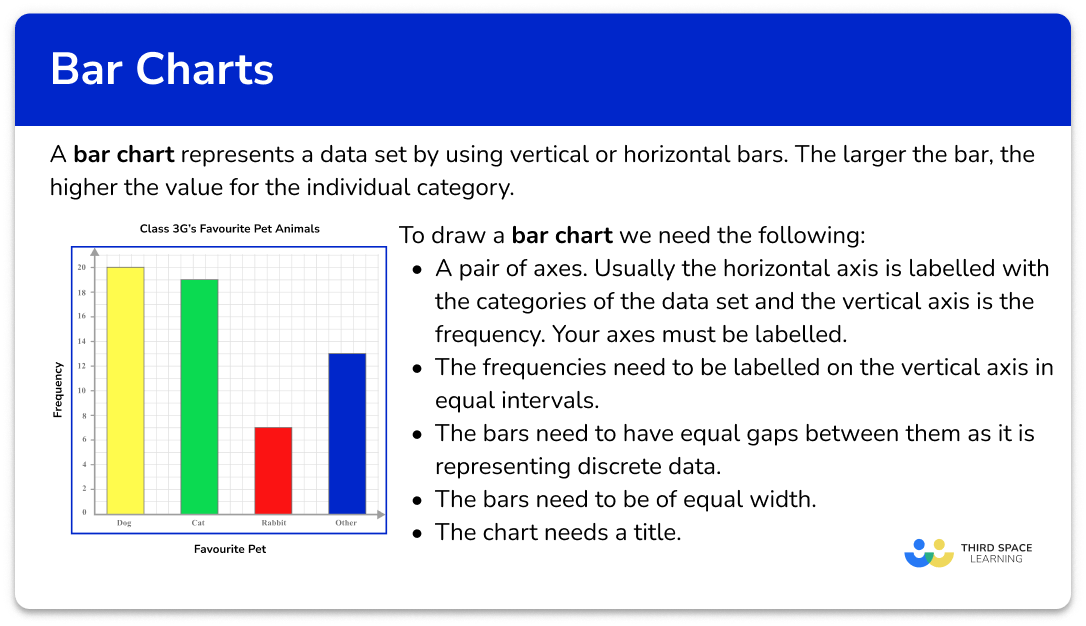
Bar Chart Gcse Maths Steps Examples Worksheet

Comments are closed.