Ascites Differential Diagnosis Table Serum Ascites Gr Vrogue Co
Ascites Differential Diagnosis Table Serum Ascites Gr Vrogue Co Successful treatment of ascites depends upon an accurate diagnosis of its cause (table 1 and table 2 and table 3 and algorithm 1) [1]. this topic will review the evaluation of adults with ascites. performance of paracentesis, specific causes of ascites, the initial therapy of ascites in patients with cirrhosis, and the treatment of refractory. Ascites is the pathologic accumulation of fluid within the peritoneal cavity. because many diseases can cause ascites, in particular cirrhosis, samples of ascitic fluid are commonly analyzed in order to develop a differential diagnosis. the concept of transudate versus exudate, as determined by total protein measurements, is outdated and the.

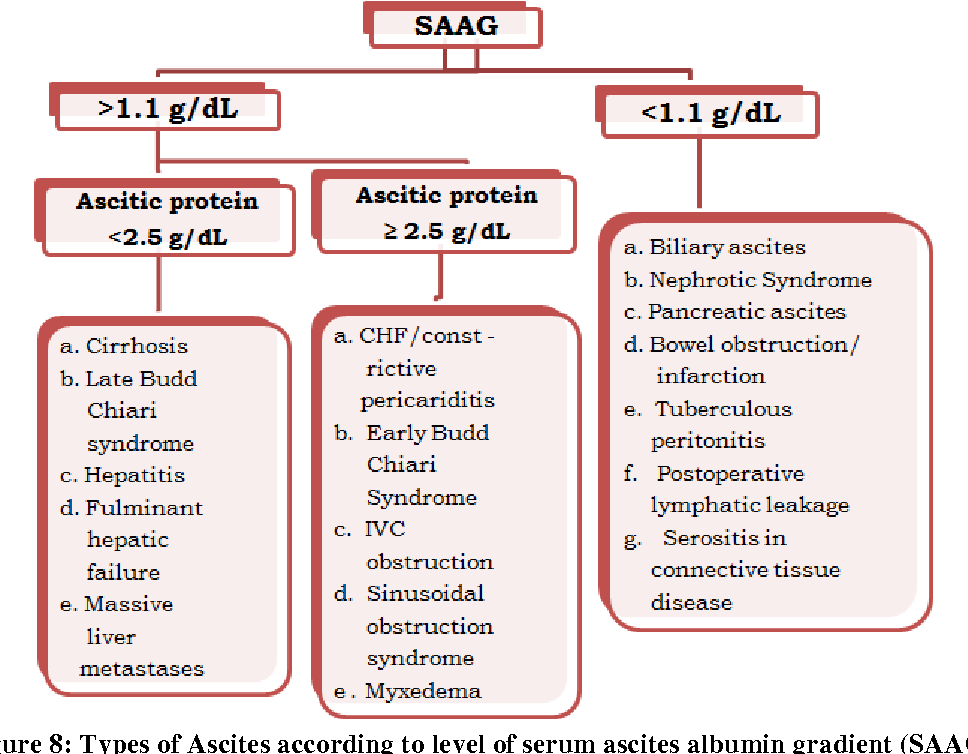
Ascites Differential Diagnosis Table Serum Ascites Gr Vrogue Co Function, serum and urine electrolytes, and a diag nostic paracentesis for analysis of the ascitic fluid t2;(fables . ig 2 4). (19,20) in evaluating the etiology of ascites, the serum albumin ascites gradient is cal the serum albumin in simultaneously obtained sam ples.(21) a serum albumin ascites gradient ≥1.1 g fig. 2. Also see medscape’s ascites albumin gradient calculator. the formula is below. saag = serum albumin – ascites albumin. a high gradient (saag >1.1 g dl) indicates portal hypertension and suggests a nonperitoneal cause of ascites. such conditions may include the following: [1, 2] cirrhosis. fulminant hepatic failure. Ascites is the pathological accumulation of fluid within the peritoneal cavity. it often occurs as results of liver cirrhosis, malignant neoplasia, tuberculous infection, cardiac insufficiency, renal diseases, etc. determining the etiology is an essential step in the management of patients with new onset ascites. abdominal paracentesis with appropriate ascitic fluid analysis is probably the. Ascites is the accumulation of ascitic fluid in the peritoneal cavity. many diseases can cause ascites, but the most common cause is portal hypertension, which is usually due to liver cirrhosis. ascites does not typically become clinically detectable until there are at least 500mls of fluid present. if large amounts of fluid accumulate, the.

Portal Hypertension Differential Diagnosis Hepatology Vrogue Co Ascites is the pathological accumulation of fluid within the peritoneal cavity. it often occurs as results of liver cirrhosis, malignant neoplasia, tuberculous infection, cardiac insufficiency, renal diseases, etc. determining the etiology is an essential step in the management of patients with new onset ascites. abdominal paracentesis with appropriate ascitic fluid analysis is probably the. Ascites is the accumulation of ascitic fluid in the peritoneal cavity. many diseases can cause ascites, but the most common cause is portal hypertension, which is usually due to liver cirrhosis. ascites does not typically become clinically detectable until there are at least 500mls of fluid present. if large amounts of fluid accumulate, the. Ultrasound, computed tomography scan, or magnetic resonance imaging can confirm the diagnosis. in the majority of patients, history and examination will provide important clues as to the etiology of ascites (e.g., signs of chronic liver disease or cardiac failure). causes include diseases that lead to portal hypertension, hypoalbuminemia, and. Abstract. ascites is a pathologic accumulation of peritoneal fluidcommonly observed in decompensated cirrhotic states.its causes are multi factorial, but principally involve significant volume and hormonal dysregulation in the setting of portal hypertension. the diagnosis of ascites is considered in cirrhotic patients given a constellation of.

Ascites Differential Diagnosis Table Serum Ascites Gr Vrogue Co Ultrasound, computed tomography scan, or magnetic resonance imaging can confirm the diagnosis. in the majority of patients, history and examination will provide important clues as to the etiology of ascites (e.g., signs of chronic liver disease or cardiac failure). causes include diseases that lead to portal hypertension, hypoalbuminemia, and. Abstract. ascites is a pathologic accumulation of peritoneal fluidcommonly observed in decompensated cirrhotic states.its causes are multi factorial, but principally involve significant volume and hormonal dysregulation in the setting of portal hypertension. the diagnosis of ascites is considered in cirrhotic patients given a constellation of.

Ascites Differential Diagnosis Table Serum Ascites Gr Vrogue Co

Comments are closed.