Are Fungi Producers Or Consumers
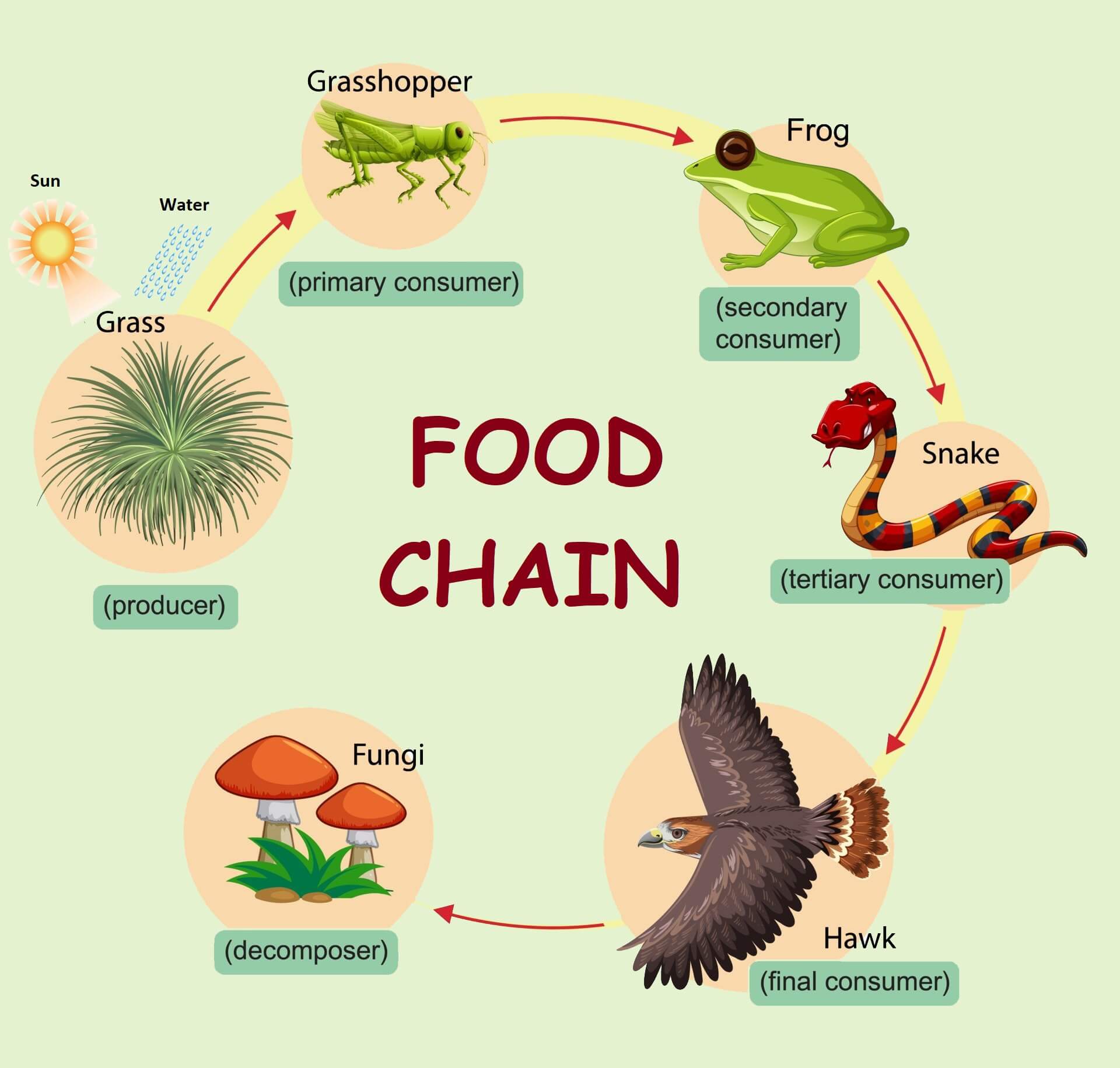
Why Bacteria And Fungi Are Called Decomposers Food Chain And Web In food chains, fungi act as decomposers, also called saprotrophs, which recycle nutrients in an ecosystem. without fungi, forest floors would be covered in plant debris and animal carcasses; similarly other ecosystems would have a vast amount of waste piled up. fungi break down plant components like lignin and cellulose, so they are. Fungi are actually more closely related to animals than they are to plants though current estimates are that the most recent common ancestor between animals and fungi lives between 1.1 and 1.5 billion years ago. in contrast, fungi and animals share a common ancestor with plants closer to 1.6 billion years ago.

Ppt By Courtney Brown Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id Noun. aquatic animal that strains nutrients from water. food chain. noun. group of organisms linked in order of the food they eat, from producers to consumers, and from prey, predators, scavengers, and decomposers. food web. noun. all related food chains in an ecosystem. also called a food cycle. The second trophic level consists of organisms that eat the producers. these are called primary consumers, or herbivores. deer, turtles, and many types of birds are herbivores. secondary consumers eat the herbivores. tertiary consumers eat the secondary consumers. there may be more levels of consumers before a chain finally reaches its top. Further trophic levels are numbered subsequently according to how far the organism is along the food chain. level 1: plants and algae make their own food and are called producers. level 2: herbivores eat plants and are called primary consumers. level 3: carnivores that eat herbivores are called secondary consumers. Dead producers and consumers are eaten by detritivores (which ingest dead tissues) and decomposers (which further break down these tissues into simple molecules by secreting digestive enzymes). invertebrate animals, such as worms and millipedes, are examples of detritivores, whereas fungi and certain bacteria are examples decomposers.

Ppt Protists And Fungi Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id Further trophic levels are numbered subsequently according to how far the organism is along the food chain. level 1: plants and algae make their own food and are called producers. level 2: herbivores eat plants and are called primary consumers. level 3: carnivores that eat herbivores are called secondary consumers. Dead producers and consumers are eaten by detritivores (which ingest dead tissues) and decomposers (which further break down these tissues into simple molecules by secreting digestive enzymes). invertebrate animals, such as worms and millipedes, are examples of detritivores, whereas fungi and certain bacteria are examples decomposers. The producers can then use the carbon to grow, while the oxygen molecules are breathed out by the producers and can then be breathed in by animals, like humans. the tiny ones. the tiniest freshwater producers are phytoplankton and algae. phytoplankton and algae can be attached to an object or rock in the water, or they may simply float around. Noun. one celled organisms in the kingdom protista, such as amoebas. (singular: protozoan) termite. noun. small insect that feeds on wood. decomposers play a critical role in the flow of energy through an ecosystem. they break apart dead organisms into simpler inorganic materials, making nutrients available to primary producers.

Comments are closed.