Approach To Murmur In Paediatrics Pptx

Approach To Murmur In Paediatrics Pptx Approach to murmur in paediatrics.pptx. this document discusses the approach to murmurs in pediatrics. it defines a murmur as a heart sound produced by turbulent blood flow across a heart valve or defect. murmurs can be innocent, pathological, or symptomatic. innocent murmurs are harmless and common in children. A murmur is a sound generated when blood travels through vessels or valves in a turbulent or energy dissipating manner. it can be an important clue to a structural abnormality of the cardiovascular system. however, over 50% of people have murmurs during childhood, but less than one percent are associated with congenital heart disease. thus, the.
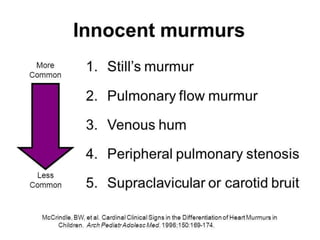
Approach To Murmur In Paediatrics Pptx Continue reading. up to 8.6% of infants and 80% of children have a heart murmur during their early years of life. the presence of a murmur can indicate conditions ranging from no discernable. Heart murmurs are common in infants and children. evaluation of a murmur is the most common reason for referral to a pediatric cardiologist [1,2]. while the prevalence of congenital heart disease is approximately 1 percent, a majority of children have innocent murmurs at some time [3,4]. being able to distinguish a murmur associated with heart. In the newborn population, the prevalence of heart murmurs is between 0.6% and 4.2%. 4 among infants and children, an estimated 90% will have a heart murmur at some point during their infancy or childhood. 5 approximately 50% to 70% of infants and children are reported to have a heart murmur identified during a routine physical exam, 6 but of. Sensitive – alters with child’s position. short duration – not holosystolic. single – no associated clicks gallops rub. small – murmur confined to small area, does not radiate. soft – low amplitude, grade 1 2 3. sweet – not harsh sounding. systolic – occurs during and is limited to systole. normal vitals, pulses and oximetry.

Approach To Murmur In Paediatrics Pptx In the newborn population, the prevalence of heart murmurs is between 0.6% and 4.2%. 4 among infants and children, an estimated 90% will have a heart murmur at some point during their infancy or childhood. 5 approximately 50% to 70% of infants and children are reported to have a heart murmur identified during a routine physical exam, 6 but of. Sensitive – alters with child’s position. short duration – not holosystolic. single – no associated clicks gallops rub. small – murmur confined to small area, does not radiate. soft – low amplitude, grade 1 2 3. sweet – not harsh sounding. systolic – occurs during and is limited to systole. normal vitals, pulses and oximetry. Murmurs are an exceedingly common physical examination finding in pediatric patients. it is imperative that all pediatricians know how to perform a complete cardiac examination and understand the components of benign versus pathologic murmurs.after completing this article, readers should be able to: the evaluation of murmurs in the pediatric patient has remained a subject of both interest and. Cardiac murmur might be the first clinical sign of a significant congenital heart disease (chd) in children. 2 other than acute rheumatic fever (arf) and rheumatic heart disease (rhd) with valvular dysfunction, cardiac murmur is not a consistent finding in most of the acquired heart diseases in children.

Approach To Murmur In Paediatrics Pptx Murmurs are an exceedingly common physical examination finding in pediatric patients. it is imperative that all pediatricians know how to perform a complete cardiac examination and understand the components of benign versus pathologic murmurs.after completing this article, readers should be able to: the evaluation of murmurs in the pediatric patient has remained a subject of both interest and. Cardiac murmur might be the first clinical sign of a significant congenital heart disease (chd) in children. 2 other than acute rheumatic fever (arf) and rheumatic heart disease (rhd) with valvular dysfunction, cardiac murmur is not a consistent finding in most of the acquired heart diseases in children.

Approach To Murmur In Paediatrics Pptx

Comments are closed.