Anatomy Of The Superior Vena Cava And Brachiocephalic Veins Thoracic
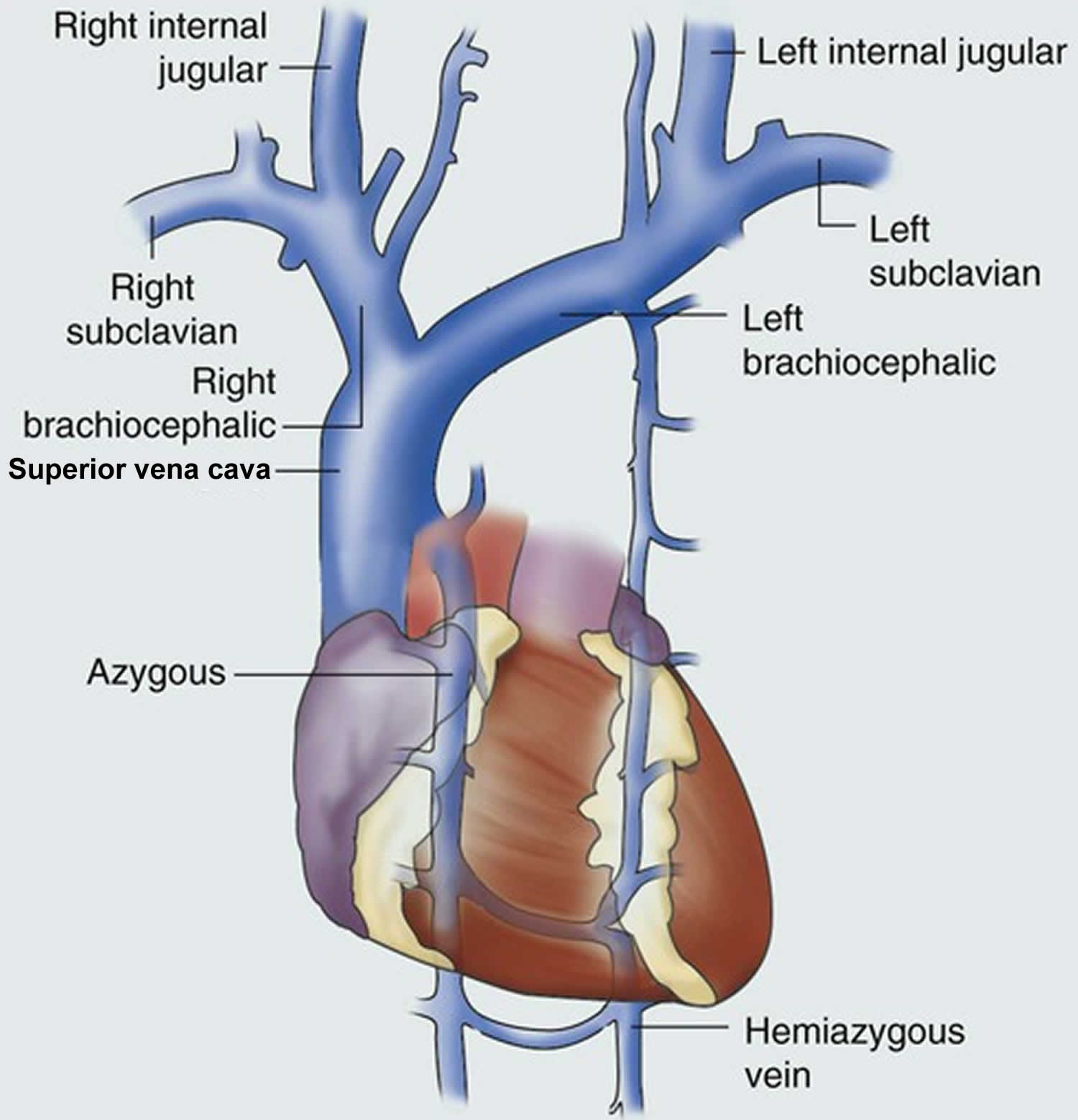
Superior Vena Cava Anatomy Function Superior Vena Cava Syn It is formed by the union of the right and left brachiocephalic veins – which provide venous drainage of the head, neck, and upper limbs. at the level of t4, the superior vena cava receives the azygous vein, which drains the upper lumbar region and thoracic wall. the svc receives tributaries from several minor vein groups: mediastinal veins. Brachiocephalic vein (vena brachiocephalica) the brachiocephalic vein, also known as the innominate vein, is a paired vein of the superior mediastinum that drains the venous blood from the head and neck, upper limbs and the upper part of the thorax. it is formed by the confluence of the internal jugular and subclavian veins on each side, just.
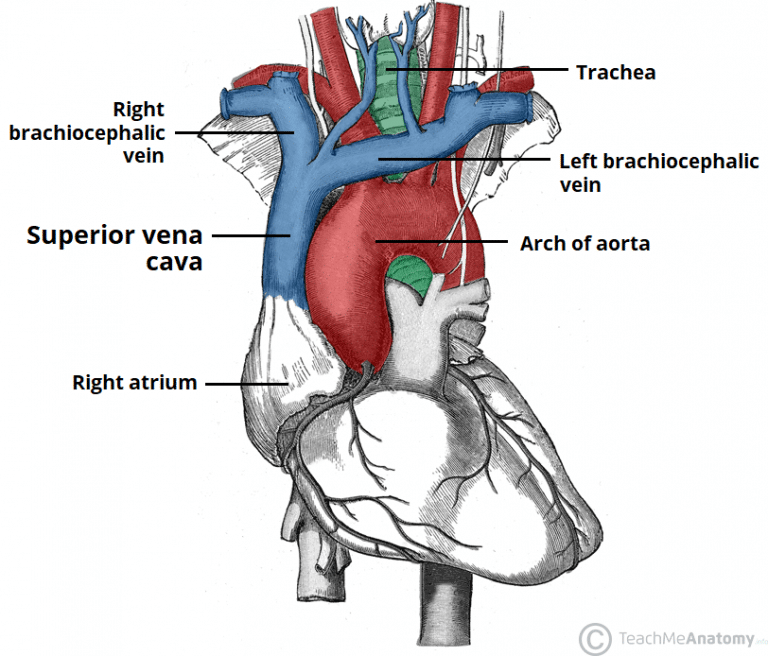
The Superior Vena Cava Teachmeanatomy Anatomy and function of the superior vena cava. the superior vena cava (svc, also known as the cava or cva) is a short, but large diameter vein located in the anterior right superior mediastinum. its latin name is related to its large pipe appearance in cadavers, 'cava' meaning 'hollow'. the superior vena cava is very important for the function. Vena cava, superior anatomy & histology*. the venous side of the systemic vascular circulation returns the left ventricular cardiac output in a converging fashion to the superior and inferior vena cava and hence to the right atrium. oxygenated blood is returned to the left atrium. the volumes of these 2 systems are in balance in a normal ph …. The superior vena cava (svc) is one of the two largest veins in the body. it is a vital part of the cardiovascular system, responsible for returning deoxygenated blood, or blood that is rich in carbon dioxide, from the upper body to the heart. the superior vena cava has thin walls that render it vulnerable to high blood pressure. The superior vena cava (svc) is a large, significant vein responsible for returning deoxygenated blood collected from the body to the right atrium. it is present within the superior and middle mediastinum. the superior vena cava handles the venous return of blood from structures located superior to the diaphragm. in contrast, its counterpart, the inferior vena cava, handles venous return from.

Anatomy Of The Superior Vena Cava And Brachiocephalic Veins Thoracic The superior vena cava (svc) is one of the two largest veins in the body. it is a vital part of the cardiovascular system, responsible for returning deoxygenated blood, or blood that is rich in carbon dioxide, from the upper body to the heart. the superior vena cava has thin walls that render it vulnerable to high blood pressure. The superior vena cava (svc) is a large, significant vein responsible for returning deoxygenated blood collected from the body to the right atrium. it is present within the superior and middle mediastinum. the superior vena cava handles the venous return of blood from structures located superior to the diaphragm. in contrast, its counterpart, the inferior vena cava, handles venous return from. The thymus gland and brachiocephalic artery are juxtaposed medially. this vessel joins the left brachiocephalic vein at the level of the lower border of the first right costal cartilage to become the superior vena cava. tributaries to the right brachiocephalic vein include the right vertebral vein joining it superiorly and the internal thoracic. Your inferior vena cava and superior vena cava are both on your heart’s right side. your right and left innominate (or brachiocephalic) veins merge to form your superior vena cava. your superior vena cava is next to the right side of your sternum and goes into your right atrium, where all the oxygen poor blood goes.

Comments are closed.