9 5 Molecular Orbital Theory General Chemistry
9 8 Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry Libretexts 22b Chad provides a comprehensive lesson on molecular orbital theory. the lesson begins by showing how overlap of atomic orbitals results in both bonding and an. This page titled 9.8: molecular orbital theory is shared under a cc by 3.0 license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by stephen lower via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the libretexts platform. the molecular orbital model is by far the most productive of the various models of chemical bonding, and serves as.

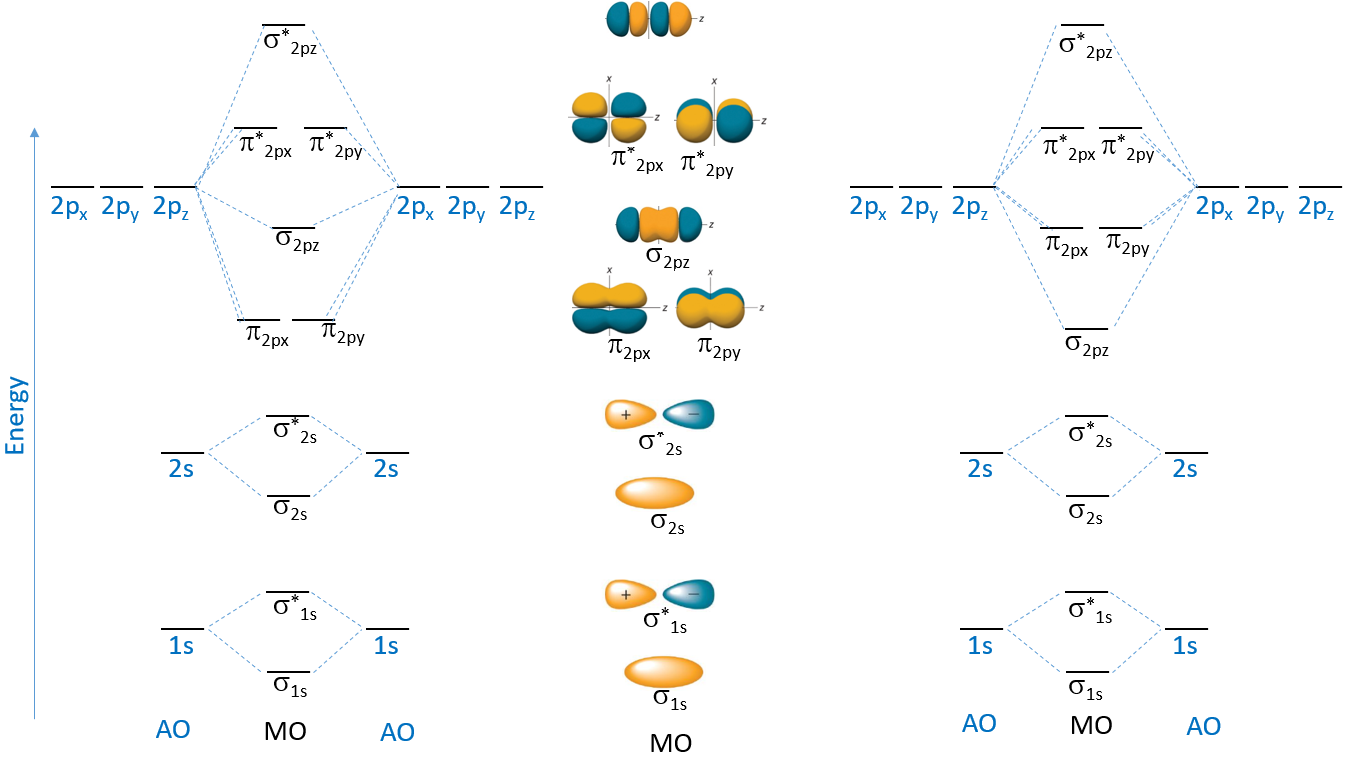
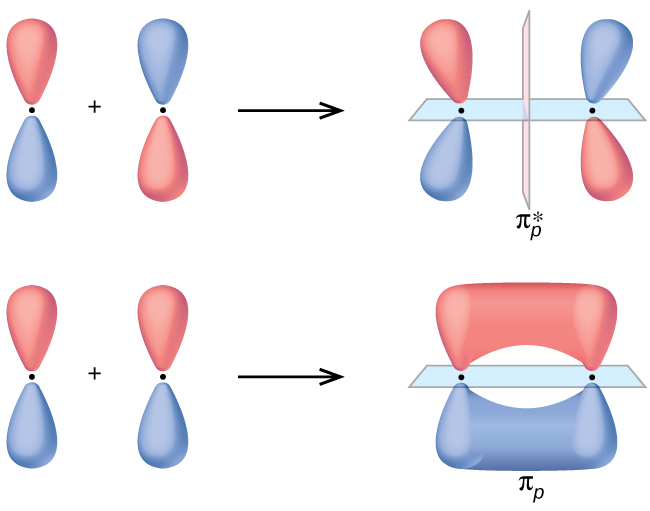
9 5 Molecular Orbital Theory General Chemistry Youtube Molecular orbital theory. considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule. creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals (s, p, d …) and hybrid orbitals (sp, sp2, sp3 …) combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals (σ, σ*, π, π*) forms σ or π bonds. 9.4 sigma and pi bonds. 9.5 molecular orbital theory. chapter 10 – gases. 10.1 properties of gases. 10.2 gas laws including the ideal gas law. 10.3 additional gas laws. 10.4 real gases & the van der waals equation. chapter 11 – intermolecular forces, liquids, and solids. 11.1 intermolecular forces. This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into molecular orbital theory. it describes the formation of bonding and antibonding molecular o. A nonbonding molecular orbital occupied by a pair of electrons is the molecular orbital equivalent of a lone pair of electrons. by definition, electrons in nonbonding orbitals have no effect on bond order, so they are not counted in the calculation of bond order. thus the predicted bond order of hcl is (2 − 0) ÷ 2 = 1.

9 8 Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry Libretexts 22b This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into molecular orbital theory. it describes the formation of bonding and antibonding molecular o. A nonbonding molecular orbital occupied by a pair of electrons is the molecular orbital equivalent of a lone pair of electrons. by definition, electrons in nonbonding orbitals have no effect on bond order, so they are not counted in the calculation of bond order. thus the predicted bond order of hcl is (2 − 0) ÷ 2 = 1. Molecular orbital theory. considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule. creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals (s, p, d …) and hybrid orbitals (sp, sp2, sp3 …) combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals (σ, σ*, π, π*) forms σ or π bonds. V. t. e. in chemistry, molecular orbital theory (mo theory or mot) is a method for describing the electronic structure of molecules using quantum mechanics. it was proposed early in the 20th century. in molecular orbital theory, electrons in a molecule are not assigned to individual chemical bonds between atoms, but are treated as moving under.

Orbital Chemistry Physics Applications Britannica Molecular orbital theory. considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule. creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals (s, p, d …) and hybrid orbitals (sp, sp2, sp3 …) combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals (σ, σ*, π, π*) forms σ or π bonds. V. t. e. in chemistry, molecular orbital theory (mo theory or mot) is a method for describing the electronic structure of molecules using quantum mechanics. it was proposed early in the 20th century. in molecular orbital theory, electrons in a molecule are not assigned to individual chemical bonds between atoms, but are treated as moving under.
9 8 Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry Libretexts 22b

Comments are closed.