6 3 Food Chains And Food Webs Biology Libretexts

6 3 Food Chains And Food Webs Biology Libretexts A food chain represents a single pathway by which energy and matter flow through an ecosystem. an example is shown in figure below. food chains are generally simpler than what really happens in nature. most organisms consume—and are consumed by—more than one species. this food chain includes producers and consumers. A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another. each organism in a food chain occupies a specific trophic level (energy level), its position in the food chain. the first trophic level in the food chain is the producers.

6 3 Food Chains And Food Webs Biology Libretexts Food chains. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally decomposers. these levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics. A food web is a graphic representation of a holistic, nonlinear web of primary producers, primary consumers, and higher level consumers used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics (figure 5.8.1.1). figure 5.8.1.1: example of simplified food chains (a) and food webs (b) of terrestrial and marine ecosystems. Trophic levels. a food chain follows one path of energy and materials between species. a food web is more complex and is a whole system of connected food chains. in a food web, organisms are placed into different trophic levels. trophic levels include different categories of organisms such as producers, consumers, and decomposers. In the interactive labs box, under food web, click step 1. read the instructions first, and then click step 2 for additional instructions. when you are ready to create a simulation, in the upper right corner of the interactive labs box, click open simulator. two general types of food webs are often shown interacting within a single ecosystem.
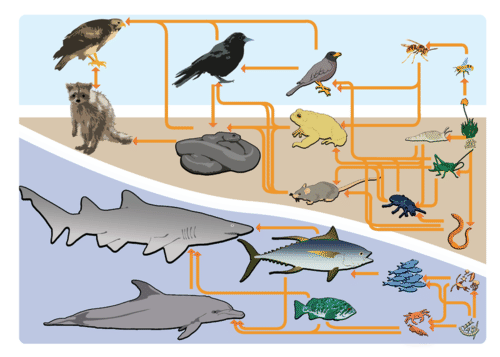
6 3 Food Chains And Food Webs Biology Libretexts Trophic levels. a food chain follows one path of energy and materials between species. a food web is more complex and is a whole system of connected food chains. in a food web, organisms are placed into different trophic levels. trophic levels include different categories of organisms such as producers, consumers, and decomposers. In the interactive labs box, under food web, click step 1. read the instructions first, and then click step 2 for additional instructions. when you are ready to create a simulation, in the upper right corner of the interactive labs box, click open simulator. two general types of food webs are often shown interacting within a single ecosystem. Summary. food chains and food webs model feeding relationships in ecosystems. they show how energy and materials are transferred between trophic levels when consumers eat producers or other organisms. a food web is a diagram of feeding relationships that includes multiple intersecting food chains. energy is passed up the food chain from one. A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and.
18 20 Food Chains And Food Webs Biology Libretexts Vrogue Co Summary. food chains and food webs model feeding relationships in ecosystems. they show how energy and materials are transferred between trophic levels when consumers eat producers or other organisms. a food web is a diagram of feeding relationships that includes multiple intersecting food chains. energy is passed up the food chain from one. A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and.

Comments are closed.