3 Uses Of Lipids In Animals Sitelip Org
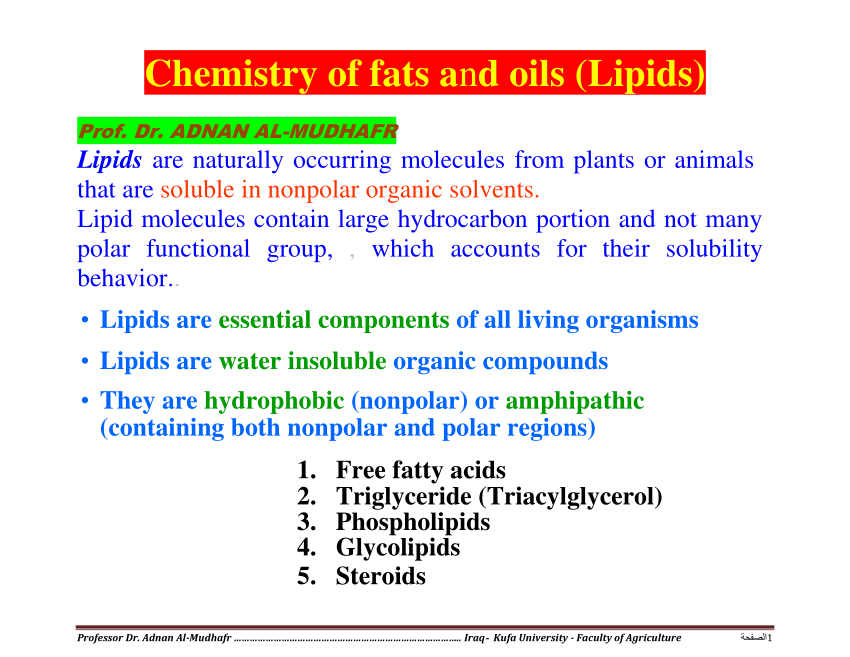
3 Uses Of Lipids In Animals Sitelip Org To obtain a higher resolution of the lipids, a tlc plate can be used to separate a single lipid sample by running it in two dimension. the separated lipids can be detected by a variety of methods including staining with iodine vapour or dyes that bind to specific lipids. however, the most common method is to use radioisotopes to label the lipids. Fats are actually a type of lipid. lipids are a major class of biochemical compounds that includes oils as well as fats. organisms use lipids to store energy and for many other uses. lipid molecules consist mainly of repeating units called fatty acids. there are two types of fatty acids: saturated fatty acids and unsaturated fatty acids.

What Is The Function Of Lipids In Animals Sitelip Org Summary. lipid storage is an evolutionary conserved process that exists in all organisms from simple prokaryotes to humans. in metazoa, long term lipid accumulation is restricted to specialized cell types, while a dedicated tissue for lipid storage (adipose tissue) exists only in vertebrates. excessive lipid accumulation is associated with serious health complications including insulin. Lipids (also known as fats) are components of plant (e.g., vegetable oils) and animal tissues (e.g., meat, eggs, milk). on a physical nature, lipids are relatively insoluble in water and are soluble in organic solvents, such as hexane, ether, and chloroform. chemically, lipids are organic compounds and esters of fatty acids and glycerol (a 3 c. Organisms use lipids to store energy, but lipids have other important roles as well. lipids consist of repeating units called fatty acids.fatty acids are organic compounds that have the general formula ch 3 (ch 2) n cooh, where nusually ranges from 2 to 28 and is always an even number. there are two types of fatty acids: saturated fatty acids. Apoe does enhance the proteolytic breakdown of it and the e4 isoform is not as efficient in these reactions as the other isoforms. 9.1: structure and function lipids and membranes. lipids are a diverse group of molecules that all share the characteristic that at least a portion of them is hydrophobic.
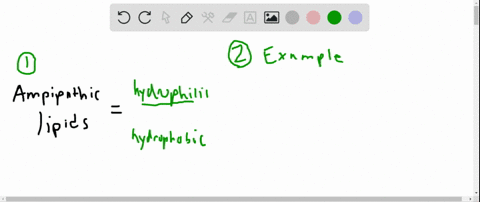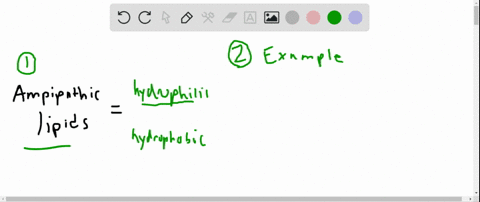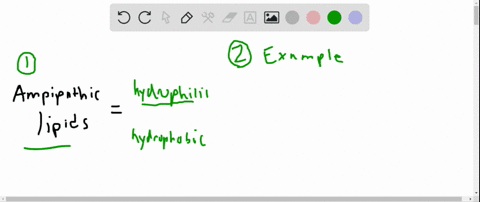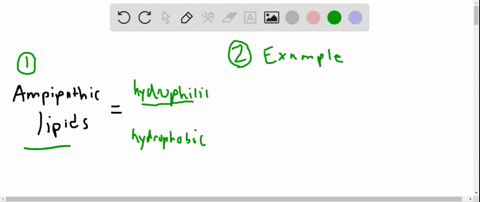
3 Uses Of Lipids In Animals Sitelip Org Organisms use lipids to store energy, but lipids have other important roles as well. lipids consist of repeating units called fatty acids.fatty acids are organic compounds that have the general formula ch 3 (ch 2) n cooh, where nusually ranges from 2 to 28 and is always an even number. there are two types of fatty acids: saturated fatty acids. Apoe does enhance the proteolytic breakdown of it and the e4 isoform is not as efficient in these reactions as the other isoforms. 9.1: structure and function lipids and membranes. lipids are a diverse group of molecules that all share the characteristic that at least a portion of them is hydrophobic. Lipids comprise a group of compounds such as fats, oils, steroids and waxes found in living organisms. both prokaryotes and eukaryotes possess lipids, which play many important roles biologically, such as membrane formation, protection, insulation, energy storage, cell division and more. in medicine, lipids refer to blood fats. Organisms use lipids to store energy, but lipids have other important roles as well. lipids consist of repeating units called fatty acids. fatty acids are organic compounds that have the general formula ch 3 (ch 2) n cooh, where n usually ranges from 2 to 28 and is always an even number. there are two types of fatty acids: saturated fatty acids.

Comments are closed.